Difference between Actin and Myosin
November 3, 2024
The main difference between Actin and myosin is on basis of their nature and structure. Actin and myosin are important proteins for eukaryotic cell structure and muscle function. Actin makes thin filaments that help with different cell activities, while myosin forms thick filaments that are important for muscle contraction. Although they have different functions and structures, both proteins are essential for cell growth and movement. They work together to support many biological processes.
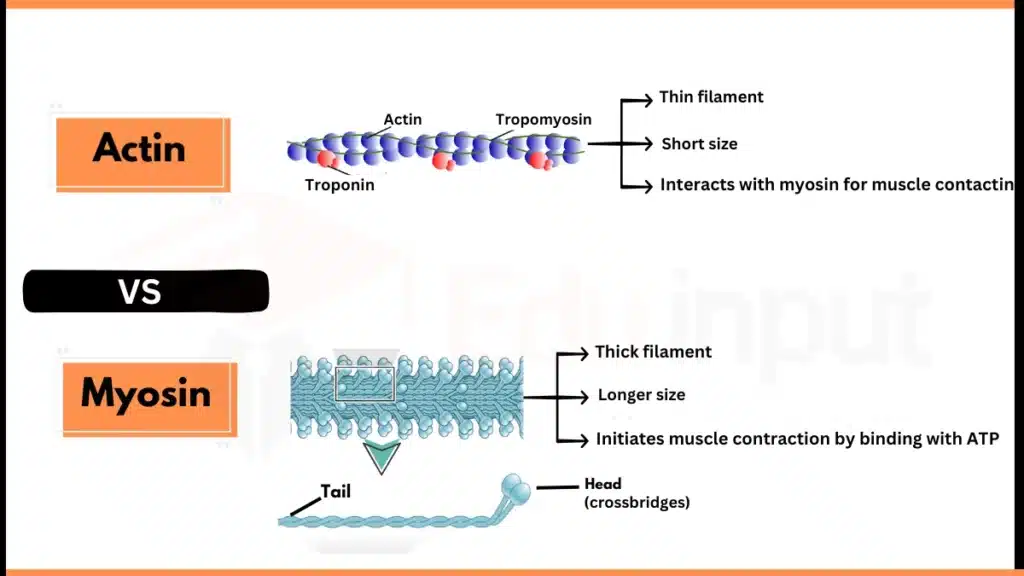
Actin VS Myosin
Here are the main differences between actin and myosin.
| Character | Actin | Myosin |
| Definition | Actin is a family of multifunctional cytoplasmic proteins in eukaryotes, that form microfilaments in cytoskeleton, and thin filaments in muscle fibrils. | A superfamily of motor (moveable) proteins that is important for muscle contraction. |
| Nature | Globular proteins | Motor proteins |
| Structure | Thin, flexible filaments composed of monomers | Thick filaments with three main parts: head, neck, and tail |
| Proteins in filaments | Actin, tropomyosin, and troponin | Myosin and meromyosin proteins. |
| Surface | Smooth | Rough |
| Function | Provides shape & structure to cell, helps in intracellular transport and muscle contraction | Uses ATP and form force for contraction of muscles |
| Location | present in muscle fiber, and beneath the cell membrane | Present in muscle cells |
| Found in | A and I bands of sarcomere. | Only in A bands of sarcomere. |
| Size | Shorter and thinner (2-2.6 µm length & 0.005 µm diameter). | Longer and thicker (4-5 µm in length & 0.01 µm diameter). |
| Molecular weight | Less in weight | High in weight |
| Abundance | More abundant | Less abundant |
| Cross bridges | Do not form cross bridges | Form cross bridges |
| Association with ATP | No association with ATP molecules | Associates with ATP |
| Sliding | Slides into H Zone during muscle contraction | No filament sliding |
| Muscle Contraction | Interacts with Myosin to support muscle contraction | Initiates muscle contraction by forming a force |
| End | Actin has one end attached to Z-lines and one free. | Myosin has both ends free, but its heads are linked to ATP for energy. |
File Under:



Leave a Reply