Thulium-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
Thulium is a chemical element with the symbol Tm and atomic number 69. It is a silvery-gray metal that belongs to the lanthanide series of the periodic table. Thulium is one of the least abundant of the rare earth elements, making up only about 0.5 parts per million of the Earth’s crust.
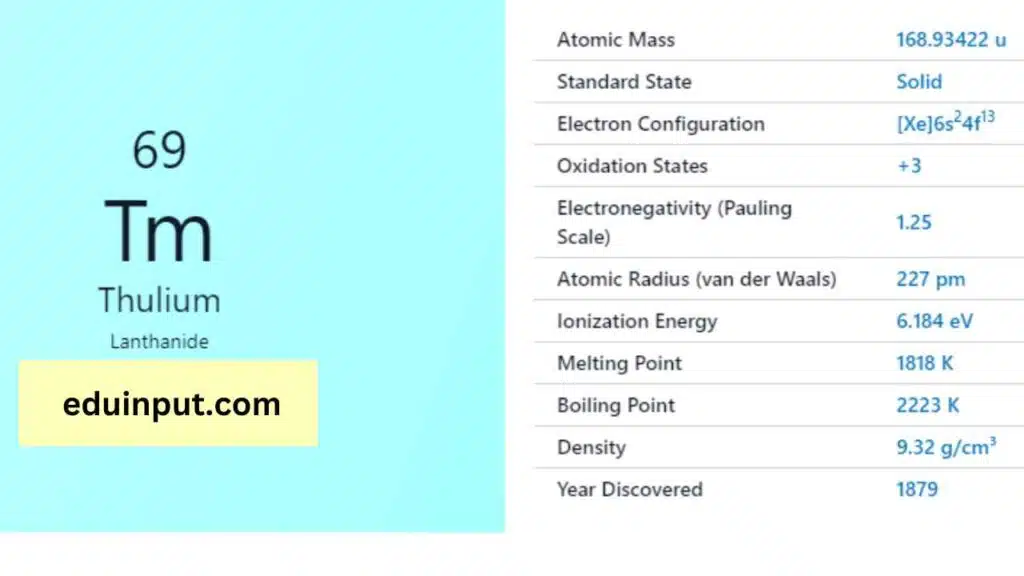
| Property | Value |
| Name | Thulium |
| Symbol | Tm |
| Atomic number | 69 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | Group in the periodic table |
| Standard state | Solid at 298 K |
| Appearance | Silvery white |
| Classification | Metallic |
| Period in the periodic table | |
| Group name | Lanthanoid |
| Block in the periodic table | 6 (lanthanoid) |
| Block in periodic table | f |
| Shell structure | 2.8.18.31.8.2 |
| CAS Registry | 7440-30-4 |
Discovery
Thulium was first discovered in 1879 by Swedish chemist Per Teodor Cleve. He separated it from the rare earth oxide erbia, which had previously been thought to be a single element. Cleve named the new element after Thule, a mythical region in Scandinavia, as he considered it to be the most northern of the rare earths.
Physical Properties
Thulium is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal, with a melting point of 1545°C and boiling point of 1947°C. It has a silver-gray appearance and tarnishes slowly in the air. Thulium has high magnetic susceptibility and has one of the largest magnetic moments among rare earth metals.
Chemical Properties
Thulium is a reactive element and reacts slowly with water and rapidly with acids. It is found in nature in only one stable isotope, 169Tm. It also has six radioactive isotopes, with the most stable being 171Tm with a half-life of 1.92 years.
Facts
- Thulium is used as a radiation source in portable X-ray devices.
- It has potential use in lasers and in high-temperature superconductors.
- Thulium is also used as a dopant in fiber optic amplifiers.
Applications
Thulium has a few practical applications, including:
- Portable X-ray machines: Thulium is used as a radiation source in portable X-ray machines.
- High-temperature superconductors: Thulium is used in the manufacturing of high-temperature superconductors.
- Lasers: Thulium-doped fiber lasers are used in material processing and medical applications.
Thulium is an important rare earth metal with unique physical and chemical properties. Despite its limited abundance, it has found practical applications in several areas, including portable X-ray machines, high-temperature superconductors, and lasers. Ongoing research on thulium’s properties may lead to new applications in the future.






Leave a Reply