Difference Between Bone And Cartilage
Bone and cartilage are two types of connective tissues. The main difference between bone and cartilage is the difference in their composition. There are both living and dead cells in a matrix. The bone marrow and blood vessels can be seen in the porous part of the bone.
Cartilage consists of chondrocyte cells that produce an extracellular matrix made up of collagen fibers, proteoglycan, and elastin fibers. There are fewer blood vessels in cartilage than there are in bone.
What is Bone?
Bone is a mineralized connective tissue found throughout the body. Bones provide support and protection to internal organs, and they also store calcium and other minerals. In biology, bone is often called osseous tissue or simply bone.
Bones are composed of two types of cells: osteoblasts which make up bone, and osteoclasts which break down bone. Osteoblasts produce collagen fibers, which form the matrix of bone. The matrix then becomes calcified into hydroxyapatite crystals, which are the main component of bone.
Osteoblasts are derived from mesenchymal stem cells. These cells differentiate into chondrocytes during embryonic development and become osteoblasts after development. They play important roles in maintaining skeletal integrity.
What is Cartilage?
Cartilage is a type of connective tissue found throughout the body. It provides support to joints and helps them move smoothly. Cartilage also cushions bones from impact forces.
There are two types of cartilage: hyaline (also known as articular) cartilage and elastic cartilage. Hyaline cartilage is found between the bones in our bodies. Elastic cartilage is located at the ends of bones where they meet the ball and socket joint.
Hyaline cartilage is found in the nose, ears, eyes, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and intervertebral discs. Elastic cartilage is found in earlobes, lips, and tongue.
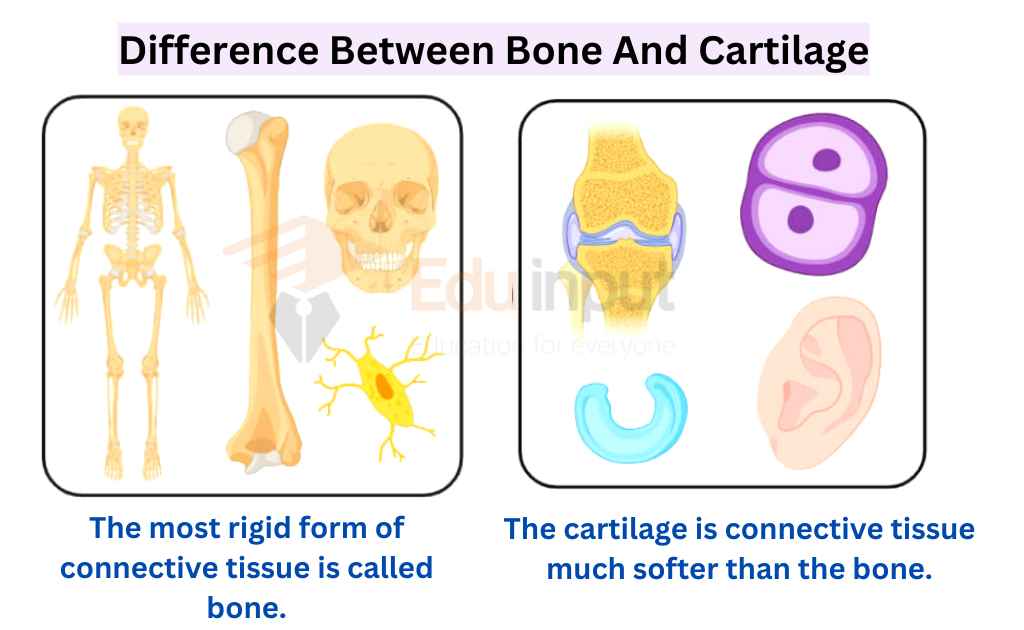
Difference Between Bone And Cartilage
Though bones and cartilage both are connective tissues, they are somehow different from each other. Key differences between bone and cartilage are enlisted here:
| Bone | Cartilage |
| The most rigid form of connective tissue is called bone. | The cartilage is connective tissue much softer than the bone. |
| The deposition of calcium carbonate hardened the collagen fibers of bone. | There is no deposition of calcium carbonate in cartilage. |
| Bones give support to the body. | Cartilage covers the ends of the bone at joints and supports the flexible portion of the nose and external ears. |
| The living cells of bones are called osteocytes. | The living cells of the cartilage are called chondrocytes. |
| Its matrix is composed of collagen and calcium carbonate. | chondrocytes secrete elastic, non-living matrix and collagen. This matrix surrounds the chondrocytes. |
| The Haversian canal system is present in Bones. | The Haversian canal system is absent in cartilage. |
| A bone is the frame of the body, that helps to move, protecting you from mechanical injury, and providing a structure that your other tissues, muscles, and organs can attach. Bones also store minerals and produce both red blood cells and white blood cells. | Cartilage supports the respiratory tract, acts as a shock absorber between bones, and maintains the shape and flexibility of appendages. |
| The Matrix of Bone is Vascular. | The matrix of cartilage is non-Vascular. |
| Bones show a bidirectional growth pattern. | Cartilage shows a unidirectional growth pattern. |
| Bone marrow is present. | Bone marrow is absent. |



Leave a Reply