Dubnium-Properties And Applications
Dubnium is a synthetic chemical element with the symbol ‘Db’ and atomic number 105. It is a highly radioactive, metallic element in the transactinide series of the periodic table. Dubnium was first synthesized in 1967 by a team of Russian scientists at the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research in Dubna, from which its name is derived. Due to its extremely short half-life and limited production, little is known about its properties and applications.
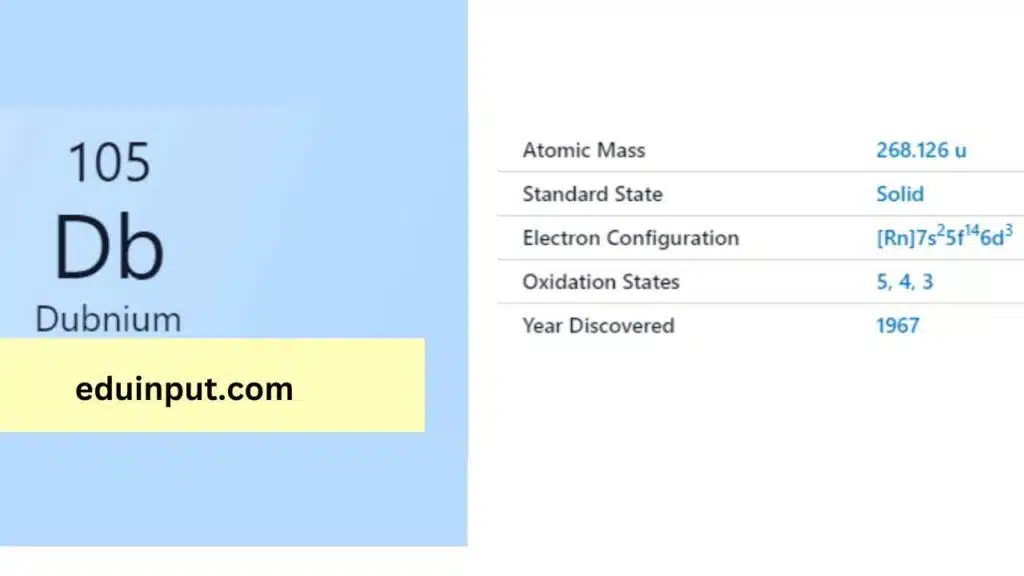
| Property | Value |
| Name | Dubnium |
| Symbol | Db |
| Atomic number | 105 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | (longest-lived isotope) |
| Standard state | Presumably a solid at 298 K |
| Appearance | Unknown, probably metallic and silvery white or grey in appearance |
| Classification | Metallic |
| Period in the periodic table | 5 |
| Group name | (none) |
| Period in periodic table | 7 |
| Block in periodic table | d |
| Shell structure | 2.8.18.32.32.11.2 |
| CAS Registry | 53850-35-4 |
Physical Properties
Dubnium is a highly radioactive metal that is not found naturally on Earth. Its physical properties, such as its melting and boiling points, density, and atomic radius, have not been accurately determined due to its limited production and short half-life.
Chemical Properties
Dubnium is a highly reactive element that readily forms compounds with other elements. It has a single oxidation state of +5 and forms unstable oxides that decompose quickly. Dubnium’s chemical properties and behavior are not well understood due to its limited production and short half-life.
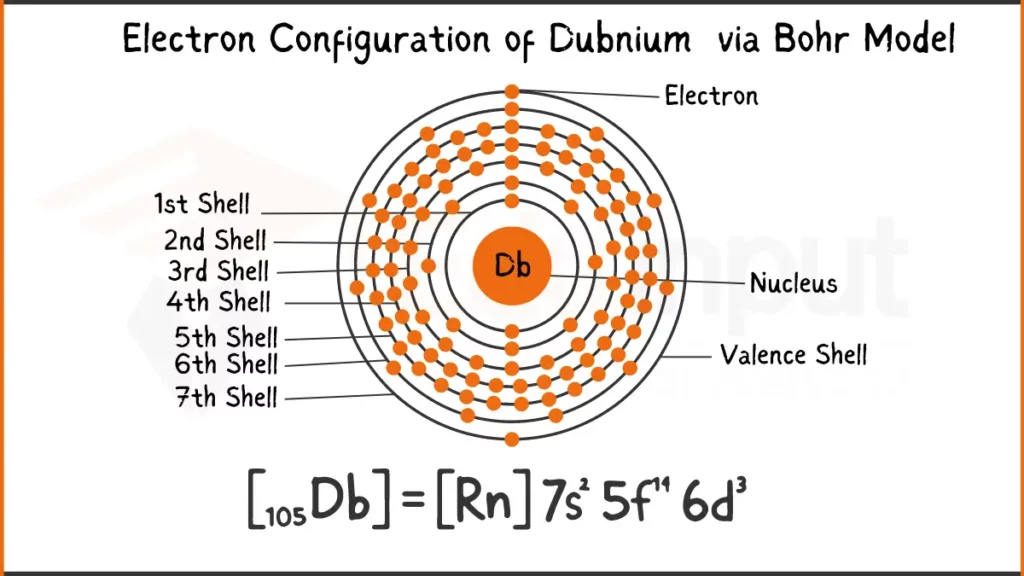
Electronic Configuration of Dubnium
Dubnium (Db) packs 105 electrons ([Rn] 5f¹⁴ 6d³ 7s². This element stands out with three electrons (6d³) in its outermost shell, influencing its unique way of bonding with other elements.
Electronic Configuration of Dubnium via Bohr Model
Electronic Configuration of Dubnium via Aufbau Principle
Facts
- Dubnium is a synthetic element that was first synthesized in 1967 by a team of Russian scientists at the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research in Dubna.
- Dubnium is highly radioactive and not found naturally on Earth.
- Dubnium’s physical and chemical properties are not well understood due to its limited production and short half-life.
Applications
Due to its highly radioactive and unstable nature, dubnium has no practical applications outside of scientific research. Its discovery and study contribute to our understanding of the structure and behavior of heavy, synthetic elements and their potential applications in nuclear energy and medicine.
Dubnium is a highly radioactive and synthetic element that was first synthesized in 1967. Its properties and behavior are not well understood due to its limited production and short half-life, and it has no practical applications outside of scientific research. However, its discovery and study contribute to our understanding of heavy, synthetic elements and their potential applications in nuclear energy and medicine.






Leave a Reply