The Most Exciting Biology Discoveries of 2022
Biology is a constantly evolving field, and every year brings new and exciting discoveries that shed light on the mysteries of the natural world.
There have been many significant discoveries in the field of Biology in 2022. They have changed our understanding of the natural world, living organisms, and Ecosystems around us.
In this article, we’ll take a look at the top discoveries in Biology that have had the greatest impact on society.
Key Points
- Advancements in vaccine technology, including inhalable vaccines and multivalent vaccines for multiple strains of a virus
- Reevaluation of the belief that amyloid protein plaques are the main cause of Alzheimer’s disease
- Discovery of a new hominin species and interbreeding between early humans and extinct species through the reconstruction of ancient DNA
- Identification of new antimicrobial peptides using AI
- Successful transplant of a genetically modified pig heart
- Improved early weather warning systems
- Solution to the problem of predicting the 3D structure of proteins using AI
- Use of CRISPR to target and repair specific genetic mutations
- Creation of a functional model of the human heart using stem cells
- Discovery of new exoplanets through the use of machine learning
Innovative Approaches in Vaccine Technology: A Success Story in the Fight Against Covid-19
In recent years, there have been significant advances in vaccine technology. Traditional vaccines work by introducing a piece of a pathogen to the body to activate the immune system. However, newly developed vaccines offer broader protection against multiple strains of a Virus.
For Example bivalent booster shots for Covid-19 and multivalent vaccines for Covid-19 and flu.
Inhalable vaccines are also being introduced, that are known as mucosal vaccines. These vaccines are already being used in China to combat Covid-19. These vaccines may offer long-term effect against respiratory viruses and may be more appealing to those who are afraid of needles. If these developments are successful, it may result in elimination of the need for annual shots.
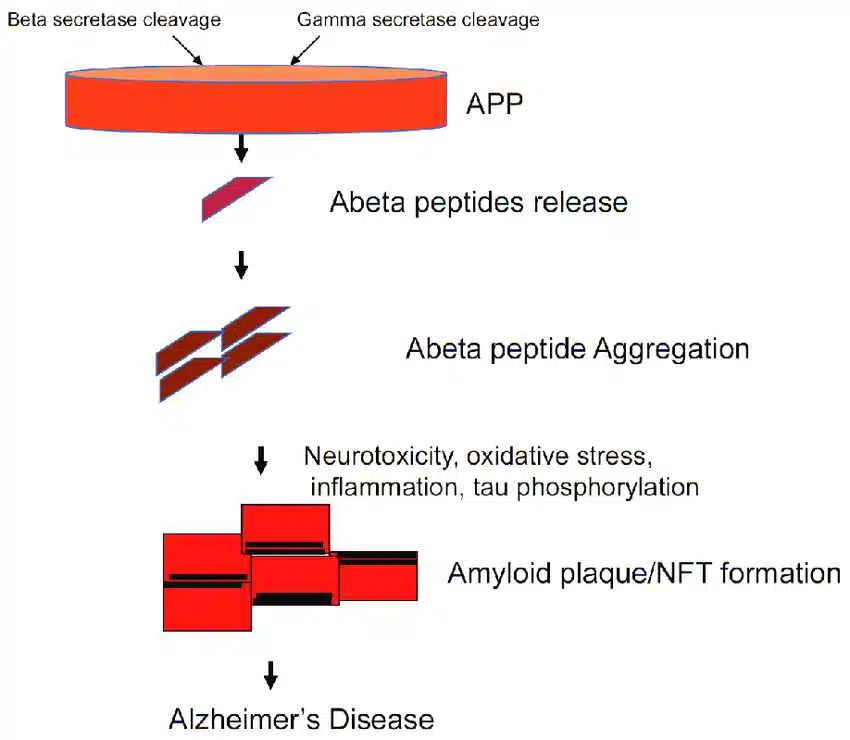
A Turning Point in Alzheimer’s Research: Is the Amyloid Hypothesis Still Relevant?
In clinical trials, two new drugs being tested for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease did not produce the desired results. The disappointing outcomes have led to a re-evaluation of the long-held belief that amyloid Protein plaques are the main cause of the disease.
Alternative theories involving inflammation and protein recycling issues within cells are gaining more attention. Research suggests that protein aggregations around cells may occur in aging tissues. This may indicate that problems with protein management may be a normal part of the aging process for cells.
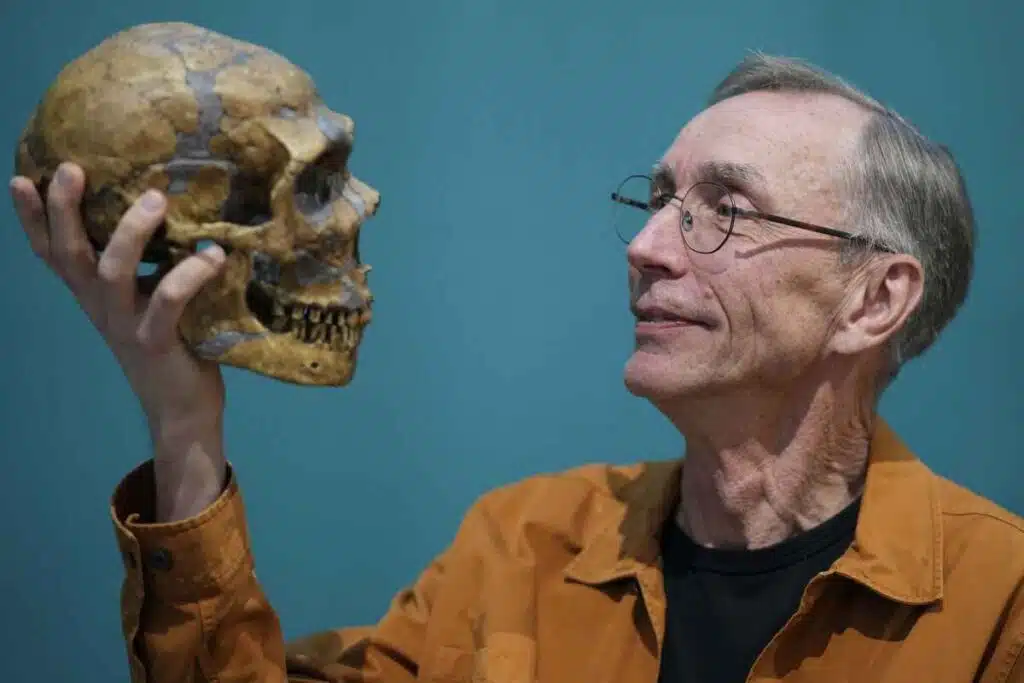
Nobel Prize-Winning Discoveries in Human Evolution
Svante Pääbo received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for his work in reconstructing ancient DNA, which led to the discovery of a new hominin species and the revelation that early humans interbred with Neandertals and Denisovans. The research also showed that traits from these extinct species are still present in some people today.

AI Discoveries of New Antibiotics
AI has been successful in identifying novel antibiotic drugs. These antibiotics offer hope in the fight against antimicrobial resistance.
Researchers used machine-learning techniques to identify antimicrobial peptides in the genome sequences of microbes like Bacteria in the human gut, and almost half of the discovered peptides were entirely new.
It means they had no obvious sequence similarity to known antimicrobials.
Animal testing showed that three of the new peptides could be used to safely and effectively treat bacterial pneumonia in mice, offering the possibility of rapid development of new treatment options for dangerous pathogenic threats.
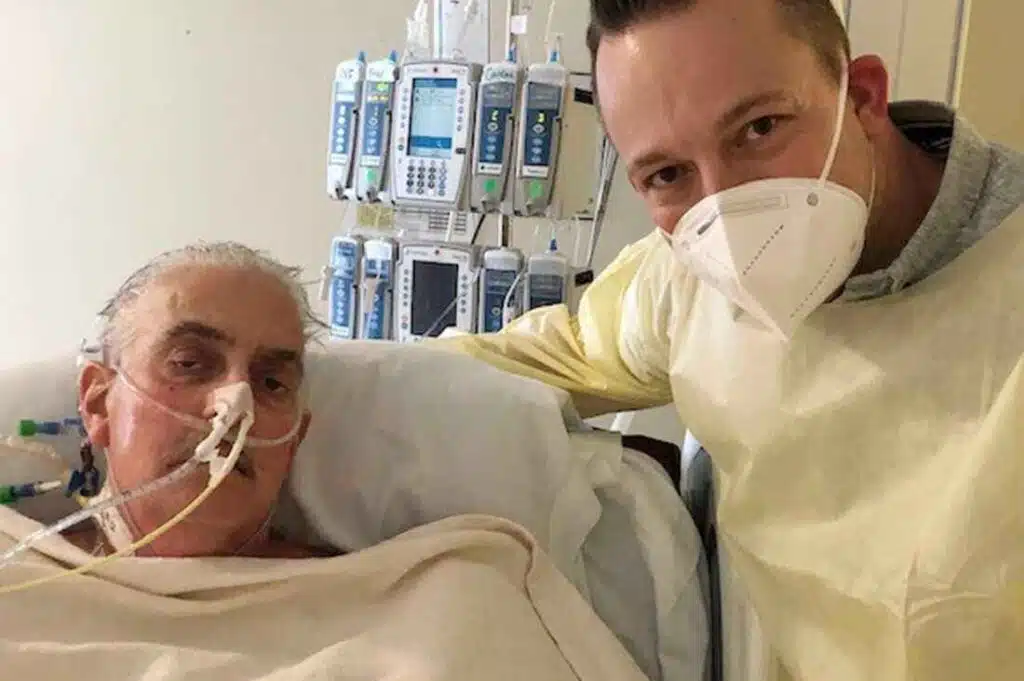
Historic Success: First Successful Xenogeneic Heart Transplant
In a first-of-its-kind surgery, a man with terminal Heart disease received a successful transplant of a genetically modified pig heart. The transplanted heart functioned well for several weeks and showed no signs of rejection, even during the autopsy. The patient died from heart failure caused by a range of factors, giving the surgeons hope for the future use of xenogeneic transplants.
Improved Early Weather Warning Systems
In 2022, technology allowed scientists to predict natural disasters like hurricanes, flooding, and wildfires in advance. However, despite these early warning systems, many people were still affected by extreme weather events caused by global heating.
The United Nations Secretary-General has called for equal access to these systems to prevent loss of life. It is important to have the necessary skills and systems, as well as the leadership to share information and act on warnings.
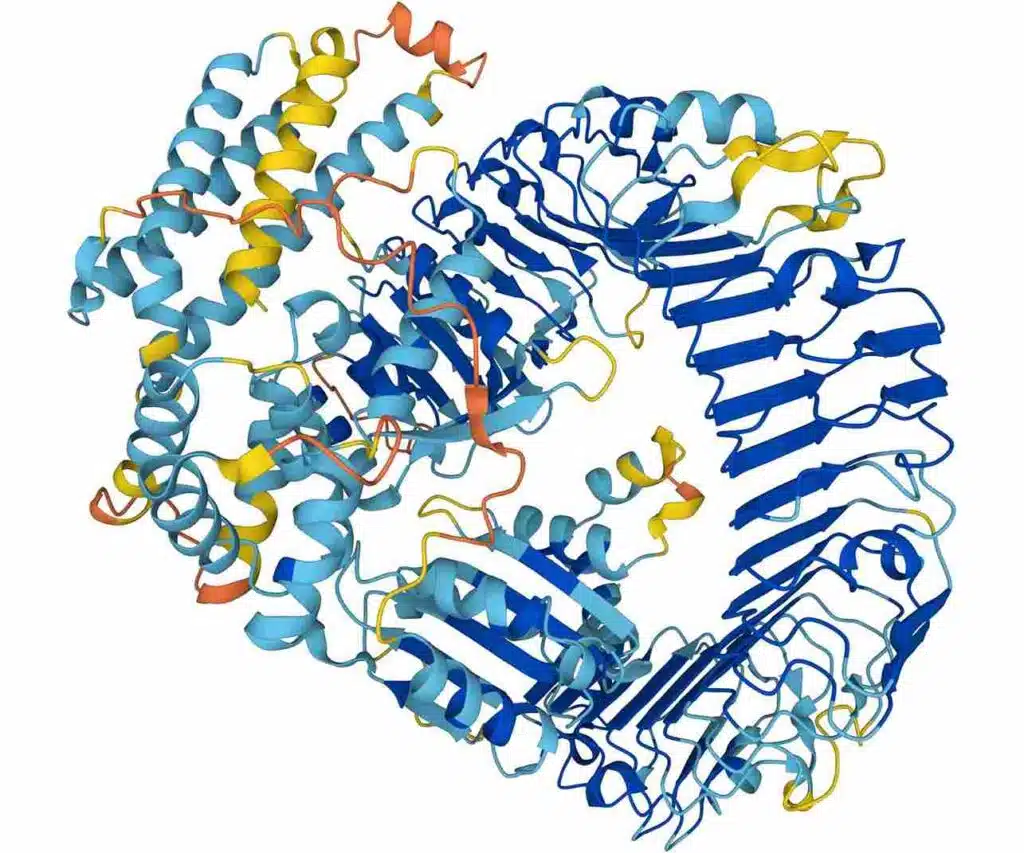
AI Breakthrough: DeepMind’s Alpha-Fold Solves 3D Protein Structure Prediction
Predicting the three-dimensional structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence has long been a challenging problem for biologists. However, this changed earlier this year when an AI program called AlphaFold, developed by DeepMind (a company owned by Google), successfully solved the structures of approximately 200 million proteins. The insights gained from these structures are already helping scientists to better understand biology and could potentially lead to the development of new pharmaceutical drugs and more sustainable crops.
Exploring the Origins of Life: Japanese Researchers Study RNA Molecules and Proto-Metabolism in Hydrothermal Vents
Scientists in Japan have been studying the evolution of RNA molecules to understand how life on Earth began. They found that different molecules can co-evolve and work together in a stable ecosystem. Other researchers are also looking at the idea that “proto-metabolism,” or early metabolic processes, may have occurred in materials near hydrothermal vents before cells existed. These studies could provide insight into the origins of life on Earth.
The Role of Physical Tension and Genetic Algorithms in the Development of Cells
Scientists are studying how a single fertilized egg cell grows into a complex adult human body with many specialized cells. They used to believe that chemical signals were the main factor, but now they think physical tension and genetic algorithms may also play a role. Synthetic biologists have made progress in understanding how these genetic algorithms control cell differentiation. They created an artificial network of genes that can transform stem cells into specialized cells and discovered that the natural system probably isn’t very complicated.
USDA Approves Sale of Genetically Modified Purple Tomato with Increased Anthocyanin
The USDA has approved the sale of a genetically modified purple tomato developed by Norfolk Plant Sciences. The tomato has a high level of anthocyanin, a pigment that gives it a vibrant purple color and is found in many natural foods. The purple tomato will be available for sale in the US starting in Spring 2023 and has a longer shelf life than regular tomatoes. The purple tomato still needs FDA approval before it can be sold commercially.
New Ultra-Rapid Genome Sequencing Method Allows for Rapid Diagnosis of Rare Genetic Diseases
Scientists at Stanford Medicine have developed a new method for rapidly sequencing genomes to diagnose rare genetic diseases. The method allowed for a diagnosis to be made in an average of 8 hours, with a record of just 5 hours in some cases.
The team was able to diagnose 42% of the patients they treated, which is higher than the average rate for diagnosing mystery diseases. One patient’s genome was sequenced in a record time of 5 hours and 2 minutes, earning a Guinness World Record for the fastest DNA sequencing technique.



Leave a Reply