What is Data Science? – Applications, Lifecycle, and data scientist
Data Science is the study that uses scientific methods, processes, algorithms, and systems to extract knowledge and insights from structured and unstructured data. It combines elements of statistics, mathematics, computer science, and domain expertise to identify patterns and relationships and make predictions or decisions based on data.
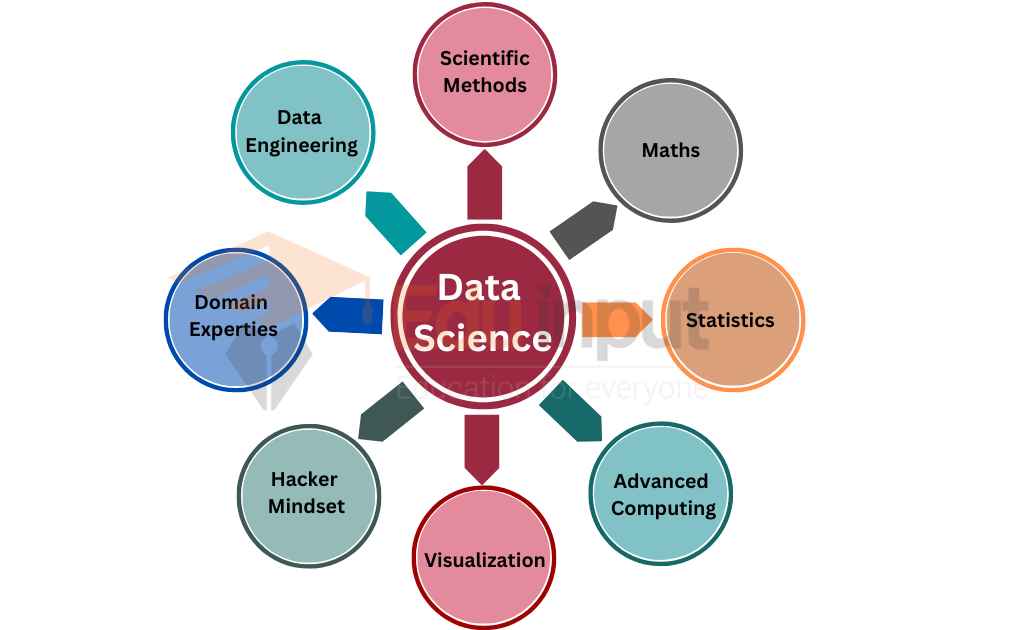
Data science aims to turn raw data into actionable insights to support decision-making and drive business value.
In this article, we will discuss data science, applications of data science, tools, and more queries about data science. After reading this blog, you will surely know all your queries about data science.
The Data Science Lifecycle
The data science lifecycle consists of the following phases:
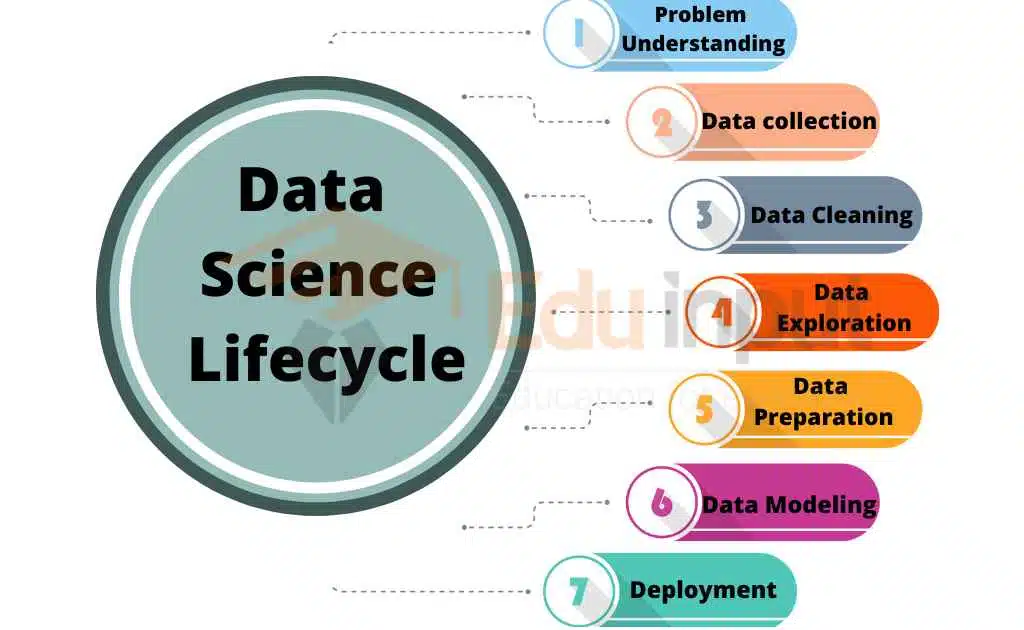
Problem Definition: In this phase, the data science team defines the problem they are trying to solve and identifies the data they need to solve it.
Data Collection: In this phase, the data science team collects data for analysis. This can involve retrieving data from databases, APIs, or web scraping.
Data Exploration: In this phase, the data science team explores the data to understand its structure and content and to identify the different issues.
Data Preparation: In this phase, the data science team cleans, transforms, and integrates the data to make it suitable for analysis.
Data Modeling: In this phase, the data science team uses statistical and machine learning techniques to build models to solve the problem.
Deployment: In this phase, the data science team deploys the selected model into a production environment, which can be used to make predictions or take actions based on the data.
Monitoring and Maintenance: In this phase, the data science team continuously monitors the performance of the deployed model and updates it as necessary to ensure it continues to deliver accurate results.
Applications of Data Science
Data science has many applications and can be used in a variety of industries and fields, including:
Healthcare: Data science is used in healthcare to analyze patient data and predict disease progression, treatment efficacy, and drug efficacy.
Image Recognition: Data science is also used to identify patterns in images and detect objects in them.
Fraud Detection: Data science is used in finance and banking institutes to detect fraudulent transactions.
Retail: Data science is used in retail to analyze customer data, identify trends and preferences, and optimize pricing and inventory management.
Marketing: Data science is used in marketing to analyze customer data, target advertising more effectively, and predict customer behavior and preferences.
Manufacturing: Data science is used in manufacturing to optimize supply chain management, improve quality control, and reduce costs.
Transportation: Data science is used in transportation to optimize routing, improve safety, and reduce emissions.
Energy: Data science is used in energy to optimize energy production and distribution, reduce costs, and improve efficiency.
Sports: Data science is used in sports to analyze player performance, predict game results, and improve player training and development.
Data science is also used in many more fields, which means it is used in every field of life today.
data scientist
A data scientist is a professional who uses data to extract insights and make informed decisions. They collect, clean, analyze, and interpret large, complex data sets to support business objectives.
Data scientists work with teams across an organization, using a combination of technical skills and business acumen to identify patterns and relationships in data. They also use machine learning algorithms and statistical techniques to build predictive models and make data-driven recommendations.
What Does a Data Scientist Do?
Data scientists perform all the activities of the data science lifecycle, which means they identify the problem, collect the data, explore the data, model the data, etc.
- Collect and clean data from multiple sources, including databases, APIs, and web scraping.
- Explore and analyze data to identify patterns, trends, and relationships.
- Build and test predictive models using machine learning algorithms and statistical techniques.
- Interpret the results of predictive models and communicate the insights and findings to non-technical stakeholders.
- Developed data-driven recommendations to support business objectives.
- Visualized and presented data clearly and meaningfully, using tools such as Tableau, matplotlib, and ggplot.
FAQs
What are the applications of Data Science?
Healthcare: Predicting diseases and treatments.
Finance: Fraud detection and risk management.
E-commerce: Recommending products.
Marketing: Analyzing customer behavior.
Transportation: Optimizing routes and traffic predictions.
Who is a data scientist?
A data scientist is an expert who works with data to find patterns, build models, and help make better decisions.
What tools are used in Data Science?
Popular tools include Python, R, Tableau, and SQL.





Leave a Reply