Labeled Plant Cell Diagram & Functions
Eukaryotic Plant Cell Diagram
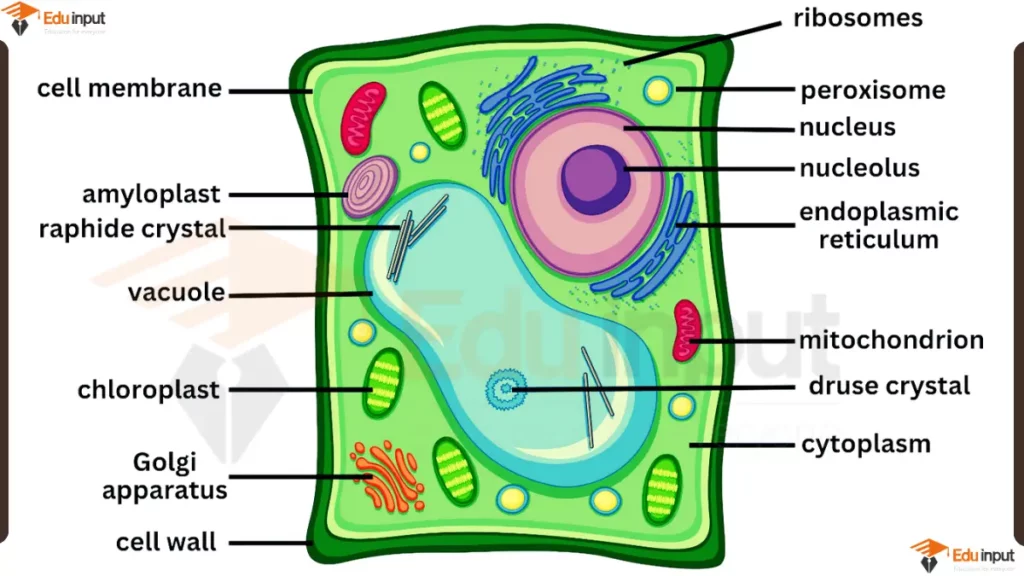
Here are the main parts of a plant cell and their functions:
Cell wall: The tough, outer layer of the plant cell that provides support and protection. It is made of cellulose, a complex carbohydrate.
Cell membrane: The semi-permeable membrane that surrounds the cell and controls the passage of materials into and out of the cell.
Cytoplasm: The gel-like substance that fills the cell and suspends the organelles. It contains enzymes and other molecules that are needed for various cell functions.
Nucleus: The “control center” of the cell, containing the cell’s genetic information (DNA) and directing its activities. It is surrounded by a nuclear envelope.
Nucleolus: A dense region within the nucleus where ribosomes are assembled. Ribosomes are structures in the cytoplasm that make proteins.
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER): A network of membranous tubules that transport materials throughout the cell and are involved in protein synthesis and lipid synthesis.
Golgi apparatus: A group of flattened sacs that package, modify, and transport materials within the cell and out of the cell.
Vacuole: A large sac that stores water, nutrients, and waste products.
Chloroplasts: Green organelles that contain chlorophyll, the pigment that allows plants to carry out photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy.
Mitochondria: The “powerhouse” of the cell, where energy is produced in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
Amyloplasts: Starch-storing organelles.
Raphide crystals: Needle-shaped crystals made of calcium oxalate, which may function in defense against herbivores.
Druse crystals: Crystals made of calcium carbonate, which may function in supporting the cell wall or storing calcium.



Leave a Reply