Chlorine-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and atomic number 17. It is a highly reactive, yellowish-green gas that belongs to the halogen family.
Chlorine was discovered in 1774 by Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele and later named by English chemist Sir Humphry Davy. Chlorine is the second lightest halogen after fluorine and is widely used for its disinfectant properties, as well as in the production of various chemicals.

| Property | Value |
| Name | Chlorine |
| Symbol | Cl |
| Atomic number | 17 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | 35.45 range: [35.446, 35.457] |
| Standard state | Gas at 298 K |
| Appearance | Yellowish green |
| Classification | Non-metallic |
| Block in the periodic table | 17 |
| Group name | Halogen |
| Period in periodic table | 3 |
| Period in the periodic table | p |
| Shell structure | 2.8.7 |
| CAS Registry | 7782-50-5 |
Discovery
Chlorine was first discovered in 1774 by Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele. However, it was not until 1810 that the element was recognized as a new element by English chemist Sir Humphry Davy. Davy named the element “chlorine” after the Greek word “chloros,” which means green-yellow.
Physical Properties
Chlorine is a highly reactive, yellowish-green gas with a pungent odor. It is a non-metal and belongs to the halogen family. Chlorine has a melting point of -100.98°C and a boiling point of -34.6°C. It is highly soluble in water and reacts with most metals to form chlorides.
Chemical Properties
Chlorine is a highly reactive element and is known for its strong oxidizing properties. It is a potent disinfectant and is commonly used in swimming pools to kill bacteria and other harmful microorganisms. Chlorine is also used in the production of a wide range of chemicals, including plastics, solvents, and pesticides.
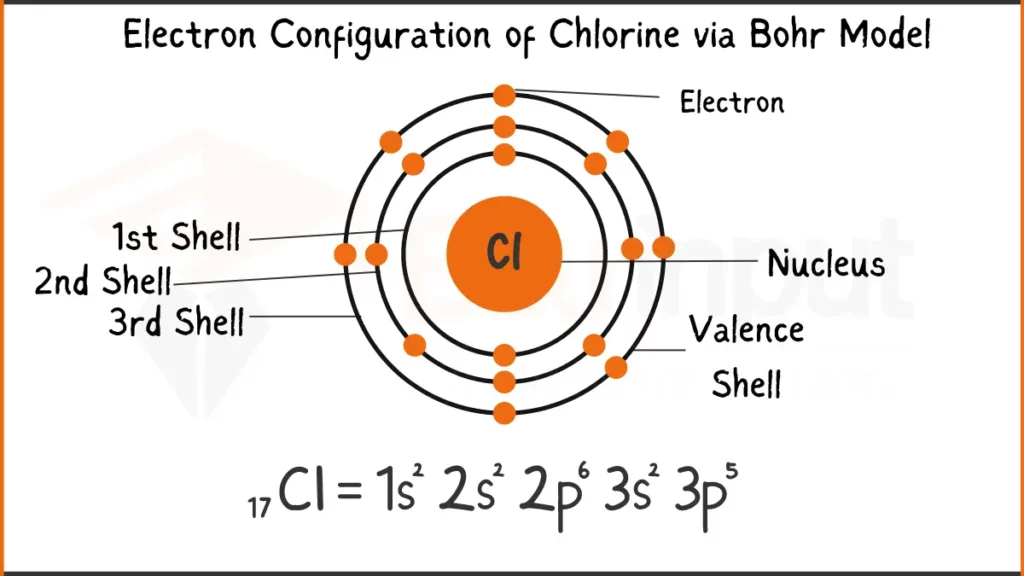
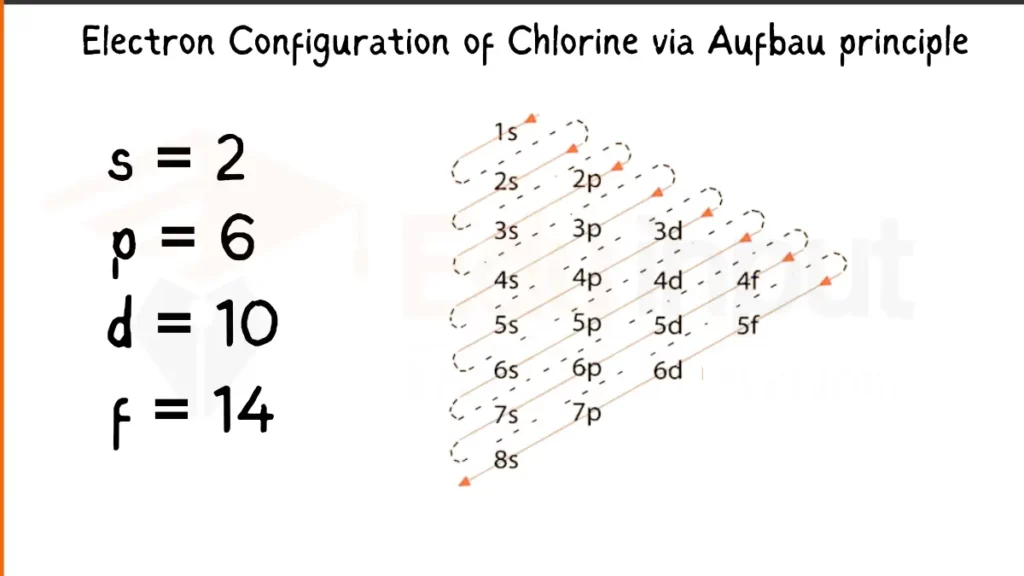
Electron Configuration of Chlorine
Chlorine (Cl) packs 17 electrons. Its configuration is either 1s²2s²2p⁵or [Ne]3s²2p⁵. Both depict the filling of subshells, with the latter referencing Neon’s (Ne) stable inner shell structure.
Electron Configuration of Chlorine Via Bohr Model
Electron Configuration of Chlorine Via Aufbau Principle
Facts
- Chlorine is the 17th most abundant element in the Earth’s crust.
- Chlorine gas was used as a weapon during World War I.
- Chlorine is highly toxic and can cause serious health problems if ingested or inhaled.
- Chlorine is used to bleach paper and textiles.
Applications
Chlorine is used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Disinfecting water and swimming pools
- Bleaching paper and textiles
- Producing a wide range of chemicals, including solvents, plastics, and pesticides
- As a refrigerant in air conditioning and refrigeration systems
- In the production of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and other plastics.




Leave a Reply