Rotational Kinetic Energy | Rotational Kinetic Energy of Disc and Hoop
The energy of an object due to its rotation about an axis is called rotational kinetic energy.
Rotational kinetic energy
The energy of an object due to spinning about an axis is called rotational kinetic energy. Rotational kinetic energy is directly proportional to the rotational inertia and the square of the magnitude of the angular velocity.
Rotational kinetic energy formula
Consider an object spinning about an axis with constant angular velocity ω. Every point of the body has some K.E due to circular motion. In order to calculate the total K.E of the spinning body, imagine that it is composed of tiny pieces of masses m1, m2…. ..,mn,.
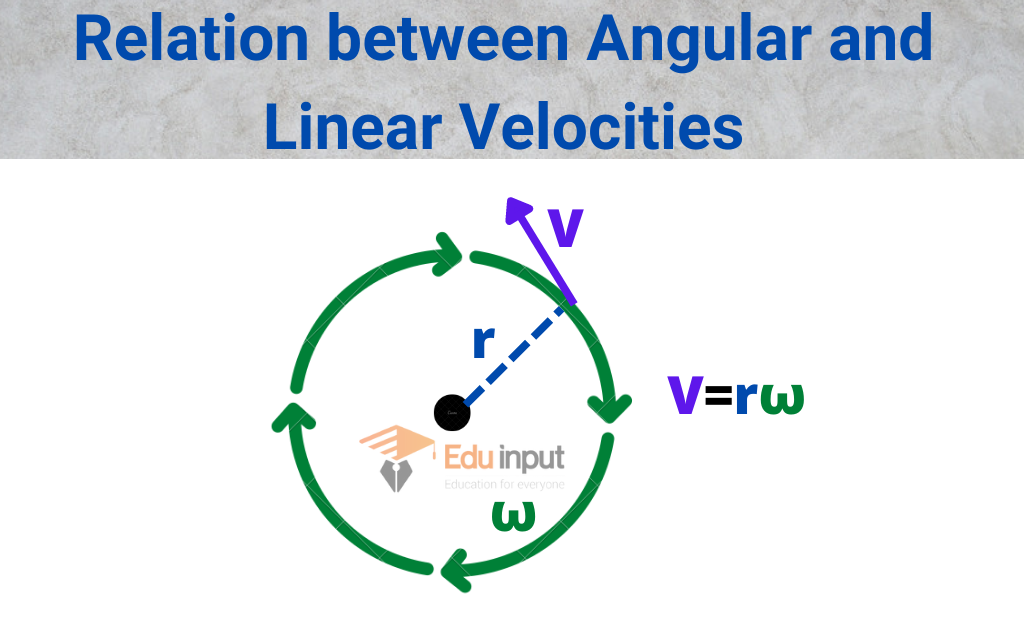
Consider a single piece of mass mi, at a distance ri from the axis of rotation moving in a circle. Then its speed is given by
Vi= riω
K.E= 1/2mivi2
=1/2mi (riω)2 =1/2mIri2ω2
The rotational K.E of the whole body is the sum of the kinetic energies of all the pieces.
K.Erot = 1/2 miri2ω2 +1/2m2r22ω2 +1/2m3r32ω2
=1/2(m1r12+ m2r22+………. ) ω2
I= m1r12 +m2r22+……
Rotational kinetic energy uses
Rotational K.E is practically used by flywheels, which are essential parts of many engines. Flywheel stores energy between powers stokes of the piston which is distributed over the full revolution of the crankshaft and rotation remains smooth.
Rotational Kinetic Energy of Disc and Hoop
Consider a disc and a hoop started moving down on an inclined plane of height ‘h’. They have rotational as well as translational motion. If there is no friction, then the total K.E of the disc or hoop on reaching the bottom of the inclined plane must be equal to its P.E at the top.

P.E at top = Rotational K.E at bottom + Translational K.E at bottom
Rotational Kinetic Energy of Disc
P.E = K.Erot +K.Etran
K.Erot=1/2lω2
K.Erot=1/2 (1/2mr2ω2)
=1/4mr2ω2
=1/4mv2
P.E=1/4mv2 +1/2mv2
mgh=mv2+2mv2/4
mgh=3/4mv2
v2= 3/4gh
v=√3/4gh
Rotational Kinetic Energy of hoop
P.E = K.Erot +K.Etran
K.Erot=1/2lω2
K.Erot=1/2mr2ω2
=1/2mv2
mgh= mv2+mv2/2
mgh =2 mv2/2
v2=gh
v=√gh
This is the final velocity of a hoop on reaching the lower end of an inclined plane. It shows that the velocity of the disc will be greater than the hoop on reaching the bottom of the inclined plane.




Leave a Reply