Classification of Lipids | Functions Of Lipids
Lipids are fats found in food and the body. They include triglycerides (fats), phospholipids (fatty acids), and sterols (cholesterol). Cholesterol is a fat that occurs naturally in animal foods such as meat, poultry, fish, eggs, milk, and cheese. The human body produces some cholesterol, but it also gets it from food.
Cholesterol is a fat-like substance found in food and produced naturally by the body. The amount of cholesterol in our blood depends on the amount present in our food.
Classification Of Lipids
Lipids are categorized into simple, complex, derived, and miscellaneous groups, which are further divided into different groups.
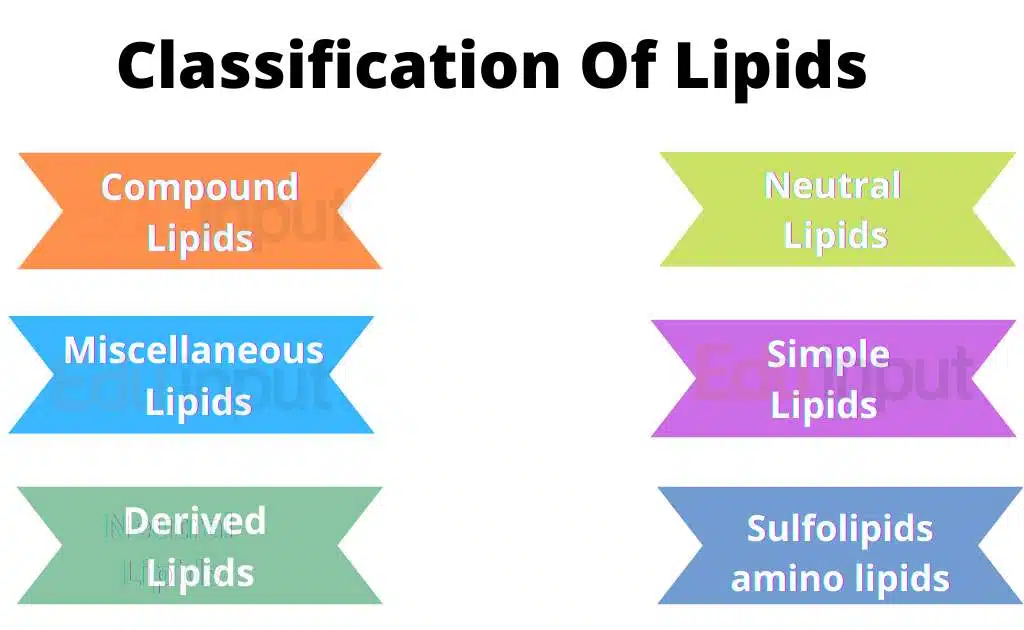
Simple Lipids:
The results of hydrolysis of these lipids are glycerol, sterols, fatty acids, and alcohols.
There are two types of simple lipids:
a) Fats and oils (triacylglycerols):
There are two types of esters with glycerol. The physical difference between oil and fat is not significant. Fat is a solid at room temperature, while oil is a liquid.
(b) Waxes:
Alcohols other than glycerol are included in the long chain of the esters of fatty acids. These alcohols may be Alicyclic or Aliphatic. The majority of cetyl alcohol is found in waxes. In the preparation of candles, lubricants, cosmetics, and other items, wax is used.
Complex or Compound Lipids:
These are esters of fatty acids with alcohols that have additional groups such as nitrogenous bases and carbohydrates. They are even further apart as follows.
(a) Phospholipids:
They have a nitrogenous base and are often filled with phosphoric acid. In addition to alcohol and fatty acids, this is also present.
(b) Glycerophospholipids:
These phospholipids contain glycerol as the alcohol e.g. lecithin, and cephalin. Sphingomyelin is one of the alcohols in this group.
(c) Glycolipids:
These lipids contain a fatty acid, carbohydrate, and nitrogenous base. The alcohol is sphingosine, hence they are also called glycosphingolipids. Glycerol and phosphate are absent e.g., cerebrosides, and gangliosides.
(d) Lipoproteins:
These are Macromolecular complexes of lipids with proteins.
Other Complex Lipids:
Sulfolipids, amino lipids, and, lipopolysaccharides are among other complex lipids.
Derived Lipids:
These are the derivatives obtained on the hydrolysis of group 1 and group 2 lipids. There are Alcohol, Fatty acids, mono- and Diacylglycerols, Vitamins, Steroid Hormones, and ketone bodies.
Miscellaneous Lipids:
There are many compounds with the characteristics of lipids, such as Squalene, and hydrocarbons, such as Pentacosane, and are known as Miscellaneous lipids.
Neutral Lipids:
The neutral lipids are the ones that are not charged. Mono-, di-, and Triacylglycerols are some of the compounds.
Functions Of Lipids
Lipids perform several important functions
- The body has a concentrated fuel reserve as lipids (Triacylglycerols)
- Cholesterol and phospholipids are the main components of the structure of the cell.
- They are present in cell membrane structure and regulate membrane permeability (phospholipids and cholesterol).
- They’re a source of fat-soluble vitamins.(Vit A, Vit D, Vit E, and Vit K).
- steroid hormones and prostaglandins are important for cellular regulations
- Lipids give shape and a smooth appearance to the body, as they protect the internal organs. they serve as an insulating material and help in thermoregulation.





Leave a Reply