Zener Diode as a Voltage Regulator
The Zener diode is used in digital or mixed-signal circuits to regulate voltage accurately. It offers a cost-effective and straightforward solution for controlling voltage inputs and outputs. In this article we will discuss the use of Zener diode as a voltage regulator.
Zener Diode as a Voltage Regulator
Voltage regulators are important in keeping the output voltage stable in electronic circuits. They also help to match the impedance. The most commonly used semiconductor device in voltage regulation is the Zener diode. Zener diode-based circuits are used to protect against overvoltages[1].
The Zener diode voltage regulator is a electric circuit that helps keep the DC output voltage constant. This means that the voltage stays the same even if the input changes or if the load current is different. The regulator uses a special type of diode called a zener diode.
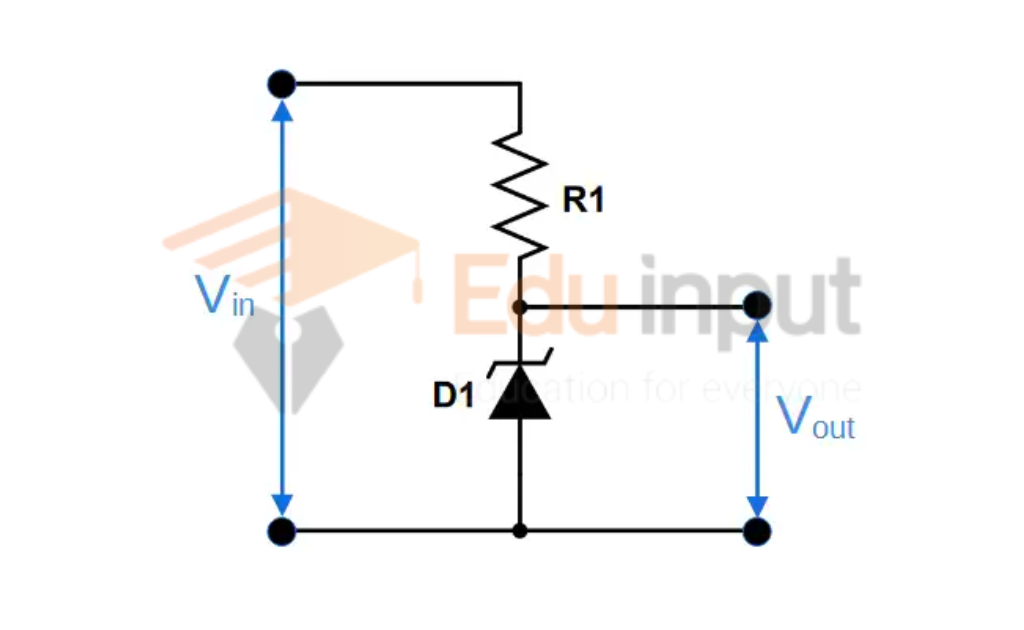
This diode has a constant voltage level, called the Zener voltage. Zener voltage stays the same even if the current changes. Zener diodes are good for use as a voltage regulator.
Zener diodes can be utilized to produce a stabilized voltage output with minimal fluctuations under different load current circumstances. This is achieved by passing a small amount of current from a voltage source through the diode and a limiting resistor (RS).
This will cause the Zener diode to conduct enough current to maintain a constant voltage drop of Vout.
Working Zener Diode as a Voltage Regulator
A Zener diode voltage regulator circuit uses a zener diode and a resistor (RS) to control the voltage output. The diode is connected to the positive side of the DC supply and the resistor is connected in series with the diode. The stabilized output voltage (Vout) is taken from the diode.

The resistor is chosen to limit the maximum current in the circuit. When there is no load connected, all the circuit’s current flows through the Zener diode, causing it to dissipate its maximum power. The correct value of the resistor must be chosen to ensure the Zener diode’s power rating is not exceeded.
The load is connected in parallel with the Zener diode, so the voltage across the load is always the same as the Zener voltage. The Zener diode must maintain a minimum current for the voltage stabilization to be effective. The supply voltage must be greater than the Zener voltage.
Sometimes the Zener diode can create electrical noise on the DC supply while trying to stabilize the voltage. This is usually not a problem, but a large decoupling capacitor may be added across the Zener’s output to provide additional smoothing.
Related FAQs
How can a Zener diode be used as a voltage regulator?
The Zener diode is used as a voltage regulator by taking advantage of its reverse bias property. The diode is designed to regulate the voltage to a constant level. The Zener diode is made of silicon semiconductor material, which is specifically designed to work in reverse bias mode.
Can the Zener diode be used as a DC voltage regulator?
Yes, zener diode are widely used as voltage regulators in small DC circuits. They are designed in a way to maintain a constant DC output voltage.

 written by
written by 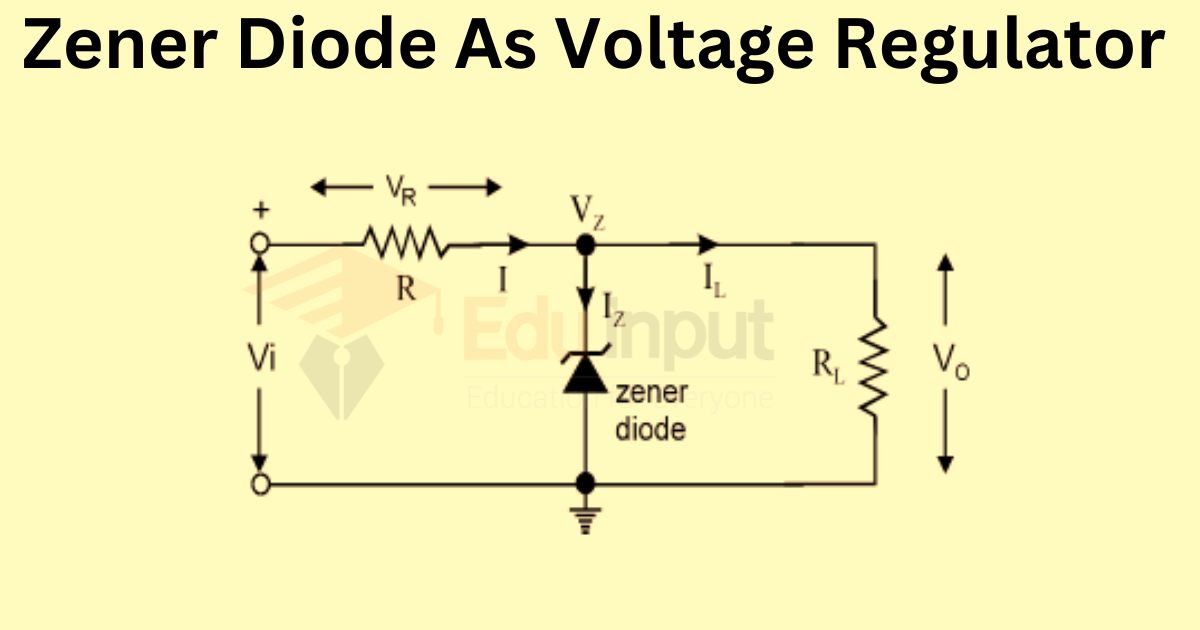




Leave a Reply