What is VPN? Types, Benefits, protocols, history of VPN
A Virtual Private Network, or VPN, provides a secure network connection while using public networks. With VPNs, your internet traffic is encrypted and your online identity is hidden, making it harder for third parties to track your online activities and steal your data. The encryption process occurs in real time.
In this article, we will explore what VPNs are, how they work, and why you might need one. Whether you’re concerned about online privacy, security, or accessing geo-restricted content, a VPN can help protect your internet activities. Let’s get started!
Virtual Private Network is often used loosely in the networking industry, much like “QoS” (Quality of Service), without clearly defining the problems and solutions. This has led to confusion among the media, experts, vendors, and consumers who use “VPN” to refer to various technologies.
| Key Points |
|---|
| 1. A Virtual Private Network (VPN) provides a secure network connection while using public networks, encrypting your internet traffic and hiding your online identity. 2. VPNs allow you to access the internet through a secure and encrypted tunnel to the VPN server as if you were connected to the VPN server’s network. 3. There are different types of VPNs available, including remote access VPNs, site-to-site VPNs, client-to-site VPNs, and mobile VPNs. 4. VPN protocols are the technology used to establish a secure connection between two devices over the internet, and there are various VPN protocols available, including IPSec, L2TP, PPTP, SSL/TLS, SSH, SSTP, IKEv2, OpenVPN, and WireGuard. 5. VPNs were first introduced in 1996 and were mostly used by businesses, but with improved encryption standards and the expansion of tunneling protocols, their use has expanded to individual users concerned about privacy and security. 6. VPNs became more popular after privacy scandals, the loss of net neutrality, and the need for secure remote access to computers and servers. |
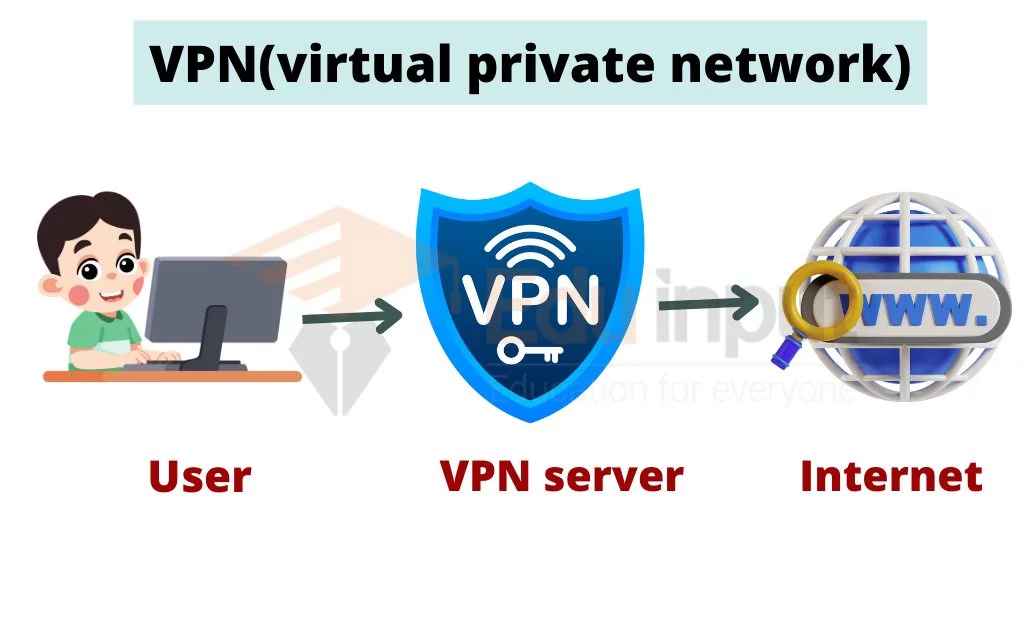
How VPN Works?
When you connect to the internet through a VPN, your device creates a secure and encrypted tunnel to the VPN server. This tunnel allows you to access the internet as if you were connected to the VPN server’s network, which can be located anywhere in the world.
Types of VPN
There are several types of VPNs available, including remote access VPNs, site-to-site VPNs, and client-to-site VPNs.
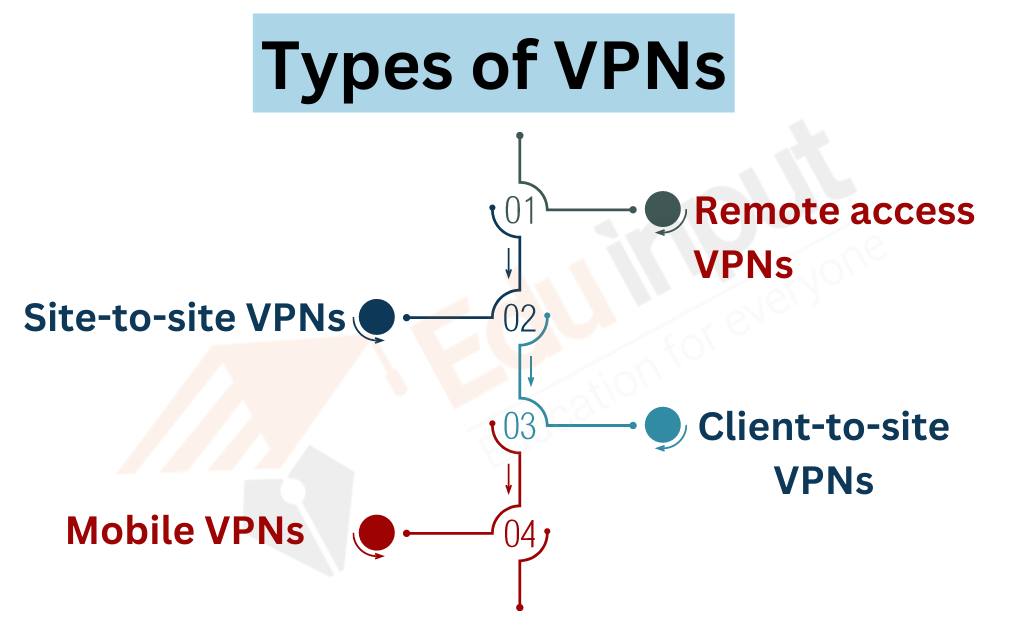
Remote access VPNs
Remote access VPNs are used by individuals who want to connect to a company’s network from a remote location. This type of VPN allows employees to access their company’s resources securely from outside the office.
Site-to-site VPNs
Site-to-site VPNs are used to connect two or more networks together securely. This type of VPN is commonly used by businesses with multiple locations or offices.
Client-to-site VPNs
Client-to-site VPNs are similar to remote access VPNs, but instead of connecting to a company’s network, they connect to a specific server or resource. This type of VPN is commonly used by individuals looking to access content that may be restricted in their region.
Mobile VPNs
Mobile VPNs are designed for use on mobile devices such as iOS or Android. They are capable of functioning on both private and public Wi-Fi networks, as well as other types of cellular networks while providing encryption for added security.
What are the VPN Protocols?
Virtual Private Network (VPN) protocol refers to the technology used to establish a secure connection between two devices over the internet. In other words, it is the method by which VPNs encrypt data to ensure privacy and security. There are various VPN protocols, and in this article, we will discuss the most commonly used ones.
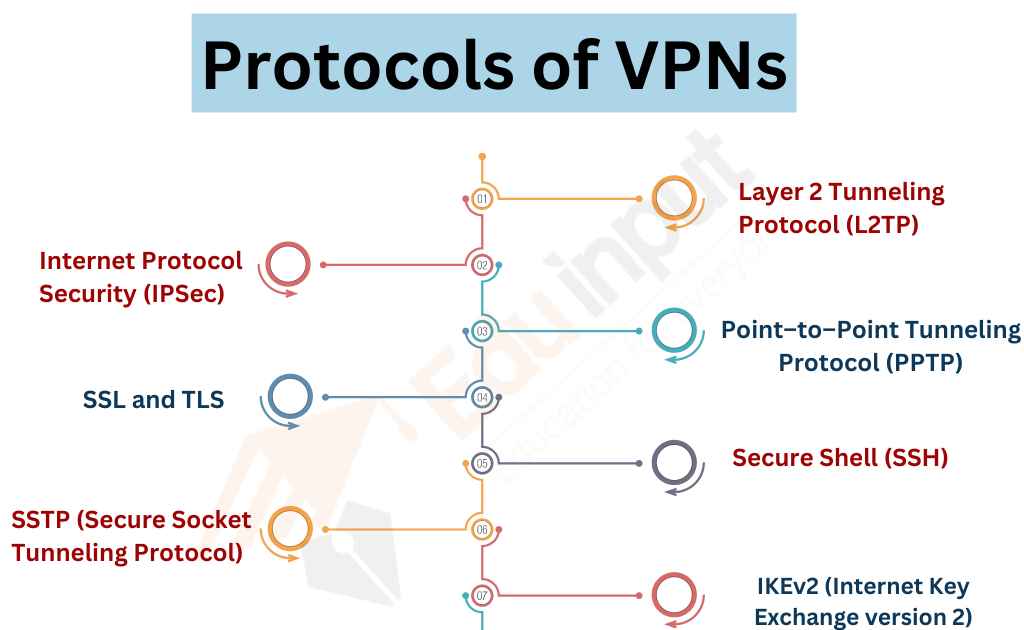
Internet Protocol Security (IPSec)
IPSec is one of the most widely used VPN protocols. It is a set of protocols to secure Internet communication by encrypting and authenticating each IP packet of data sent over the Internet. IPSec provides end-to-end security, ensuring that data is secure from the sender to the recipient.
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP)
L2TP is another popular VPN protocol used to establish a secure connection over the internet. It is a combination of Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) and Layer 2 Forwarding Protocol (L2F). L2TP provides strong encryption and authentication, making it a secure VPN protocol.
Point–to–Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP)
PPTP is an older VPN protocol that is still widely used today. It is a simple protocol that provides basic encryption and authentication. However, PPTP has some security vulnerabilities and is not recommended for use in situations where strong security is required.
SSL and TLS
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) and TLS (Transport Layer Security) are protocols used to secure internet communication. They are commonly used in web browsers to secure online transactions such as online banking and e-commerce.
SSL and TLS provide strong encryption and authentication, making them a secure choice for VPN protocols.
Secure Shell (SSH)
SSH is a protocol used for secure remote access to a computer or server over the internet. It provides strong encryption and authentication, making it a secure choice for VPN protocols. SSH is commonly used by network administrators to securely manage remote servers.
SSTP (Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol)
SSTP is a VPN protocol developed by Microsoft. It uses SSL/TLS encryption to provide a secure connection over the internet. SSTP is a secure choice for VPN protocols, as it provides strong encryption and authentication.
IKEv2 (Internet Key Exchange version 2)
IKEv2 is a VPN protocol that provides strong encryption and authentication. It is commonly used on mobile devices and is supported by most modern operating systems. IKEv2 is a secure choice for VPN protocols, as it provides excellent security and performance.
OpenVPN
OpenVPN is an open-source VPN protocol that provides excellent security and performance. It uses SSL/TLS encryption to provide a secure connection over the internet. OpenVPN is a popular choice for VPN protocols due to its ease of use and flexibility.
WireGuard
WireGuard is a newer VPN protocol that provides excellent security and performance. It is a lightweight protocol that uses state-of-the-art cryptography to provide strong encryption and authentication.
WireGuard is a secure choice for VPN protocols, as it provides excellent security and performance.
What are the VPN Protocols?
- In 1996, VPN technology was introduced when a Microsoft employee created the PPTP protocol to establish a secure connection between a user’s device and the internet. The protocol’s specification was later published in 1999.
- In the early 2000s, VPNs were mostly used by businesses for accessing private networks and secure file sharing between different offices.
- Encryption standards improved, and new tunneling protocols were developed, leading to the expansion of VPN use to individual, at-home users concerned about online threats and privacy issues.
- Privacy scandals, such as WikiLeaks and Edward Snowden’s security leaks, contributed to the increased demand for VPNs.
- In 2017, ISPs in the US were found to be collecting and selling browsing history, leading to the loss of net neutrality, and the use of VPNs became a more legitimate need for individuals.
- In 2019, a bill was passed to bring back net neutrality, but it was ultimately blocked by the Senate. Different states have since enacted their own versions of net neutrality laws.
Why Do I Need a VPN?
There are several reasons why you might need a VPN, including:
Protecting your online privacy
A VPN encrypts your internet connection, making it difficult for anyone to monitor your online activities.
Accessing restricted content
A VPN can allow you to access content that may be restricted in your region, such as streaming services or social media sites.
Using public Wi-Fi networks
Public Wi-Fi networks are often unsecured, making them a prime target for hackers. A VPN can help protect your device and data when using these networks.
Avoiding online censorship
Some countries restrict access to certain websites or online services. A VPN can help you bypass these restrictions and access the content you need.
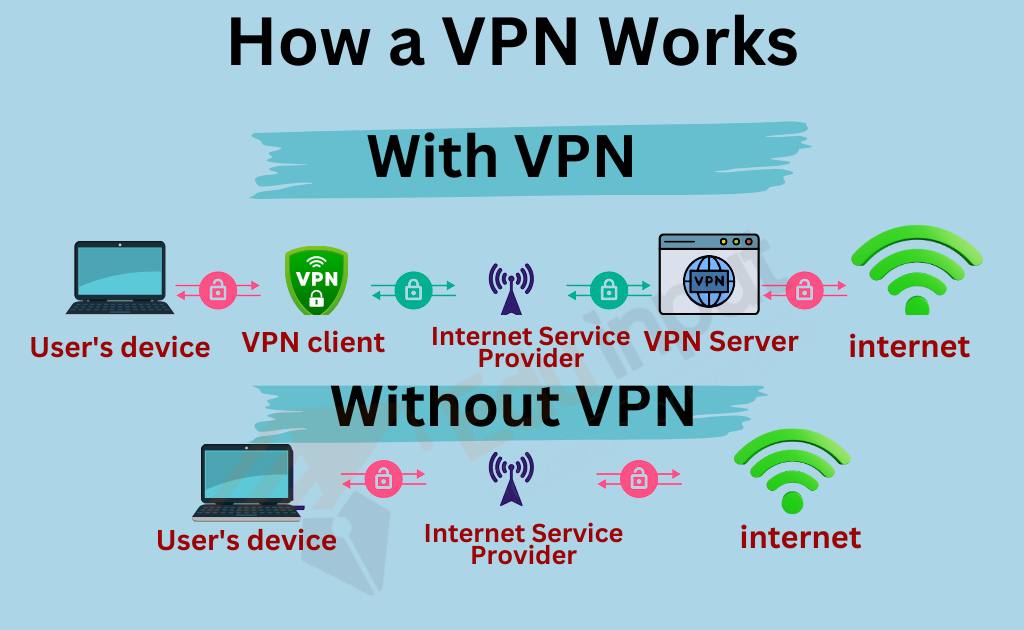
Principle of VPN Working
When you connect to a VPN, your device first encrypts all of your internet traffic. This encryption ensures no one can intercept or decipher your data as it travels over the internet.
Once your data is encrypted, it is sent to the VPN server through a secure and private connection. This server decrypts your data and then sends it on to its final destination, such as a website or online service.
Because your data is encrypted and routed through a remote server, it is much more difficult for anyone to monitor your online activities or intercept your data. This can help protect your online privacy and security, especially when using public Wi-Fi networks or accessing content that may be restricted in your region.
Benefits of VPN
VPN provides many benefits including:
Increased security
A VPN encrypts your internet connection, making it much more difficult for anyone to monitor your online activities or intercept your data.
Enhanced privacy
By routing your internet traffic through a remote server, a VPN helps protect your online privacy and can help prevent your internet service provider (ISP) from tracking your activities.
Access to restricted content
A VPN can allow you to access content that may be restricted in your region, such as streaming services or social media sites.
Improved performance
In some cases, a VPN can actually improve your internet performance by reducing latency and increasing download speeds.
How to Set Up a VPN
Setting up a VPN can be a relatively simple process, depending on the device and VPN provider you are using. Here are some general steps to follow when setting up a VPN:
Installation process
Choose a reputable VPN provider: Research and choose a VPN provider that has a good reputation for security and privacy.
Download and install the VPN software: Once you have chosen a VPN provider, download and install their software on your computer.
Connect to a VPN server: Open the VPN software and connect to a VPN server. This will create a secure and private connection to the internet.

 written by
written by 



Leave a Reply