Sodium-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white metal that belongs to the alkali metal group in the periodic table. Sodium is highly reactive and is found in nature only in the form of compounds. It is an essential element for life, as it plays a crucial role in various biological processes.
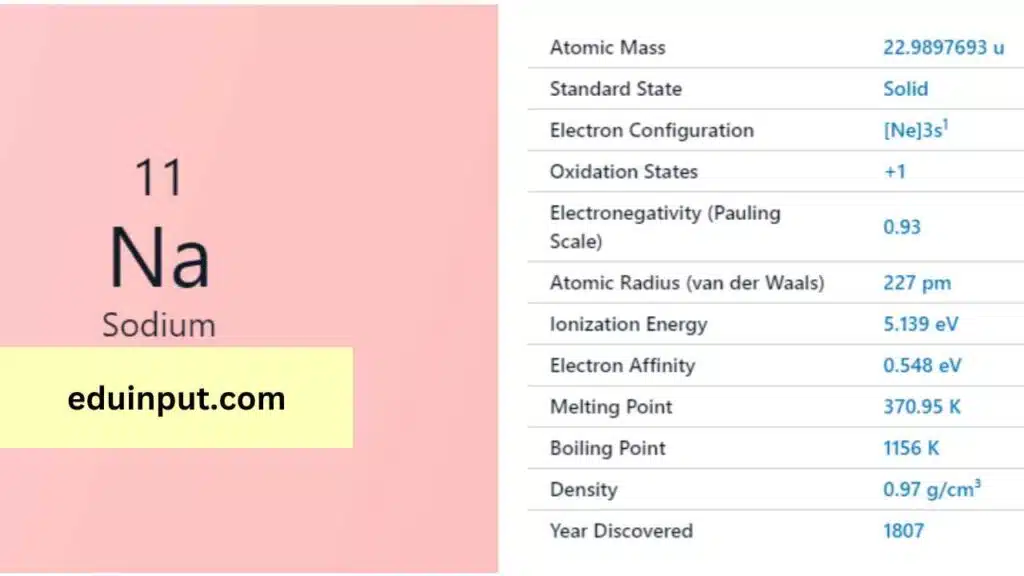
| Property | Sodium (Na) |
|---|---|
| Name | Sodium |
| Symbol | Na |
| Atomic number | 11 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | ~22.99 |
| Standard state | Solid at 298 K |
| Appearance | Metallic |
| Classification | Metallic |
| Group in periodic table | 1 |
| Group name | Alkali metal |
| Period in periodic table | 3 |
| Block in periodic table | s |
| Shell structure | 2.8.1 |
| CAS Registry | 7440-23-5 |
Discovery
Sodium was first isolated by Sir Humphry Davy in 1807 by the electrolysis of sodium hydroxide. He named the element sodium after the Greek word “natrium,” which means “soda,” as sodium compounds were commonly used in making soap and glass at that time.
Physical Properties
Sodium has a melting point of 97.79 °C and a boiling point of 883 °C. It is a soft metal with a density of 0.97 g/cm³. Sodium is a good conductor of electricity and heat, and it is highly reactive with water, which can lead to explosive reactions.
Chemical Properties
Sodium is a highly reactive metal that reacts vigorously with water, acids, and many other substances. It readily loses its single outermost electron to form the sodium ion Na+, which has a noble gas configuration. This property makes it a strong reducing agent and an important element in the chemical industry. Sodium also reacts with chlorine to form sodium chloride (table salt), which is an essential component of our diet.
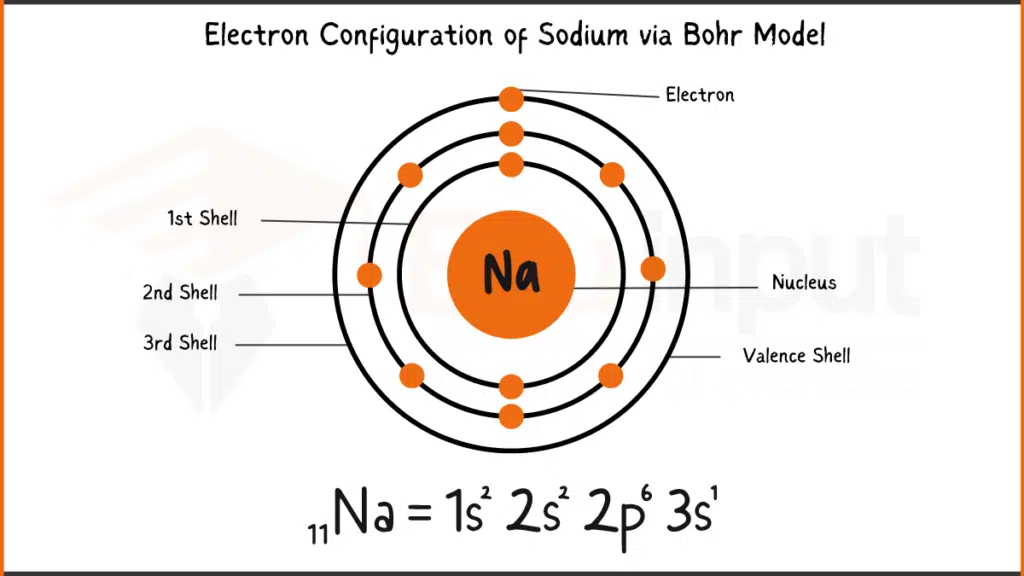
Electronic Configuration of Sodium
Sodium (Na) with 11 electrons has the electronic configuration: 1s²2s²2p⁶3s¹. In simpler terms, it has 2 electrons each in the first two shells (1s and 2s), 6 electrons in the next shell (2p), and a single electron in the outermost shell (3s).
Electronic Configuration of Sodium via Bohr Model
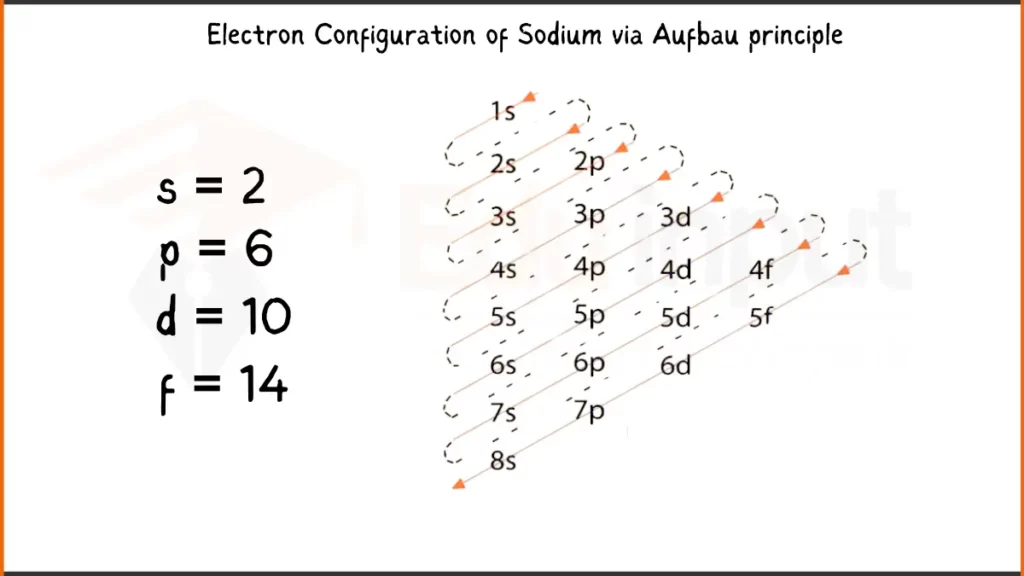
Electronic Configuration of Sodium via Aufbau Principle
Facts
- Sodium is the sixth most abundant element on Earth.
- Sodium is essential for life, and it plays a crucial role in regulating fluid balance, transmitting nerve impulses, and maintaining blood pressure.
- Sodium is used in many industrial processes, including the production of soap, glass, and paper.
- Sodium vapor lamps are used in streetlights and other outdoor lighting applications.
- Sodium is also used as a coolant in nuclear reactors.
Applications
Sodium has many important applications in industry and daily life. Some of its key applications include:
- Production of soap and glass
- Paper manufacturing
- Water treatment
- Sodium vapor lamps for streetlights
- Food preservation and flavoring
- Pharmaceutical industry
- Coolant in nuclear reactors
Sodium is an important chemical element with a range of important properties and applications. Its discovery and properties have contributed significantly to the development of modern science and technology. From industrial processes to everyday life, sodium continues to play a vital role in various fields.





Leave a Reply