Cobalt-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
Cobalt is a chemical element with the atomic number 27 and the symbol Co. It is a transition metal with a silvery-white appearance and a lustrous finish. Cobalt is a relatively rare element on Earth and is usually found in conjunction with other metals such as nickel and copper. Cobalt has many uses in various industries due to its unique properties.
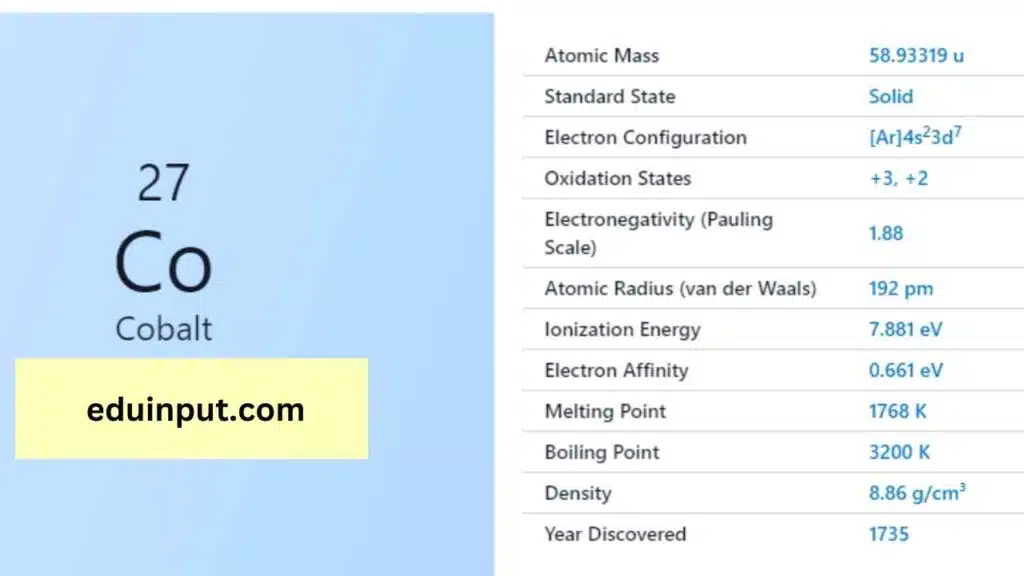
| Property | Value |
| Name | Cobalt |
| Symbol | Co |
| Atomic number | 27 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | Group in the periodic table |
| Standard state | Solid at 298 K |
| Appearance | Lustrous, metallic, greyish tinge |
| Classification | Metallic |
| Group in periodic table | 9 |
| Group name | (none) |
| Period in periodic table | 4 |
| Period in the periodic table | d |
| Shell structure | 2.8.15.2 |
| CAS Registry | 7440-48-4 |
Discovery
Cobalt was first discovered in 1735 by Swedish chemist Georg Brandt. He was trying to identify the mineral that gave glass a deep blue color, and discovered that cobalt was responsible. He named the element after the German word for “goblin,” as miners in the area where cobalt was found believed that the metal was the work of mischievous spirits.
Physical Properties
Cobalt is a hard, brittle, and relatively rare metal. It is a silvery-white color with a lustrous finish. Cobalt is magnetic and has a high melting point, which makes it useful in high-temperature applications. It is also a good conductor of electricity and has a high resistance to corrosion.
Chemical Properties
Cobalt is a relatively stable metal that does not react with oxygen or water at normal temperatures. It is, however, susceptible to attack by acids. Cobalt forms a variety of compounds, many of which are brightly colored. Cobalt is also used in the production of alloys, which are mixtures of metals that have unique properties.
Facts
- Cobalt is a relatively rare element that was first discovered in 1735 by Swedish chemist Georg Brandt.
- Cobalt is a hard, brittle, and silvery-white metal that is magnetic and has a high melting point.
- Cobalt is used in various applications, including in the production of high-strength alloys, batteries, and pigments.
Applications
Cobalt has a variety of applications due to its unique properties. Some common uses of cobalt include:
- Production of high-strength alloys: Cobalt is used in the production of superalloys, which are used in jet engines, gas turbines, and other high-temperature applications.
- Battery production: Cobalt is used in the production of rechargeable batteries, including those used in smartphones, laptops, and electric cars.
- Pigment production: Cobalt is used in the production of blue and green pigments for ceramics, glass, and paint.
- Medical applications: Cobalt is used in medical implants, such as artificial joints and dental implants.
Cobalt is a relatively rare transition metal with a variety of applications due to its unique properties. It is used in the production of high-strength alloys, batteries, pigments, and medical implants. Despite its diverse uses, cobalt is also an important element in the production of nuclear weapons, and its mining and extraction can have negative environmental and social impacts.






Leave a Reply