Tellurium-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
Tellurium is a chemical element with the symbol Te and atomic number 52. It is a brittle, silver-white metalloid that belongs to the chalcogen group of elements.
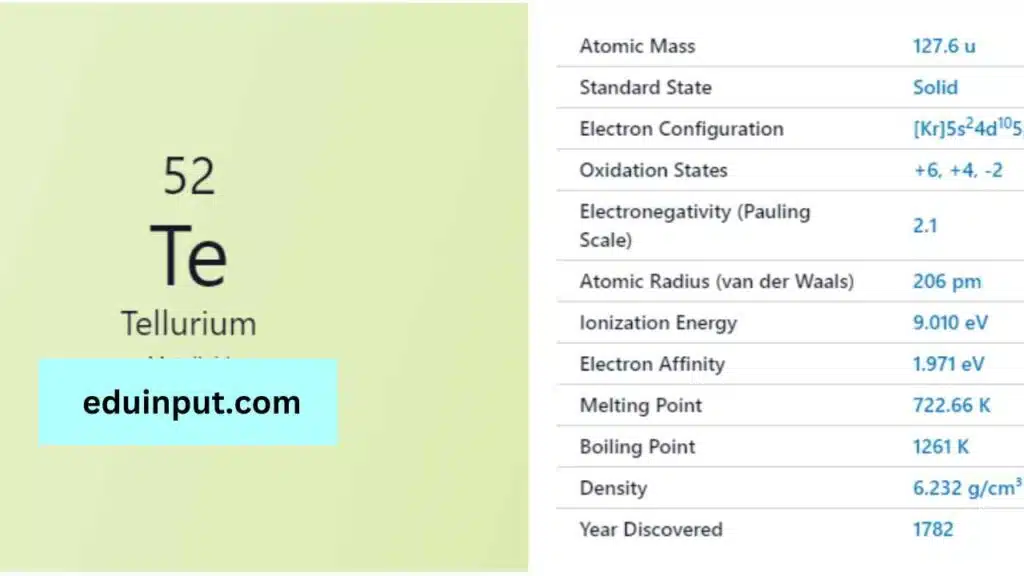
| Property | Value |
| Name | Tellurium |
| Symbol | Te |
| Atomic number | 52 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | Block in the periodic table |
| Standard state | Solid at 298 K |
| Appearance | Silvery lustrous grey |
| Classification | Semi-metallic |
| Group in periodic table | 16 |
| Group name | Chalcogen |
| Period in periodic table | 5 |
| Block in periodic table | p |
| Shell structure | 2.8.18.18.6 |
| CAS Registry | 13494-80-9 |
Discovery
Tellurium was discovered by Franz-Joseph Müller von Reichenstein, a Romanian mining official, in 1782. However, it was not until 1798 that it was isolated in pure form by Martin Heinrich Klaproth.
Physical Properties
Tellurium has a melting point of 449.5°C and a boiling point of 988°C. It is a brittle, silver-white metalloid with a metallic luster. It is a p-type semiconductor and has an electrical conductivity that increases slightly with exposure to light.
Chemical Properties
Tellurium is a moderately reactive element that forms compounds with many elements, including gold, silver, and copper. It is also used to produce alloys with lead, copper, and stainless steel. Tellurium has six stable isotopes and more than 30 radioactive isotopes.
Facts
- Tellurium is a rare element, making up only about 0.001 parts per million of the Earth’s crust.
- It is used in the production of blasting caps and as a coloring agent in ceramics.
- Tellurium is toxic and can cause severe damage to the nervous system and internal organs.
Applications
- Tellurium is used in the production of semiconductors and electronic devices such as solar cells, LED lights, and thermoelectric generators.
- It is also used in the production of alloys with other metals, such as copper and stainless steel.
- Tellurium is used as a catalyst in the refining of petroleum and as a coloring agent in ceramics.






Leave a Reply