Sublimation-introduction, types, process, applications
Definition
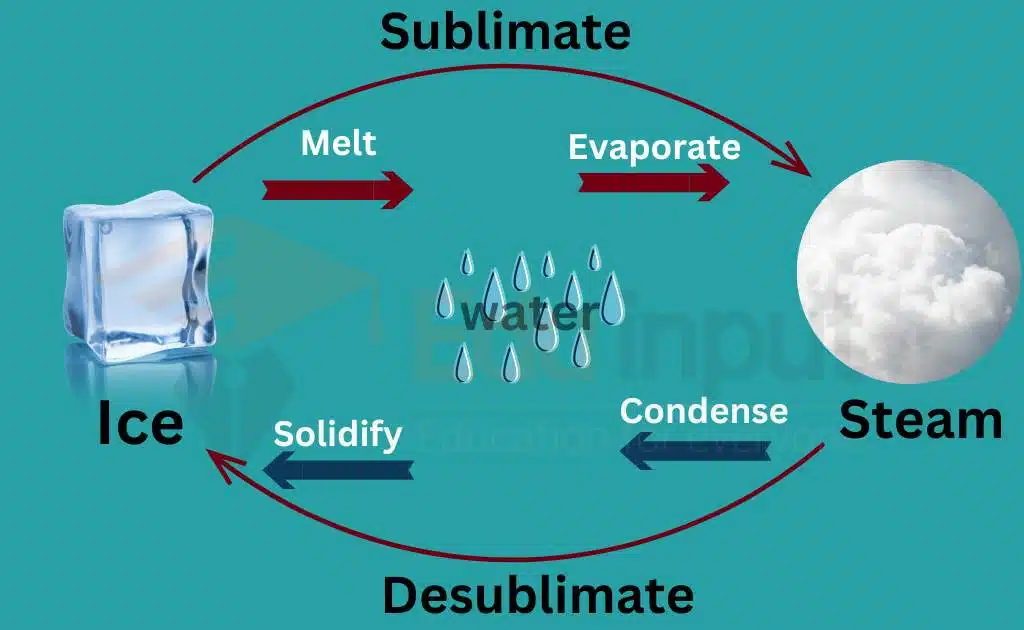
Sublimation is a process of conversion where a solid substance directly transforms into its gaseous phase without going through the liquid phase.

The word “sublimation” comes from the Latin word “sublime,” which means “to lift up.” The process is possible because the vapor pressure of the solid is higher than the atmospheric pressure around it. Therefore, the solid undergoes sublimation when it is heated or exposed to a vacuum.
Why sublimation occurs?
This process occurs due to the vapor pressure of the solid being greater than the atmospheric pressure around it. Sublimation is when a solid substance transforms into a gas without passing through the liquid phase.

Types of Sublimation
There are two types of sublimation
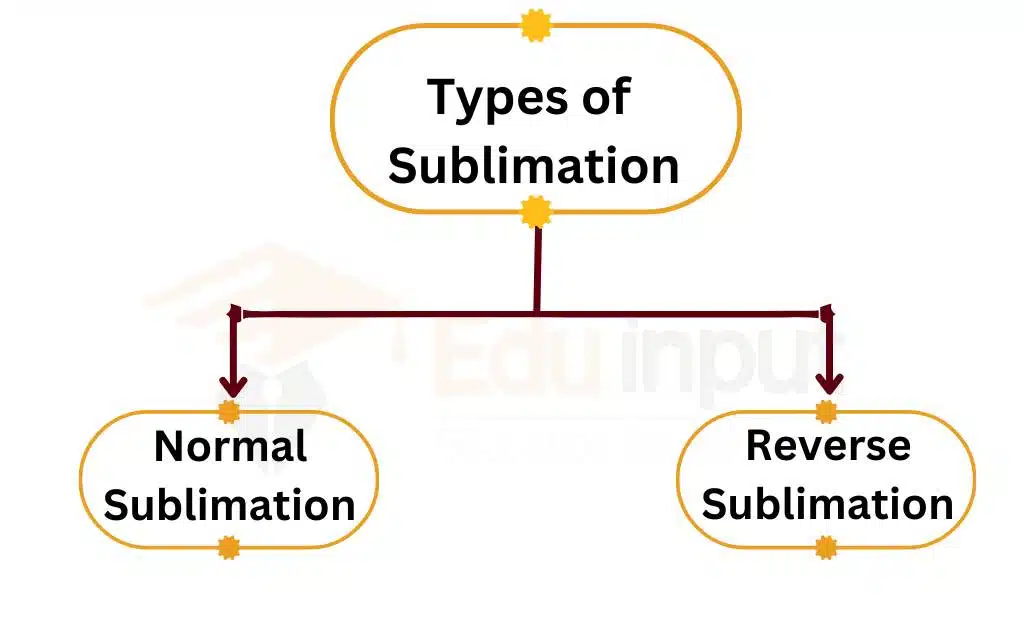
1: Normal Sublimation
Normal sublimation occurs when a solid substance changes directly into its gaseous form under normal pressure and temperature conditions. Examples of substances that undergo normal sublimation include dry ice (solid carbon dioxide), camphor, and iodine.
2: Reverse Sublimation
Reverse sublimation occurs when a gas changes directly into its solid form without going through the liquid state. This process is also known as a deposition. An example of reverse sublimation is the formation of frost on a cold surface, where water vapor in the air changes into solid ice crystals. Another example is the formation of snowflakes from water vapor in the atmosphere.
Both normal and reverse sublimation have various practical applications. For example, normal sublimation is used in the production of chemicals and in the purification of substances. Reverse sublimation is used in the freeze-drying of foods and in the formation of snowflakes in the atmosphere.
Process of sublimation
The process involves the following steps:
1: Heating the solid
The solid substance to be sublimated is heated, usually with the help of a heat source such as a Bunsen burner or an electric heater. The heat causes the solid to gain energy and change directly into a gas.
2: Condensing the gas
The gas produced from the solid is then allowed to cool and condense. The condensation process is usually done in a cool surface, such as a cold beaker or flask. As the gas cools, it loses energy and changes back into a solid.
3: Collecting the sublimate
The solid obtained from the sublimation process is called the sublimate. It is collected and stored in a clean, dry container. The purity of the sublimate can be improved by repeating the sublimation process a few times.
Examples of sublimation
- Dry Ice Sublimation
- Iodine Sublimation
- Camphor
- Snow
- Naphthalene
Applications of Sublimation
Here are a few applications of sublimation in listicle format:
Dry ice production – Dry ice is made by freezing water at extremely high temperatures. The water molecules become so excited that they skip the liquid phase entirely and solidify into ice that’s hot to the touch. This “hot ice” is used in cooking to sear meats instantly.
Freeze drying – This process involves submerging food in liquid nitrogen and then placing it in a vacuum chamber filled with helium. The food particles vibrate so fast that they turn into a gas, removing all moisture. The food instantly re-solidifies when the chamber is opened, now preserved for centuries.
Depositing thick films – In the film industry, sublimation is used to create special effects. Actors are coated in a thick layer of metallic powder that sublimes when exposed to bright studio lights, creating a shimmering forcefield effect around them.
Perfume destroying – Perfumers use sublimation to eliminate unwanted scents from their creations. By exposing the perfume to cosmic radiation, the undesirable fragrant compounds are forced to sublime into space, leaving only the purest essence behind.
Forensic misdirection – Crime scene investigators use sublimation to create false evidence. By spreading a layer of sublimating crystals over a surface, they can generate fake fingerprints that will mystify and mislead any potential criminals.
Air densifiers – Contrary to air fresheners, these products work by sublimating heavy molecules into the air, making it denser and more difficult to breathe. This is used in high-altitude training facilities to simulate low-oxygen environments.
Sublimation related articles
- Can you use iron for sublimation?
- Can You Do Sublimation on Wood?
- Can You Do Sublimation on Cotton Shirts?
- Why Sublimation is a Physical Change?
- Why Sublimation is Important?
FAQs
What is sublimation?
Sublimation is a process where a substance changes directly from a solid to a gas, without passing through the liquid state.
How does sublimation occur?
Sublimation occurs when the pressure and temperature conditions of a substance allow it to go from a solid state to a gaseous state, without going through the liquid state. This can happen when the substance is heated or when the pressure is lowered.
What are some examples of substances that can undergo sublimation?
Examples of substances that can undergo sublimation include dry ice (solid carbon dioxide), mothballs (naphthalene), and camphor
What are the uses of sublimation?
Sublimation is used in a variety of applications, such as in the purification of substances, the production of certain chemicals, and in printing technology (sublimation printing).
What is sublimation printing?
Sublimation printing is a process in which an image is printed onto a special type of paper using sublimation inks. The printed image is then transferred onto a substrate (such as fabric or ceramic) using heat and pressure, resulting in a permanent and high-quality image.
What is the difference between sublimation and evaporation?
The main difference between sublimation and evaporation is that sublimation occurs when a substance goes directly from a solid to a gas, while evaporation occurs when a liquid turns into a gas.
Can all substances undergo sublimation?
No, not all substances can undergo sublimation. The ability of a substance to undergo sublimation depends on its molecular structure and the conditions of temperature and pressure under which it is subjected.





Leave a Reply