What are Lipids?-Discovery, Sources, Classification, and Importance
Lipids are a heterogeneous (different chemical nature) group of compounds related to fatty acids. They are soluble in organic solvents, like alcohol, ether chloroform, and benzene, Lipids include fats, oils, waxes, cholesterol, and related compounds but are insoluble in water.
Source of Lipid
Excessive carbohydrates in the diet are converted into triglycerides, which involve the synthesis of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA through the lipogenesis process. And this process takes place in the endoplasmic reticulum.
Discovery of Lipids
For a century, chemists regarded “fats” as only simple lipids made of fatty acids and glycerol (glycerides), but new forms were described later. Theodore Gobley (1847) discovered phospholipids in mammalian brains and hen eggs. He named them “lecithins”.
Classification of Lipids
Lipids have been classified as
• Acylglycerols
• Waxes,
• Phospholipids
• Sphingolipids
• Glycolipids
• Terpenoids (carotenoids and steroids)
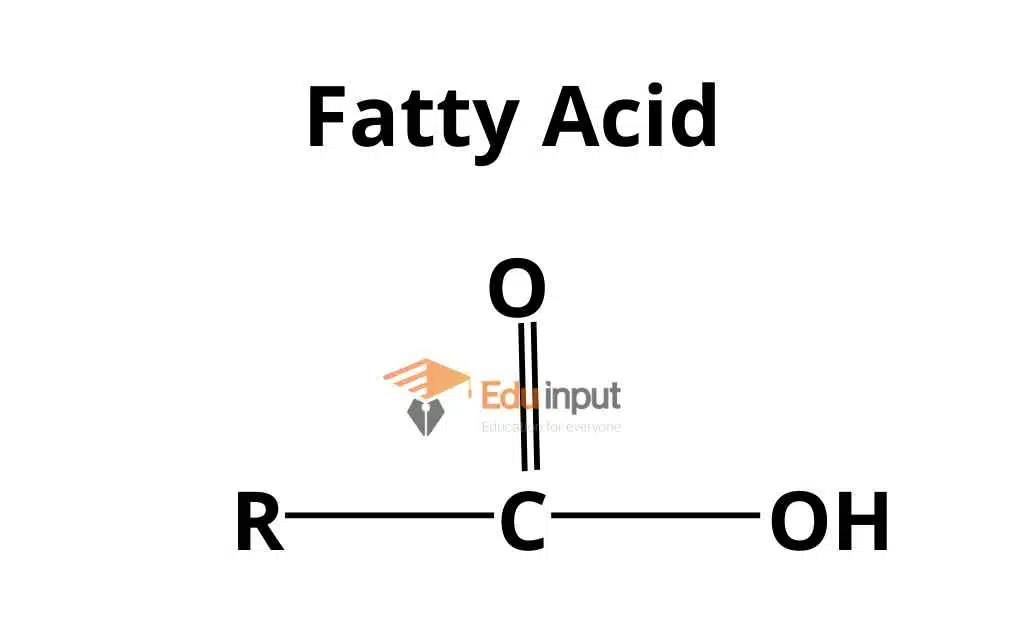
Acylglycerols (Fats)
Chemically, Acylglycerols are defined as esters of fatty acids and alcohol.
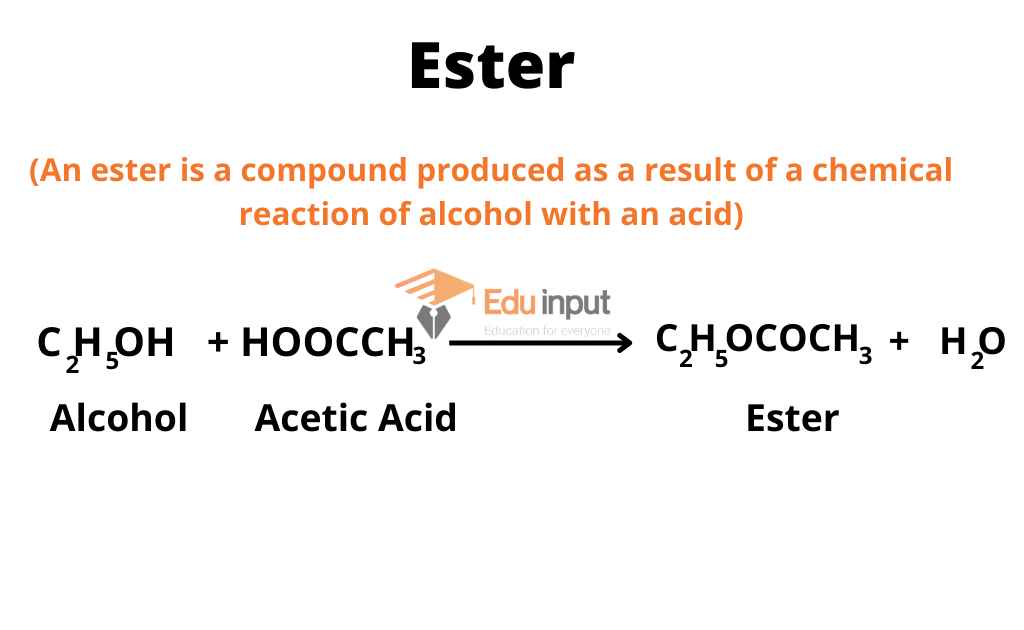
What is Ester?
An ester is a compound produced as a result of a chemical reaction of alcohol with an acid. During this reaction, a water molecule is released.
Triglycerides
The most abundant acylglycerol is triacylglycerol. It is also called triglycerides.
Waxes
Chemically, waxes are a mixture of long chain alkanes with an odd number of carbon from (C25 to C30), alcohols, ketones, and esters of long chain fatty acids.
Functions of Waxes
They perform different functions in plants and animals:
In plants: They form a protective coating on fruits and leaves. Waxes protect plants from water loss and abrasive damages
In animals: Some insects secrete waxes. They also provide water barriers for insects and birds.
Phospholipids
Phospholipids are derivatives of phosphatidic acid.

Composition of Phospholipids
• Phosphatidic acid is composed of glycerol, fatty acids, and phosphoric acid.
• Nitrogen bases like choline, ethanolamine, and serine are important components of phospholipids. Phospholipids are present in bacterial, animal, and plant cells. They form a part of the cell membrane in combination with proteins and carbohydrates. Phosphatidylcholine is the most common phospholipid.
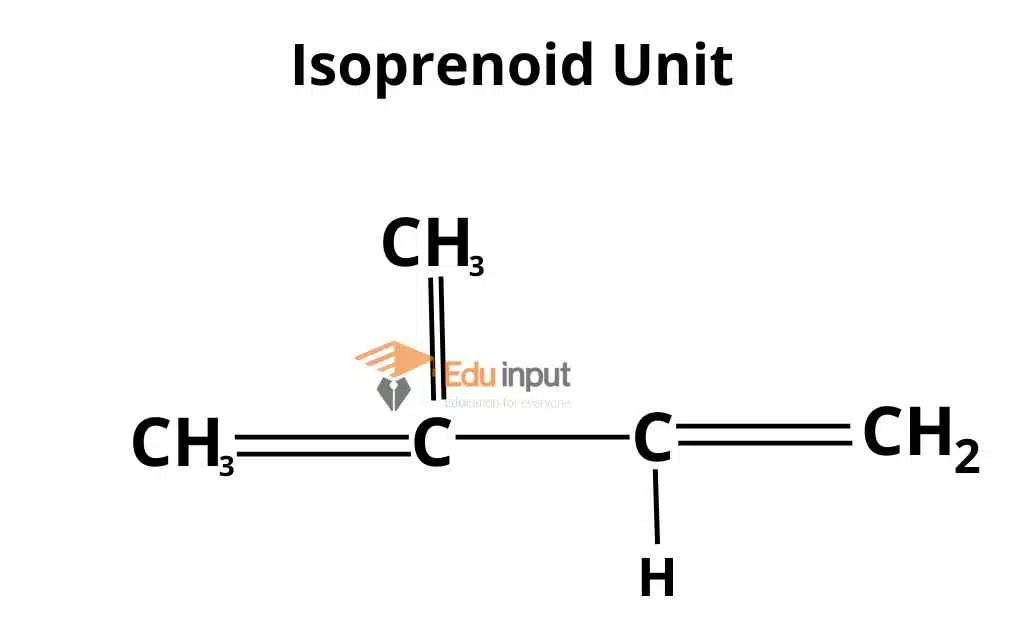
Terpenoids
Terpenoids are very large and important compounds. Terpenoids are made up of the simple repeating units of isoprenoids. This unit undergoes condensation in different ways and forms different compounds. Some of these compounds are rubber, carotenoids, steroids, terpenes, etc.
Importance of Lipids
Lipids perform the following functions:
1. Lipids are hydrophobic. Therefore, they form components of the cell membrane.
2. Lipids act as storage compounds like fats.
3. Lipids have a high proportion of C-H bonds and a low proportion of oxygen. Thus lipids store double the amount of energy compared to carbohydrates.
4. Some lipids provide insulation against atmospheric heat and cold. They also act as waterproof materials, For example, waxes in the exoskeleton of insects. A wax cutin forms an additional protective layer on the cuticle of the epidermis of some plant organs like leaves, fruits, seeds, etc.
5. Some lipids like steroid hormones, and cholesterol perform important functions in the bodies of animals.
Related FAQs
What are Lipids?
Lipids are a heterogeneous (different chemical nature) group of compounds related to fatty acids.
What are Esters?
An ester is a compound produced as a result of a chemical reaction of alcohol with an acid. During this reaction, a water molecule is released.
What are the types of Lipids?
Lipids have been classified as
• Acylglycerols
• Waxes,
• Phospholipids
• Sphingolipids
• Glycolipids
• Terpenoids (carotenoids and steroids)
What are lipids made up of?
Lipids are made up of monomers of fatty acids, that consist of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. Sometimes it also contains phosphorus, nitrogen, and sulfur.





Leave a Reply