Difference Between Transcription And Translation
May 30, 2023
The main difference between transcription and translation lies in their processes and outcomes. Transcription involves the synthesis of RNA from a DNA template, converting the DNA code into a complementary RNA code, while translation involves the synthesis of a protein from an mRNA template, converting the mRNA code into an amino acid sequence within a protein.
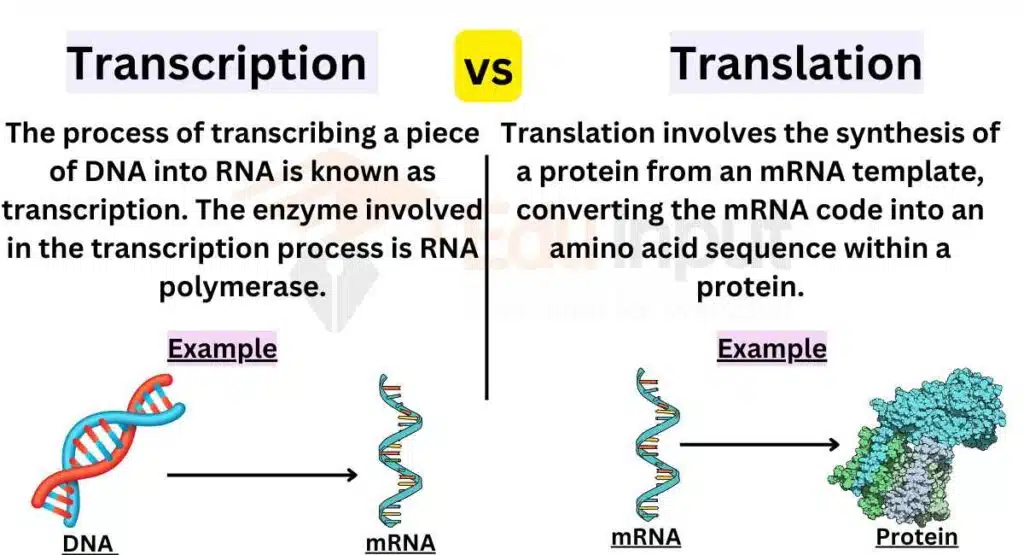
Transcription vs. Translation
Here are the main Difference Between Transcription And Translation:
| Factors | Transcription | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of copying DNA into RNA | Process of synthesizing proteins using RNA |
| Location | Nucleus of the cell | Cytoplasm of the cell |
| Starting Molecule | DNA | mRNA (messenger RNA) |
| Enzyme Involved | RNA polymerase | Ribosomes |
| Resulting Molecule | mRNA (messenger RNA) | Protein |
| Sequence of Bases | DNA sequence is transcribed into RNA sequence, with complementary base pairing | mRNA sequence is translated into amino acid sequence |
| Purpose | To transfer genetic information from DNA to RNA | To convert the RNA message into a functional protein |
| Process | Initiation, elongation, and termination | Initiation, elongation, and termination |
| Occurrence | Occurs before translation | Occurs after transcription |
| Key Players | DNA, RNA polymerase | mRNA, ribosomes, tRNA (transfer RNA) |
| Location of Result | Nucleus or cytoplasm (depending on the organism) | Cytoplasm |
| Examples | DNA → mRNA | mRNA → Protein |
File Under:




Leave a Reply