Difference Between Phytosomes and Liposomes
Key Difference
Phytosomes and liposomes are both types of delivery systems used in pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals to enhance the absorption of active ingredients, but they differ in their composition and the way they interact with the body’s cells.
Liposomes are spherical vesicles with at least one lipid bilayer, used to encapsulate drugs or nutrients to improve their delivery and efficacy. They are made primarily of phospholipids and are used to increase the bioavailability of both water-soluble and fat-soluble compounds.
Phytosomes, on the other hand, are a specific type of complex where the active herbal constituents are bound to phospholipids. They enhance the absorption and bioavailability of the phytoconstituents. Phytosomes are particularly effective for compounds that have poor bioavailability in their natural form.
Comparative Analysis
- Composition
- Liposomes: Made of phospholipids forming a bilayer structure.
- Phytosomes: Complex of phytoconstituents and phospholipids.
- Function
- Liposomes: Encapsulate active ingredients to improve delivery.
- Phytosomes: Enhance absorption and bioavailability of plant extracts.
- Bioavailability
- Liposomes: Effective for both water-soluble and fat-soluble compounds.
- Phytosomes: Particularly improve bioavailability of poorly absorbed phytochemicals.
- Usage
- Liposomes: Used in various drugs and nutrients delivery.
- Phytosomes: More specifically used in enhancing efficacy of herbal supplements and extracts.
- Interaction with Cells
- Liposomes: Fuse with cell membranes to deliver contents.
- Phytosomes: Facilitate the entry of phytoconstituents into cells.
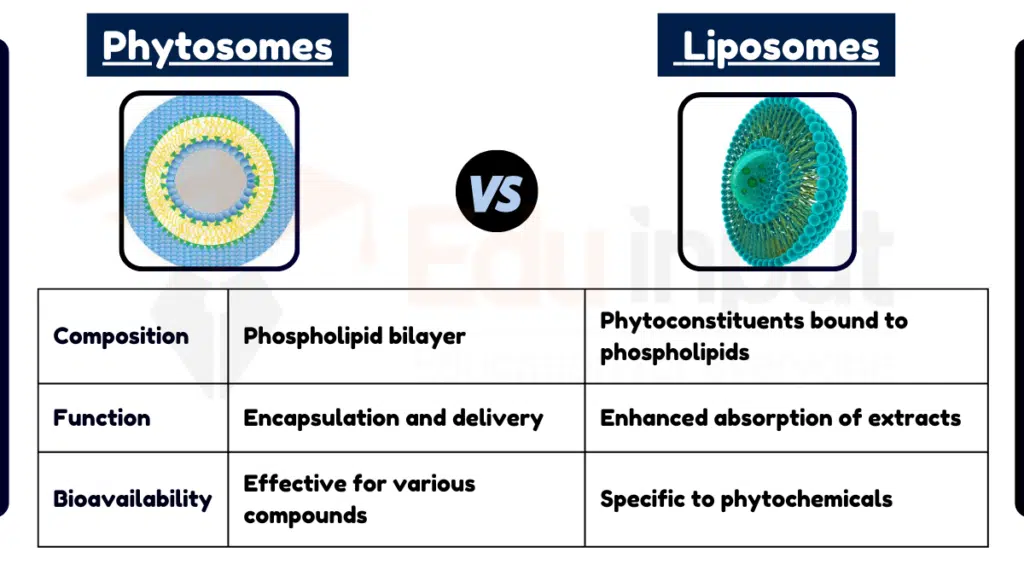
Table Summary
| Feature | Liposomes | Phytosomes |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Phospholipid bilayer | Phytoconstituents bound to phospholipids |
| Function | Encapsulation and delivery | Enhanced absorption of extracts |
| Bioavailability | Effective for various compounds | Specific to phytochemicals |
| Usage | Broad pharmaceutical and nutritional use | Herbal supplements and extracts |
| Cell Interaction | Fuse with membranes | Facilitate phytoconstituents entry |
Also Read:




Leave a Reply