Cesium-Discovery, Properties, and Applications
Cesium is a chemical element with the symbol ‘Cs’ and atomic number 55. It is an alkali metal and belongs to the same group as sodium, potassium, and rubidium. Cesium is a soft, silvery-white metal that is highly reactive and can ignite spontaneously when exposed to air.
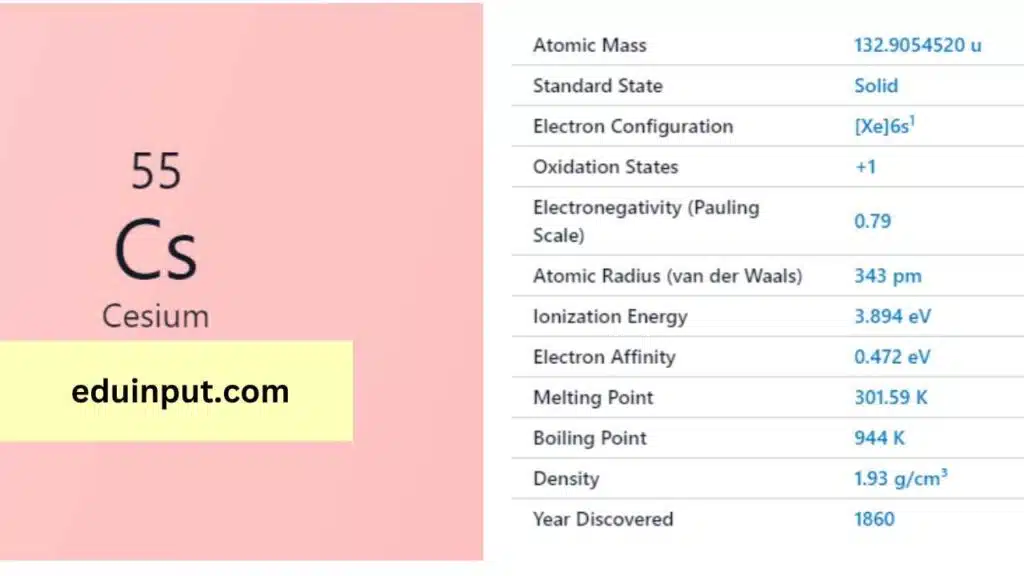
| Property | Value |
| Name | Cesium |
| Symbol | Cs |
| Atomic number | 55 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | 132.90545196 |
| Standard state | Solid at 298 K (melts slightly above) |
| Appearance | Silvery gold |
| Classification | Metallic |
| The group in the periodic table | 1 |
| Group name | Alkali metal |
| Period in periodic table | 6 |
| Block in periodic table | s |
| Shell structure | 2.8.18.18.8.1 |
| CAS Registry | 7440-46-2 |
Discovery
Cesium was first discovered in 1860 by German chemists Robert Bunsen and Gustav Kirchhoff. They identified it as a new element in the mineral water from the Durkheim springs in Germany.
Physical Properties
Cesium is a soft, ductile metal that has a low melting point of 28.5°C and a boiling point of 671°C. It is a highly reactive element and can ignite spontaneously when exposed to air. Cesium is also one of the most reactive metals with water and reacts vigorously to produce cesium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
Chemical Properties
Cesium is a highly reactive element and reacts with a variety of other elements and compounds. It reacts vigorously with water to produce cesium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. It also reacts with oxygen, halogens, and other elements to form a variety of compounds.
Facts
- Cesium is a relatively rare element and is the 45th most abundant element in the Earth’s crust.
- Cesium is the most electropositive element and has the lowest ionization energy of all elements.
- Cesium is used in atomic clocks, as it has a stable isotope that can be used to measure time accurately.
- Cesium has some potential medical applications, including the treatment of cancer.
Applications
Cesium has a range of applications in various industries. Some of the major applications of cesium include:
- Atomic clocks: Cesium is used as a timekeeping element in atomic clocks, as it has a stable isotope that can be used to measure time accurately.
- Petroleum industry: Cesium is used in the drilling of oil wells, as it can be used to make drilling muds that can prevent the collapse of the wellbore.
- Medical applications: Cesium has some potential medical applications, including the treatment of cancer.
- Catalysts: Cesium is used as a catalyst in some chemical reactions, such as the conversion of ethanol to ethylene.
Cesium is a highly reactive element with a range of applications in various industries. Its unique physical and chemical properties make it a valuable element for use in atomic clocks, the petroleum industry, and as a catalyst. Despite being a relatively rare element, cesium has potential medical applications that are currently being researched.







Leave a Reply