Effect of Current | Heating Effect, Magnetic Effect, Chemical Effect
The presence of electric current can be detected by the various effect of the current that it produces.
Effect of Current
There are 3 types of effects of current
1. Heating effect
2. Magnetic effect
3. Chemical effect
Download the pdf notes of Effect of Current Class 12 Physics
Heating Effect:
Current flows through a metallic wire due to the motion of free electrons. These electrons collide with the atoms of the metal and give some of their kinetic energy to these atoms.
As a result, it increases the kinetic energy of the vibrations of the atoms of the metal, ie, it generates heat in the wire. The heat ‘H’ produced by a current in the wire of resistance ‘R’ during the time ‘T’ is
Energy=qΔv= (it) (IR)
H=I2Rt
Uses of heating effect
- Electric heater
- Electric Kettles
- Toaster
- Electric iron etc.

Magnetic Effect:
When current flows in a straight wire, coil, or solenoid, a magnetic field is produced around them. The strength of the field depends on the value of the current and distance from the wire.
Uses of magnetic effect:
The magnetic effect is used in galvanometers to detect the current in Motors, fans, drill machines, grinders, etc use this effect.

Chemical Effect:
Certain liquids like dilute H2SO4, and CuSO4, in solution conduct electricity due to some chemical reactions that take place within them. This process is called Electrolysis
The chemical changes produced during the electrolysis of a liquid are due to the chemical effects of the current. It depends upon the nature of the liquid and the quantity of electricity passed through it.
Different terms used in electrolysis are
Electrolyte:
The liquid that conducts electric current is called an electrolyte.
Electrode:
The material in the form of wire, rod, or plate at which electric current enters or leaves the electrolyte is called the electrode
Anode:
The electrode connected to the positive terminal of the battery is called Anode.
Cathode:
The electrode connected with the negative terminal of the battery is called Cathode
Voltameter
The vessel containing the two electrodes and the liquid is called a Voltameter.
Working of voltameter
Consider CuSO4 solution in a voltameter whose both electrodes are made of Cu.
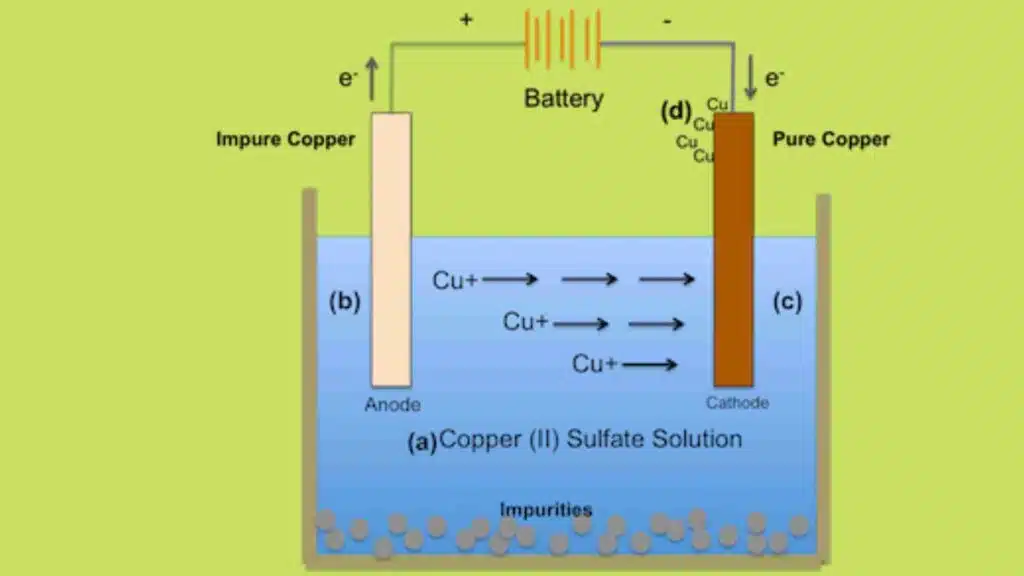
Cu++and SO4— are present in the solution. When current passes through the solution, Cu++ ions move towards the cathode and the following reaction takes place at the cathode
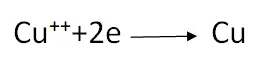
The Cu atoms thus formed are deposited on the cathode. The SO4— ions move towards the anode, take two Cu++ from it and form CuSO4, Following reaction takes place at the anode
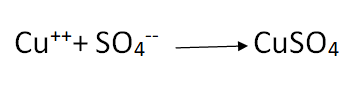
As the process of electrolysis continues, copper is deposited on the cathode. At the same time, an equal amount of copper is dissolved into the solution from the anode keeping the density of the CuSO4 solution constant.
Use of chemical effect
The process in which a thin layer of an expensive metal (gold, silver) is deposited on a cheap metal(iron) is called electroplating.
Frequently Asked Questions-FAQs
What are the three effects of electric current?
These are three effects of electric current.
Chemical Effect
Magnetic Effect
Heating Effect
What is the heating effect of current?
When current pass through the wire the kinetic energy of the atom of the wire increase which produces heat. This is called the heating effect of Current.
What is the magnetic effect of current?
When electric current pass through a conductor a magnetic field is produced around the conductor which is known as the magnetic effect of current.
What is the chemical effect of current?
The chemical changes produced during the electrolysis of a liquid are due to the chemical effects of the current.






Leave a Reply