Protactinium-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
Protactinium is a chemical element with the symbol Pa and atomic number 91. It is a highly radioactive metal, and its chemistry is similar to that of other actinides.

| Property | Value |
| Name | Protactinium |
| Symbol | Pa |
| Atomic number | 91 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | 231.03588 |
| Standard state | Solid at 298 K |
| Appearance | Silvery metallic |
| Classification | Metallic |
| Period in the periodic table | |
| Group name | Actinoid |
| Block in the periodic table | 7 (actinoid) |
| Block in periodic table | f |
| Shell structure | 2.8.18.32.20.9.2 |
| CAS Registry | 7440-13-3 |
Discovery
Protactinium was discovered in 1913 by two German scientists, Kasimir Fajans and Oswald Helmuth Göhring. It was the first element discovered by the nuclear transmutation of another element, uranium. It was also the first element discovered using the methods of radiochemistry.
Physical Properties
Protactinium is a dense, silvery-grey metal that tarnishes in air. It has a melting point of 1,569 °C and a boiling point of 4,027 °C. Protactinium is highly radioactive, and its isotopes have half-lives ranging from microseconds to thousands of years.
Chemical Properties
Protactinium is a highly reactive element and forms a variety of compounds with other elements. It is similar in its chemical properties to other actinides, particularly uranium and thorium. Protactinium can exist in four oxidation states, ranging from +3 to +5, with the +5 state being the most stable.
Electronic Configuration of Protactinium
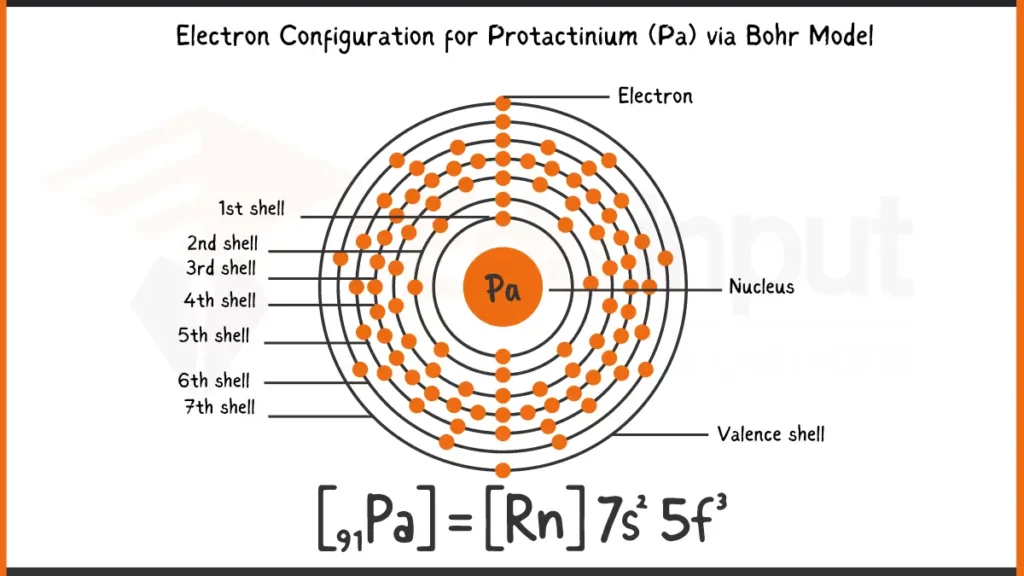
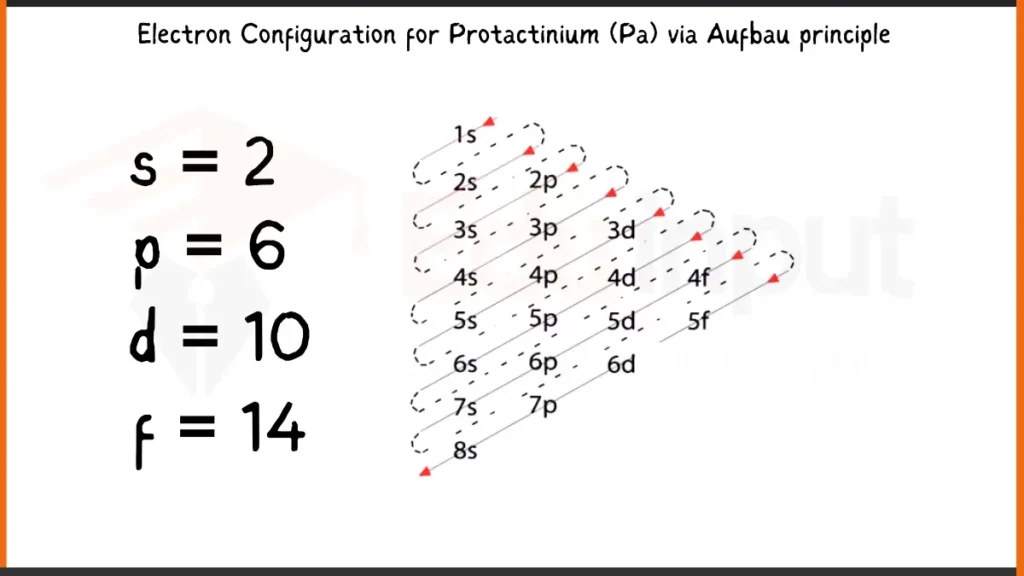
Protactinium (Pa), element number 91, has 91 electrons arranged as 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶4s²3d¹⁰4p⁶5s²4d¹⁰5p⁶5f²6d¹7s². This electronic configuration defines the energy levels for Protactinium’s electrons. The outermost electrons (5f², 6d¹, 7s²) play a crucial role in bonding by participating in the sharing or transfer of electrons to form chemical compounds.
Electronic Configuration of Protactinium via Bohr Model
Electronic Configuration of Protactinium via Aufbau Principle
Facts
- Protactinium is one of the rarest and most expensive elements on Earth.
- The most stable isotope of protactinium, protactinium-231, has a half-life of over 32,000 years.
- Protactinium is used in some nuclear reactors and as a target material for producing other radioactive isotopes.
Applications
Protactinium has a limited number of applications due to its rarity and high radioactivity. Some potential uses include:
- Nuclear reactors: Protactinium can be used as a fuel in certain types of nuclear reactors.
- Research: Protactinium-231 is used in scientific research to study the geochemistry of the Earth’s crust.
- Target material: Protactinium can be used as a target material for producing other radioactive isotopes, such as actinium-225.
Protactinium is a highly radioactive metal that was discovered through nuclear transmutation. It has a variety of potential uses, including as a fuel for nuclear reactors and as a target material for producing other radioactive isotopes. However, its rarity and high radioactivity make it difficult and expensive to work with.





Leave a Reply