Ytterbium-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
Ytterbium is a chemical element with the symbol Yb and atomic number 70. It is a rare earth metal and a member of the lanthanide series. Ytterbium is a soft, silvery-white metal that is relatively stable in air. It is one of the least abundant lanthanides, with an abundance in the Earth’s crust estimated to be about 3 parts per million.
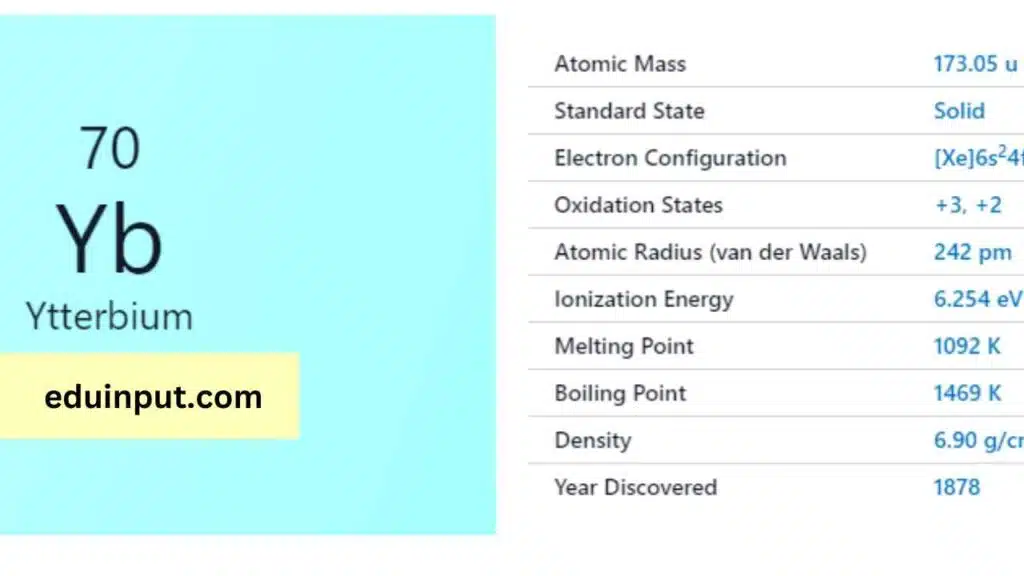
| Property | Value |
| Name | Ytterbium |
| Symbol | Yb |
| Atomic number | 70 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | Period in the periodic table |
| Standard state | Solid at 298 K |
| Appearance | Silvery white |
| Classification | Metallic |
| The group in the periodic table | |
| Group name | Lanthanoid |
| Block in the periodic table | 6 (lanthanoid) |
| Block in periodic table | f |
| Shell structure | 2.8.18.32.8.2 |
| CAS Registry | 7440-64-4 |
Discovery
Ytterbium was discovered by Swiss chemist Jean Charles Galissard de Marignac in 1878. He discovered the element in the mineral gadolinite, which had been previously discovered in a quarry near the town of Ytterby in Sweden.
Physical Properties
Ytterbium is a soft, silvery-white metal that is relatively stable in air. It is both ductile and malleable and has a melting point of 824°C and a boiling point of 1466°C. It has a density of 6.90 g/cm³.
Chemical Properties
Ytterbium is a reactive element that slowly reacts with water and is soluble in acids. It is a strong reducing agent and has two stable oxidation states, +2 and +3.
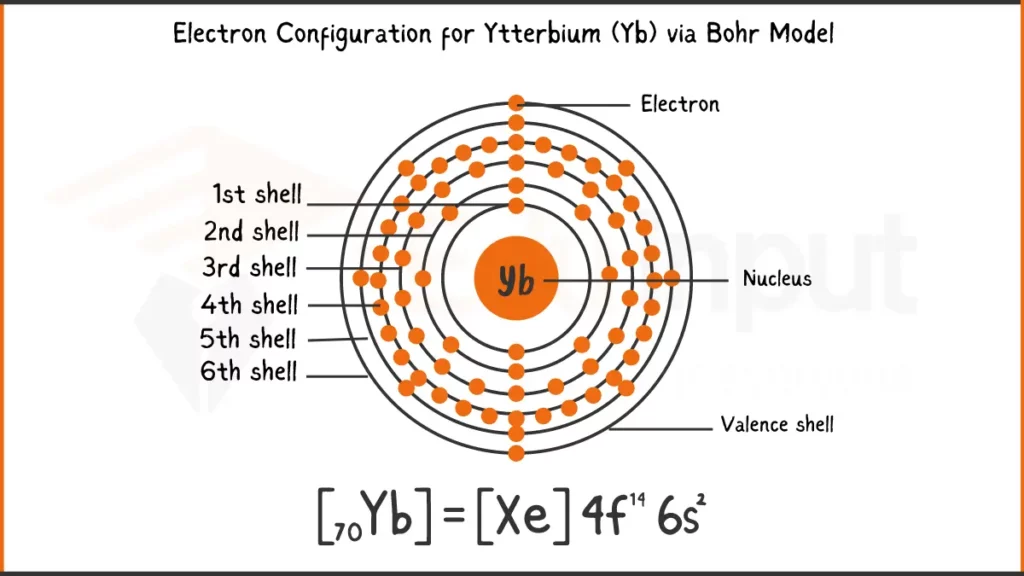
Electronic Configuration of Ytterbium
Ytterbium (Yb) with 70 electrons has the electron configuration 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶4s²3d¹⁰4p⁶4d¹⁰4f¹⁴6s². In short form, it’s written as [Xe]4f¹⁴6s², showing a xenon with a filled 4f subshell and two valence electrons in the 6s subshell.
Electronic Configuration of Ytterbium via Bohr Model
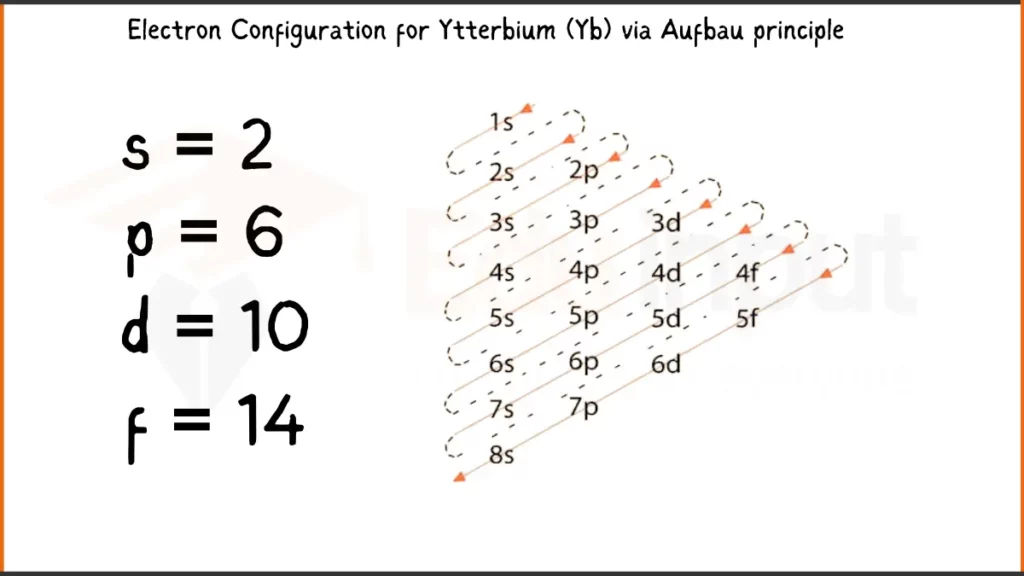
Electronic Configuration of Ytterbium via Aufbau Principle
Facts
- Ytterbium is used in atomic clocks, which are the most accurate timekeepers available today.
- It is also used in some stainless steel and as a radiation source in portable X-ray machines.
- Ytterbium has the highest known neutron capture cross-section of any isotope.
Applications
- Ytterbium is used in atomic clocks, where it provides the reference signal that keeps the clock accurate.
- It is also used in the production of stainless steel and in the nuclear industry.
- Ytterbium has potential uses in cancer treatment and as a radiation source for portable X-ray machines.
Ytterbium is a rare earth metal that is relatively stable in air and has a number of important applications. Its use in atomic clocks is particularly significant, as these clocks are used in a wide range of applications, from GPS systems to telecommunications networks. With its unique properties and potential uses, ytterbium is likely to continue to be an important element in the future.







Leave a Reply