Platinum-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
Platinum is a chemical element that has the symbol Pt and atomic number 78. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal that belongs to the platinum group of elements. Platinum is one of the most valuable precious metals and has a wide range of applications due to its unique properties, including its high resistance to corrosion and tarnishing.
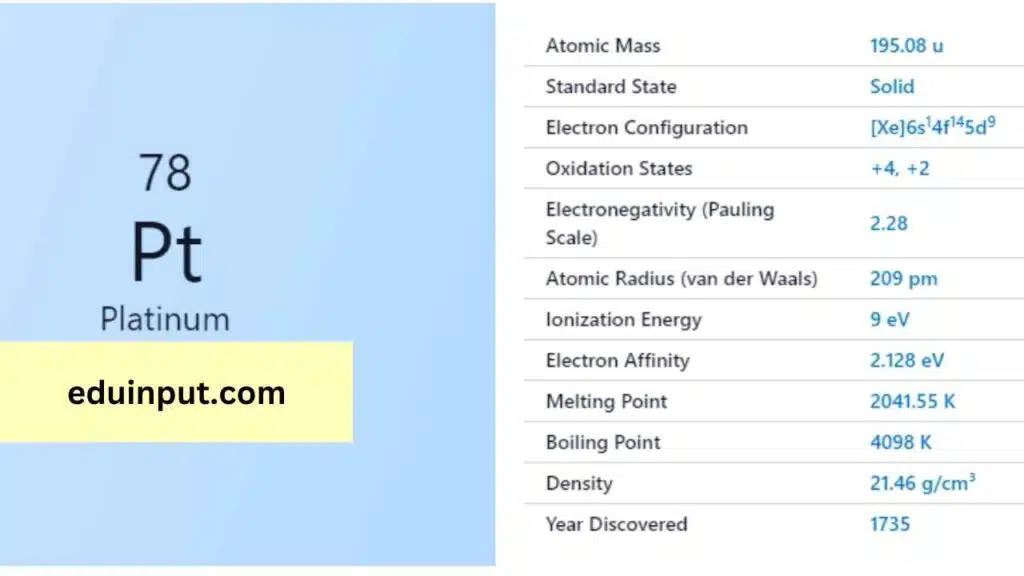
| Property | Value |
| Name | Platinum |
| Symbol | Pt |
| Atomic number | 78 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | 195.084 (9) |
| Standard state | Solid at 298 K |
| Appearance | Greyish white |
| Classification | Metallic |
| Group in periodic table | 10 |
| Group name | Precious metal or platinum group metal |
| Period in periodic table | 6 |
| Block in periodic table | d |
| Shell structure | 2.8.18.32.17.1 |
| CAS Registry | 7440-06-4 |
Discovery
Platinum was first discovered by Spanish conquistadors in South America in the 16th century. However, it was not recognized as a distinct element until the 18th century, when it was studied by chemists in Europe.
Physical Properties
Platinum is a dense, malleable, and ductile metal with a silvery-white appearance. It has a melting point of 1,768.3°C and a boiling point of 3,825°C. Platinum has a density of 21.45 g/cm³, which is much higher than that of other precious metals, such as gold and silver. It is a good conductor of electricity and has a high resistance to corrosion and tarnishing.
Chemical Properties
Platinum is a highly unreactive metal that does not react with most chemicals, including acids and alkalis. It has the ability to absorb large amounts of hydrogen, making it an important component in fuel cells used in automobiles. Platinum also has catalytic properties in various chemical reactions, including the oxidation of ammonia and the reduction of nitrogen oxides.
Facts
- Platinum is one of the rarest elements on Earth.
- Platinum is used in jewelry, catalytic converters, and laboratory equipment.
- South Africa, Russia, and Zimbabwe are the largest producers of platinum in the world.
- Platinum is a byproduct of nickel and copper mining.
Applications
Platinum has a wide range of applications due to its unique properties. It is commonly used in jewelry due to its high resistance to tarnishing and corrosion. Platinum is also used in catalytic converters in automobiles to convert harmful pollutants into less harmful substances. It is also used in laboratory equipment, such as crucibles and electrodes, due to its high melting point and resistance to corrosion. In addition, platinum is used in the chemical industry as a catalyst in various chemical reactions.






Leave a Reply