Are Fungi Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic?
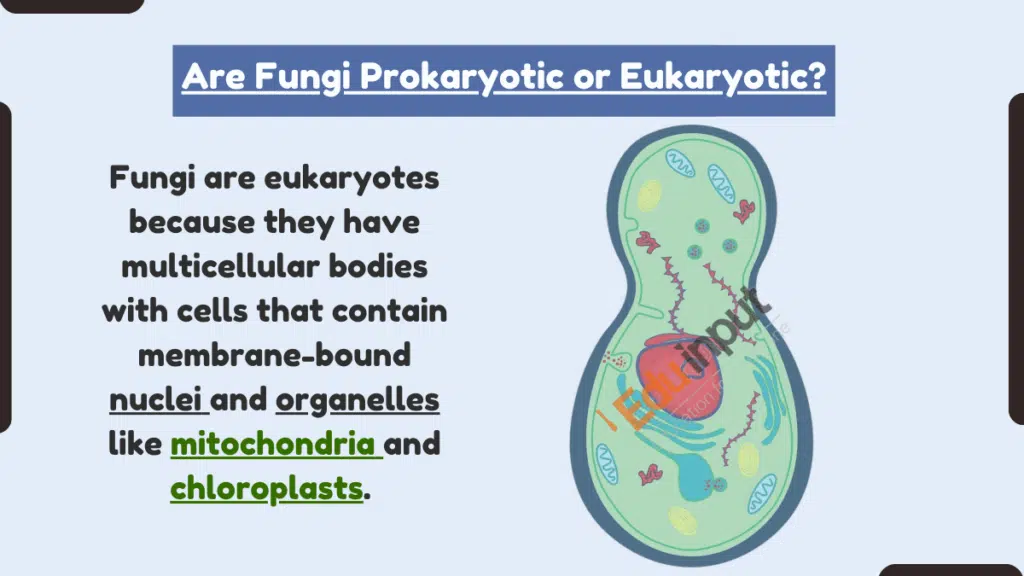
Are fungi prokaryotic or eukaryotic? Fungi are eukaryotic organisms. Their cells contain a true, membrane-bound nucleus and organelles. Prokaryotes like bacteria and archaea lack these structures.
Is fungi prokaryotic? No. The fungus kingdom belongs to Domain Eukarya, alongside plants and animals. Common types include yeasts, molds, and mushrooms. All have complex cells with nuclear walls protecting their chromosomes.
Are fungi prokaryotes? Never. Fungi are eukaryotes with organized cell walls and internal compartments. Despite being microorganisms like bacteria, their cellular structure is far more complex. Fungi eukaryotic or prokaryotic? Always eukaryotic. Studies show fungi are actually closer to animals than to any prokaryotes. Their membrane-bound nucleus and specialized organelles clearly separate them from bacteria and archaea, making fungi prokaryotic or eukaryotic an easy question to answer—definitively eukaryotic.
Why Fungi Are Considered Eukaryotic?
To answer common queries such as “fungi prokaryotic or eukaryotic” or “fungi is prokaryotic or eukaryotic”, let’s break down the key reasons why fungi are considered eukaryotic:
1. Presence Of Distinct Nuclei
Fungi have membrane-bound nuclei. Their genetic material is contained within an envelope called the nuclear membrane, which is a distinguishing feature of eukaryotic cells.
2. Presence of organelles
Fungi have organelles. Key eukaryotic organelles like mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum, and vacuoles are present in fungal cells. Prokaryotes lack these more complex cellular structures.
3. Sexual mode of reproduction
Reproduction in fungi often involves microscopic spores that can travel long distances through the air. Fungi undergo mitosis and meiosis. Eukaryotes reproduce sexually via meiosis or asexually by mitosis. Fungi reproduce both ways, while prokaryotes typically only divide via binary fission.
4. Presence of Linear Chromosomes
Fungi have multiple linear chromosomes. Prokaryotic chromosomes are usually singular and circular. Fungi, like other eukaryotes, have multiple linear chromosomes present in the nucleus.
5. Multicellularity
Fungi are multicellular. Most fungi grow as multicellular filaments or bodies made up of many cells. Only eukaryotes develop true multicellular complexity.



Leave a Reply