Brassinosteroids (BR) – Structure, Biosynthesis, and Functions
Plants produce a class of Polyhydroxylated steroidal hormones called Brassinosteroids (BRS). It is defined as the sixth plant hormone after the classic plant hormones Auxin, gibberellins, Cytokinin, Abscisic acid, and Ethylene.
These hormones are similar in structure to steroids found in animals, and they play a role in plant growth and development. BRs have been found in a wide variety of plant species, including freshwater algae and brown algae.
The distribution of BRs varies among different tissues in individual plant species. Pollens, immature seeds, roots, and flowers have the highest content. While shoots and leaves have lower amounts of BRs.
History of Brassinosteroids
BRs were first identified in the 1970s as compounds that promote cell elongation in plants. However, the role of BRs in plant hormone signaling was not fully realized until the 1990s. BRs exert their effects by binding to specific receptor proteins in the cell membrane, which leads to changes in gene expression.
Biosynthesis Of Brassinosteroids
Japanese researchers were the first to discover how BRs are created, and subsequent studies involving Arabidopsis thaliana, tomatoes, and peas helped confirm their findings. There is still much unknown about where BRs are made in plants. Some scientists believe that every tissue creates BRs, due to the widespread expression of BR biosynthetic and signal transduction genes across different plant organs.
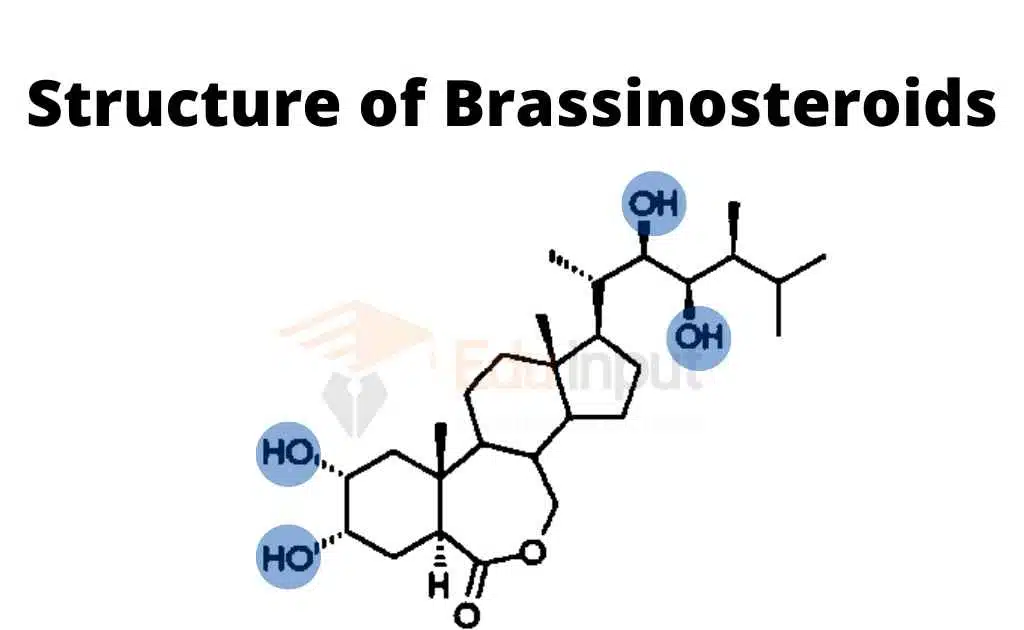
Structure of Brassinosteroids
There are three types of Brassinosteroids, which are classified according to the alkyl-substitution patterns of their side chains. In order for a Brassinosteroid to be active, it must have a trans-fused a/b ring system with two hydroxyl groups at ring a and a 6-ketone or 7-oxa-6-ketone system at ring b.
Additionally, BRs conjugated forms with sugars or fatty acids have also been found, which are the inactive products of BR metabolism. The parts within the dashed lines can be substituted by different groups.
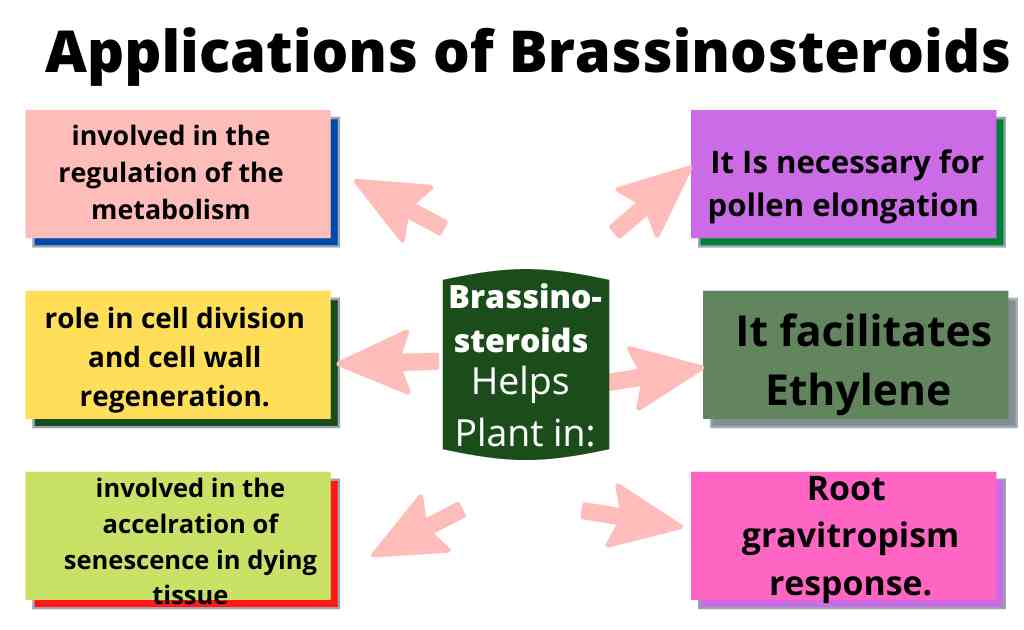
Roles of Brassinosteroids in Plants
BRs are involved in numerous plant processes:
- It promotes cell expansion and cell elongation.
- Brassinosteroids are also involved in the regulation of the metabolism of plant oxidation radicals.
- It influences vascular differentiation.
- BR’s signal transduction has been studied during vascular differentiation.
- It plays important role in cell division and cell wall regeneration.
- It is involved in the acceleration of senescence in dying tissue cultured cells.
- It Is necessary for pollen elongation (for pollen tube formation).
- It facilitates Ethylene synthesis and root gravitropism response.
- Biochemical reactions (BRs) play an important part in helping plants adapt to and recover from various types of stress, such as freezing temperatures, drought, the high salt concentration in the soil, disease, heat, and lacking key nutrients.



Leave a Reply