Preposition-Elements, Features, Types, And Common Preposition Confusions
What is A Preposition?
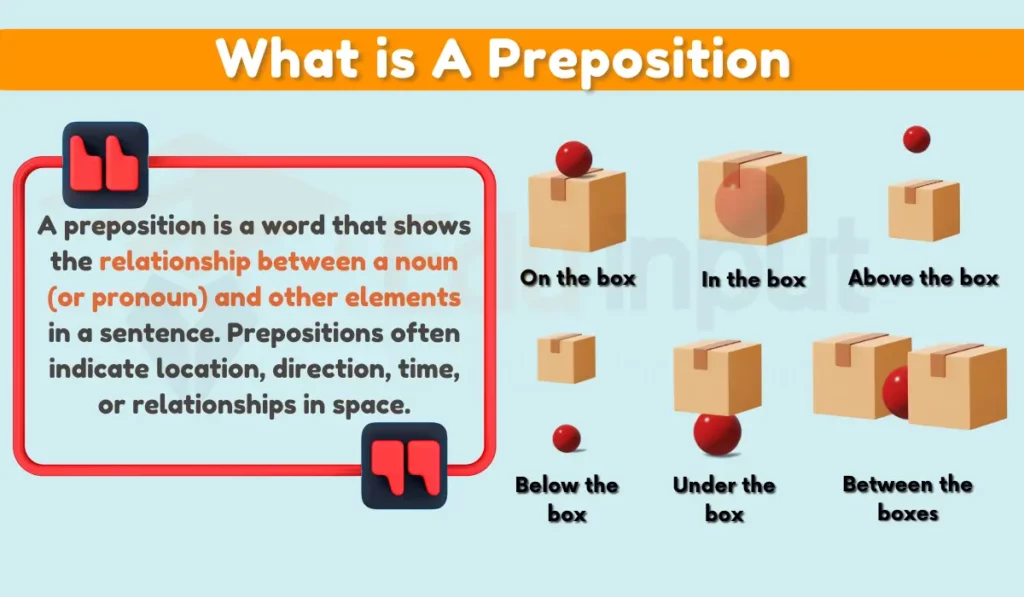
A preposition is a word that shows the relationship between a noun (or pronoun) and other elements in a sentence. Prepositions often indicate location, direction, time, or relationships in space.
Prepositions List
Elements of Preposition
The primary elements of a preposition include:
1. Preposition
The core word that indicates the relationship between the noun (or pronoun) and other elements in the sentence. Examples include “in,” “on,” “at,” “under,” and “between.”
2. Object of Preposition
The noun or pronoun that follows the preposition and forms the core of the relationship. For example, in the phrase “on the table,” “on” is the preposition, and “the table” is the object of the preposition.
3. Modifiers
Prepositions can be modified by adjectives or other words that provide additional details or information about the relationship. In the phrase “under the old bridge,” “under” is the preposition, and “the old bridge” serves as both the object and a modified element.
Features of Preposition
Here are the basic features of prepositions:
- Prepositions express a relation between two entities, typically linking a noun or pronoun to another word in the sentence. Examples: in the house, after class, by the tree.
- They usually indicate relationships involving time, location, direction, causation, accompaniment, manner, and more.
- Common prepositions include words like in, on, at, to, from, of, with, near, above, under, behind, inside, outside, without, before, after, during etc.
- Prepositions usually occur before a noun or pronoun which is called the object of the preposition. Example: We walked along the beach. (The object is “beach”)
- Prepositions can be used to form prepositional phrases like “in the house” that act as adjectives or adverbs.
- A single preposition can have different meanings depending on the context. For example, “at” can indicate a location or refer to a time.
- Some prepositions are two or more words like “in front of” or “because of” which serve as complex prepositions.
- Prepositions may be left out in some cases like “She is [at] school today.”
Prepositions Rules
Here is a list of some important rules for using prepositions in English:
- Prepositions usually come before nouns or pronouns and connect them to other words in a sentence. For example: “He drove to the stadium” or “I left my keys in the car.”
- When using verbs of motion (like go, come, leave, arrive), we often use prepositions to talk about movement from one place to another. For example: We flew from Paris to Rome.
- Certain verbs, adjectives and nouns are followed by specific prepositions. These combinations have to be memorized. For example: apply for, interested in, divide into, etc.
- Prepositional phrases (preposition + noun) can act as adjectives or adverbs in a sentence. For example: The book on the table is mine. I ran quickly down the street.
- The preposition determines the case of the pronoun that follows it. For example: He gave the book to me. This house belongs to them.
- Don’t end a sentence with a preposition. This can sometimes happen with relative clauses or questions. For example: The candidate I wrote about vs The candidate about whom I wrote.
- Pay attention to compound prepositions like according to, because of, in front of etc. Don’t split them unnecessarily in a sentence.
- Some verbs can be used with different prepositions, changing the meaning. For example: talk to, talk about, talk over etc.
- In questions and relative clauses, the preposition often comes at the end. For example: Who did you go out with last night? The house (that) they live in is very old.
Types of Preposition
Here are the main types of preposition:
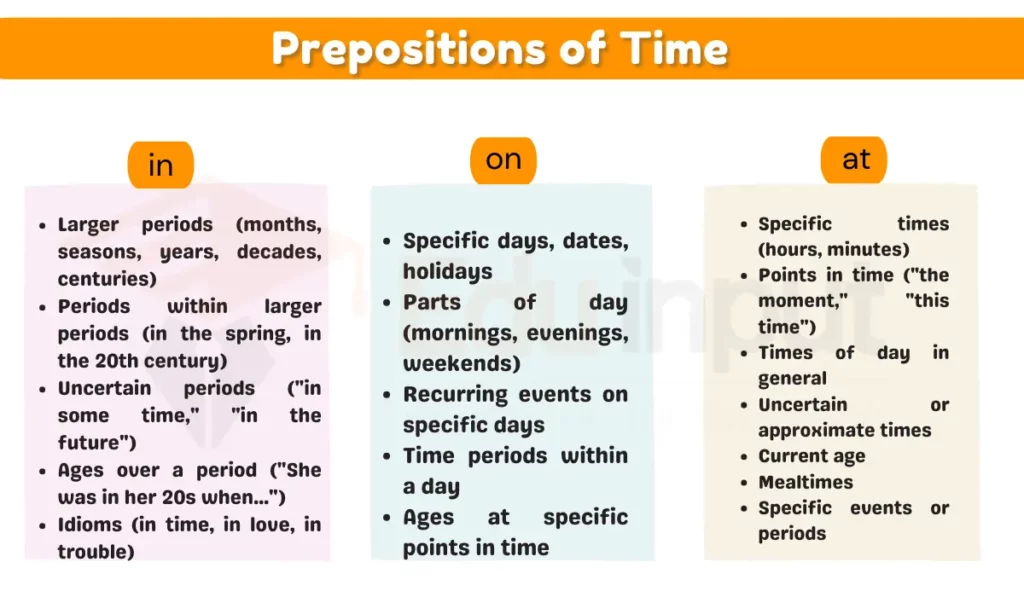
1: Prepositions of Time
Prepositions of time indicate when an action takes place, and they help specify the timing or duration of an event.
Examples
- We’ll meet at the park at 3 PM.
- The concert is scheduled for Friday night.
- They went on a vacation during the summer.
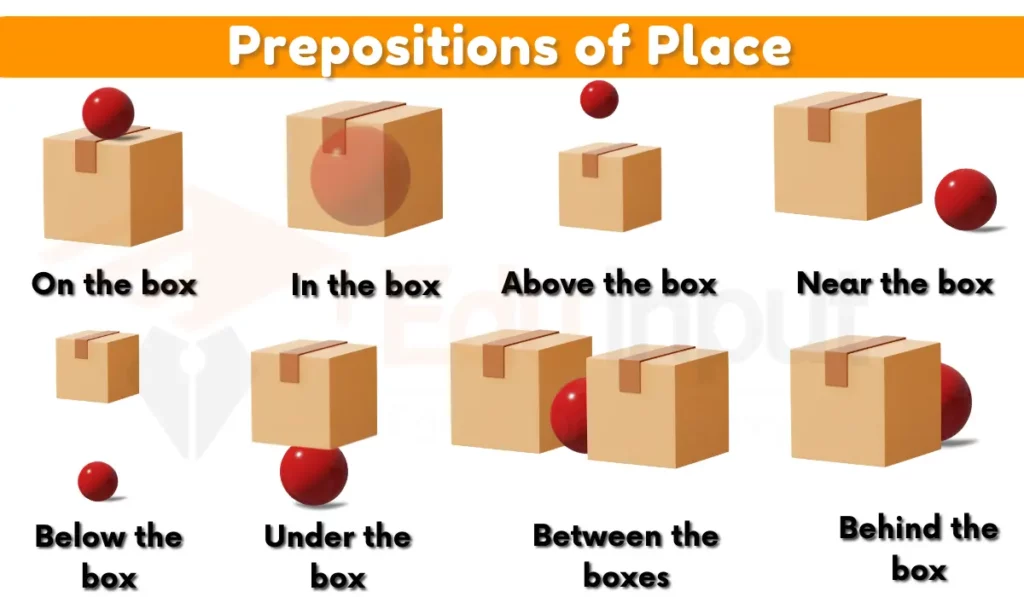
2: Prepositions of Place
Prepositions of place describe the location or position of an object or person in relation to another.
Examples
- The cat is sitting on the windowsill.
- The keys are in the drawer.
- She found her shoes underneath the bed.
3: Prepositions of Frequency
Prepositions of frequency convey how often an action or event takes place.
Examples
- I go to the gym three times a week.
- They have meetings once a month.
- She checks her email every day.
4: Prepositions of Origin
Prepositions of origin indicate the source or starting point of a person, object, or idea.
Examples
- The novel comes from a famous author.
- The tradition originates in ancient cultures.
- The technology was developed by innovative minds.
5: Prepositions of Manner
These prepositions indicate how something is done. Examples include: with, without, by, like, according to, in, on, upon, at, against.
Examples
- She completed the project with great efficiency.
- He solved the problem by thinking creatively.
- The team won the game through strategic planning.
6: Simple Prepositions
Simple prepositions are basic prepositions that establish a straightforward relationship between a noun or pronoun and another word in the sentence.
Examples
- The cat is on the roof.
- She found her keys under the table.
- The book is beside the lamp.
7: Compound Prepositions
Compound prepositions are formed by combining two or more words to create a single preposition. They express more complex relationships.
Examples
- The park is in front of the school.
- He walked alongside his friend.
- They live next to the bakery.
8: Participle Prepositions
Participle prepositions are formed by using present participles (-ing) or past participles (-ed) as prepositions.
Examples
- The child ran down the hill, laughing.
- The car drove through the tunnel, surrounded by darkness.
- She found herself in a room, decorated with flowers.
9: Double Prepositions
Double prepositions involve the use of two prepositions consecutively to convey a more specific relationship.
Examples
- He stood between the trees, among the wildflowers.
- The path led through the forest, into a hidden clearing.
- She walked along the river, past the old bridge.
10: Phrase Prepositions
Phrase prepositions are groups of words that function as a single preposition, often expressing more intricate relationships.
Examples
- She succeeded in spite of the challenges.
- They traveled the world with the exception of Antarctica.
- The event was canceled due to unforeseen circumstances.
11: Prepositions of Movement
Prepositions of movement indicate the direction or manner in which an action is performed.
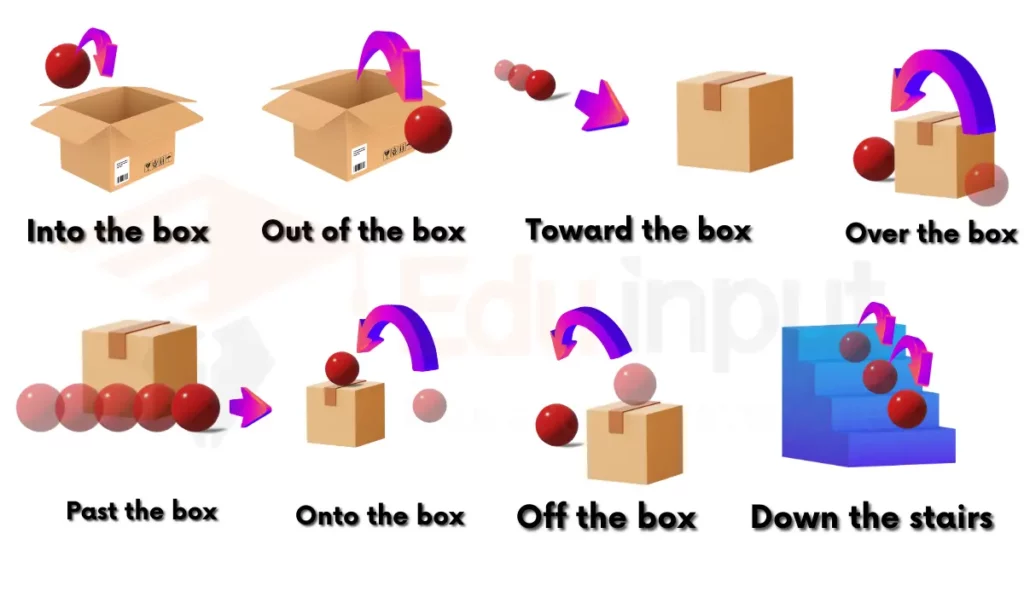
Examples
- They walked toward the city.
- The bird flew across the sky.
- We ran along the beach.
12: Prepositions of Agent
Prepositions of agent identify the person or thing responsible for an action or event.
Examples
- The novel was written by a famous author.
- The message was delivered via email.
- The cake was baked by my grandmother.
13: Prepositions of Purpose
Prepositions of purpose indicate the reason or intention behind an action.
Examples
- She went to the store for groceries.
- He studied hard to pass the exam.
- They traveled to the mountains for relaxation.
14: Prepositions of Condition
Prepositions of condition express the circumstances under which an action occurs.
Examples
- I’ll go to the beach unless it rains.
- They’ll start the project provided that they have enough resources.
- She’ll come to the party in case her schedule allows.
15: Prepositions of Contrast
Prepositions of contrast highlight differences between ideas or actions.
Examples
- His opinion stands against popular belief.
- The new policy is in contrast to the old one.
- She chose the adventurous route rather than the safe one.
16: Prepositions of Measurement
Prepositions of measurement provide information about the extent or degree of something.
Examples
- The tree is about ten feet tall.
- The journey will take approximately two hours.
- She needs the fabric to be at least three meters long.
17: Prepositions of Source
Prepositions of source indicate the origin or starting point of an action or object.
Examples
- The gift came from a distant land.
- The river flows out of the mountains.
- The idea originated with the research team.
18: Prepositions of Accompaniment
Prepositions of accompaniment convey the presence of someone or something alongside another.
Examples
- She walked to the park with her dog.
- They attended the event alongside their friends.
- He went on the trip in the company of his colleagues.
19: Prepositions of Connection
Prepositions of connection establish links or relationships between different elements.
Examples
- The bridge connects the two islands across the river.
- The train travels between major cities.
- The internet allows communication beyond geographical boundaries.
20: Prepositions of Emotion
Prepositions of emotion express feelings or emotions in relation to a particular situation or person.
Examples
- She smiled at the heartwarming gesture.
- He felt gratitude towards his supportive friends.
- The movie left everyone with a sense of joy.
21: Prepositions of Agreement
Prepositions of agreement convey alignment or concurrence with a particular idea or statement.
Examples
- I am in favor of the proposed changes.
- They voted for the new policy.
- She expressed strong support with the team’s decision.
Commonly Confused Prepositions
Here are some of the most frequent Confused Prepositions pairs:
1. In vs. On
- In: Used for locations inside something or for abstract areas.
- Example: The book is in the library. He is in love.
- On: Used for locations on top of a surface or for specific days/dates.
- Example: The keys are on the table. They met on Monday.
2. Between vs. Among
- Between: Used for two things only.
- Example: The book is between the lamp and the vase.
- Among: Used for three or more things.
- Example: The prize was shared among the winners.
3. To vs. For
- To: Used for indicating movement towards something or for the recipient of an action.
- Example: She walked to the store. This gift is for you.
- For: Used for indicating purpose, duration, or a specific recipient.
- Example: He studied hard for the exam. They waited for hours. I cooked dinner for my family.
4. Beside vs. Besides
- Beside: Used as a preposition meaning next to something.
- Example: The cat is sleeping beside the fireplace.
- Besides: Used as an adverb or conjunction meaning in addition to something.
- Example: He is tall, besides being very strong.
5. Into vs. In to
- Into: Used as a single preposition indicating movement inside something.
- Example: She put the letter into the envelope.
- In to: Used as a separate prepositional phrase, where “in” indicates location and “to” indicates movement.
- Example: I am not really in to going out tonight.
6. By vs. With
- By: Used for
- Agent performing an action: The cake was baked by my grandma.
- Means of doing something: She wrote the letter by hand.
- Point in time: We need to finish this report by tomorrow.
- With: Used for
- Accompaniment: I went to the park with my friend.
- Instrument: She painted the picture with a brush.
- Manner: He did his homework with care.
7. Since vs. For
- Since: Used for a starting point in time
- Example: I haven’t seen him since yesterday.
- For: Used for a duration.
- Example: The movie lasted for two hours.

 written by
written by 



Leave a Reply