What is filtration? A-Z guide for students
Filtration is the method used to remove insoluble or suspended solid particles from a liquid using a filter material.
In other words, the technique of removing solid particles from a liquid or gaseous fluid by passing the fluid through a filter media while keeping the solid particles behind.
The desired product could be the fluid that has been cleared or the fluid that has had solid particles removed from it. Both the liquid filtrate and the solid filter cake are recovered in several chemical manufacturing processes. You can filter out other types of media as well, including electricity, light, and sound.
The ability to filter water was known to early humans, who dug a hole in the sand on the bank of a muddy river to a depth below the water’s surface. Sand-filtered, clear water would seep into the opening. The same procedure is frequently used to purify water for cities, although on a greater scale and with improvements.
Purpose of Filtration
The main purpose of filtering is to remove insoluble particles from liquid. It can be carried out using a variety of filter media.
Filter Media
Filtration is carried out using a variety of filter media. The kind of filter medium to be employed depends on the precipitate’s composition and other elements. Filter paper, paper pulp, filter crucibles, and cotton cloth are common filter media used in filtration.
Different Methods of Filtration
The following are the two most suitable and convenient methods of filtration:
- Through filter paper
- Through filter crucible
Filtration through Filter Paper
A range of porosities is available in filter sheets. The size of the particles in the precipitate will determine the appropriate pore size.
Filtration with filter paper and a glass funnel is typically a slow process. As the mixture is poured onto the filter paper, the solvent passes through leaving behind the suspended particles on the filter paper.
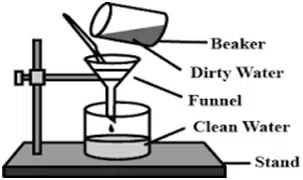
For better filtration following are some points
- The filter paper should be so large that it is one-fourth to one-half full of precipitate at the end of filtration.
- The funnel should be large enough for its rim to extend 1 to 2 cm above the top circumference of the paper.
- Filtration by a glass funnel and filter paper is a relatively slow process.
- To run the process of filtration smoothly, the stem of the funnel should remain continuously full of liquid as long as there is liquid in the conical portion.
- The stem of the funnel should be several inches long so that it can extend a few centimeters down into the receiving beaker and the tip should touch the side of the beaker. In this way, the filtrate runs down the side of the beaker without splashing.
Filtration Assembly
(i) Funnel (ii) Filter paper (iii) filtrate (iv) Beaker (v) Residue (vi) Stirrer (vii) Stand (viii) Liquid with precipitates
Folding of Filter Paper
- The folding of filter paper is important and the following points should be kept in mind:
- The paper should be folded twice. The first fold should be along the diameter of the paper. The second fold should be such that the edges do not quite match.
- The paper should be opened on the slightly larger section. This provides a cone with a three-fold thickness halfway around and one thickness the other halfway around and an apex angle very slightly greater than 60°.
- The paper may then be inserted into a 60° funnel, moistened with water, and firmly pressed down.
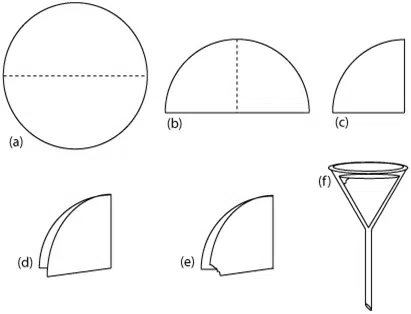
Steps To Increase the Rate of Filtration
The rate of filtration can be increased by following methods:
By Gentle Suction
The filtering operation could be very time-consuming. If it were not aided by a gentle suction as the liquid passes through the stem. This suction cannot develop unless the paper fits tightly all around its upper circumference.
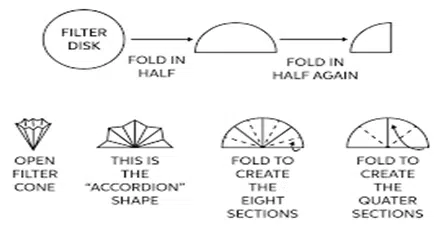
By Fluted Filter Paper
The rate of filtration through the conical funnel can be considerably increased by using fluted filter paper.
For the preparation of such a paper ordinary filter paper is folded in such a way that a fan-like arrangement with alternate elevations and depressions at various folds is obtained.
As a result, the rate of filtration increases.
Filtration through Filter Crucible
This is a convenient way to filter a precipitate by suction through a crucible. Two types of crucibles are generally used.
Gooch Crucible
- It is made up of porcelain.
- It has a perforated bottom which is covered with paper pulp or a filter paper cut to its size.
Quick filtration can be done by placing the crucibles in a suction-filtering apparatus.
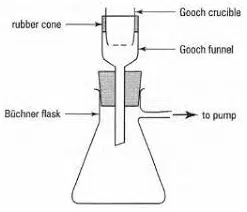
Advantages of using Gooch crucible
- It is useful for the filtration of precipitates, which need to be ignited at a higher temperature.
- If its perforations are covered with asbestos mat then it may be used to filter solutions that react with paper. For example concentrated HCl, KMnO4 solutions, etc.
- Sintered Glass Crucible It is a glass crucible with a porous glass disc sealed into the bottom.
Sintered Glass Crucible
It is a glass crucible with a porous glass disc sealed into the bottom.

Advantages of sintered glass crucible
- There is no need to place any kind of filter paper on its bottom.
- There is no contamination of filter paper when we collect the residue. No preparation is needed as with the Gooch crucible.
Why is filtration important?
Filtration is extremely important to keep things like water, chemicals, and pharmaceuticals clean, pure, and free of contaminants. If it wasn’t for filtration, we might not have safe drinking water, because it plays a crucial role in eliminating sediment, sand, gravel, carbon, and other suspended particles.
What are 3 examples of filtration?
Brewing coffee involves passing hot water through the ground coffee and a filter.
The kidneys are an example of a biological filter. …
Air conditioners and many vacuum cleaners use HEPA filters to remove dust and pollen from the air.
What is the principle of the filtration method?
The principle of filtration is that substances with particle sizes larger than the pore size of filter paper are retained on the filter paper and the rest of the fluid passes through it.
What is the application of filtration?
Applications: Filtration is used to separate particles and fluid in a suspension, where the fluid can be a liquid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Depending on the application, either one or both of the components may be isolated.
What are the factors affecting filtration?
Factors Affecting Filtration Rates and Cake Moistures
Particle Size of Solids.
The ratio of slimes to coarser particles.
Filter aids.
Feed solids concentration.
Filter Thickening.
Slurry pH.
Flocculation/Dispersion of fine solids.
Slurry Age.
What is the difference between sieving and filtration?
Sieves are used with different-sized holes to trap the impurities, whereas semi-permeable filters are generally put to use to remove fine particles that are found in the chemical solutions.
What is the effect of filtration?
Filtration always leads to an increase in the resistance to flow. In the case of a dead-end filtration process, the resistance increases according to the thickness of the cake formed on the membrane, which would be expected to be roughly proportional to the total volume of filtrate passed.






Leave a Reply