Introduction To Muscles | Functions, and Types of Muscles
Muscles and bones are responsible for movement in the animal’s body. The term muscle was derived from the Latin word ‘musculus’ which means a little mouse. It may refer to the shape of some muscles or the shape of muscle when it contracts.
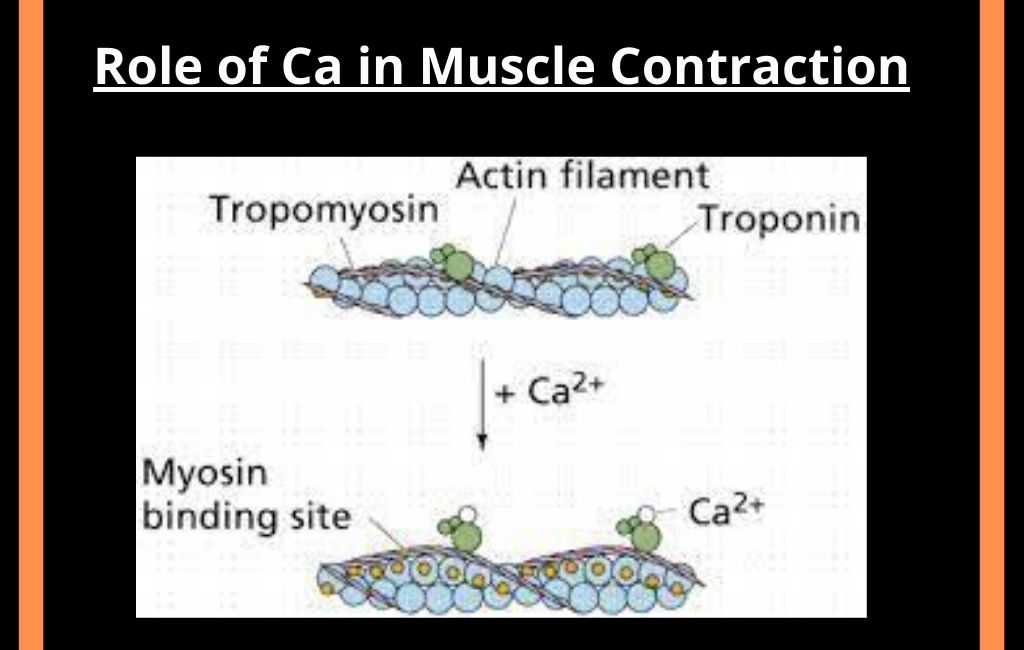
The muscle cell comprises four types of proteins Actin, Myosin, Troponin, and Tropomyosin. According to the sliding filament model, these proteins form a cross-bridge to cause the movement of muscle.
Number of Muscles in the Human body
There are more than 650 muscles in the human body. The human muscular device includes greater than 600 muscular tissues, which make up about 40 to 50 consistent with a cent of the complete body weight.
These muscle tissues are linked to bones, blood vessels, and other inner organs of our body and are particularly composed of skeletal muscular tissues, tissue, tendons, and nerves. The muscular tissues of the human muscular system are composed of a shape of elastic tissue.
The power required for the functioning of muscle mass is predominantly powered through the oxidation of fat, carbohydrates in particular, and from the saved strength molecules adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Functions Of Muscles
There are the following basic functions of muscles;
- Involved in the movement of internal organs, for example, the contraction of the heart
- To provide movement
- To provide support to posture
- Heat generation
- Blood circulation
Types of Muscles
There are three types of muscles in vertebrates:
1. Skeletal muscles
2. Cardiac muscles
3. Smooth muscles
Types of muscles on basis of Action type
Muscles are classified into two types based on their action;
1. Voluntary muscles
2. Involuntary muscles
Skeletal muscle:
The muscles that are attached to the skeleton and associated with the movement of the bone are called skeletal muscles.
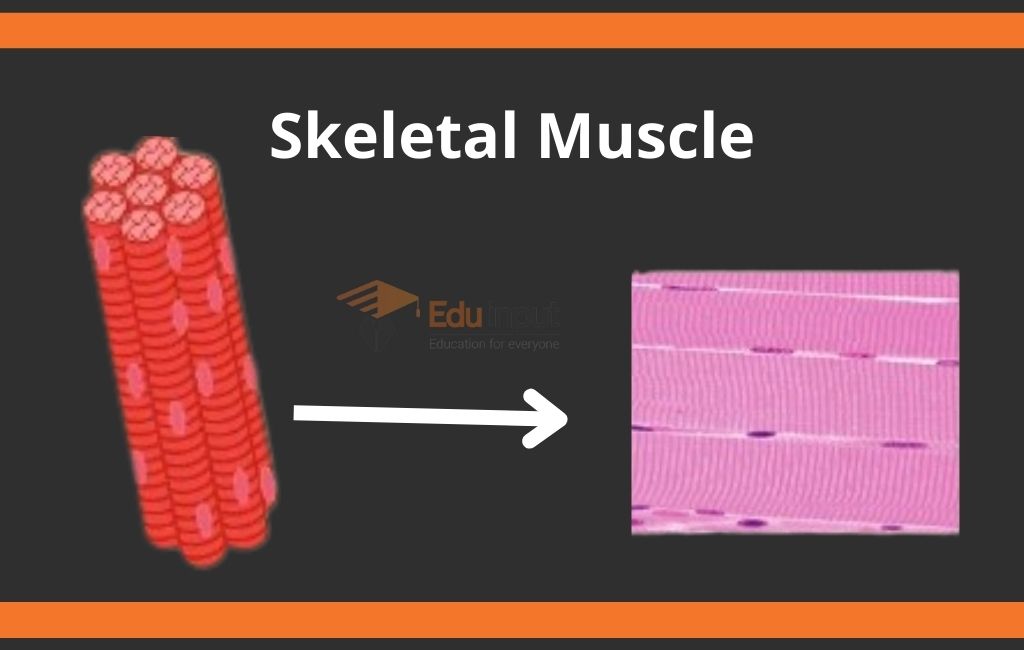
Functions of Skeletal Muscles
Here are some important functions of skeletal muscle:
- Regulation of body temperature
- Maintenance of body posture
- Movement of body
- Protects internal organs from injury or shock.
- Involves involuntary movement
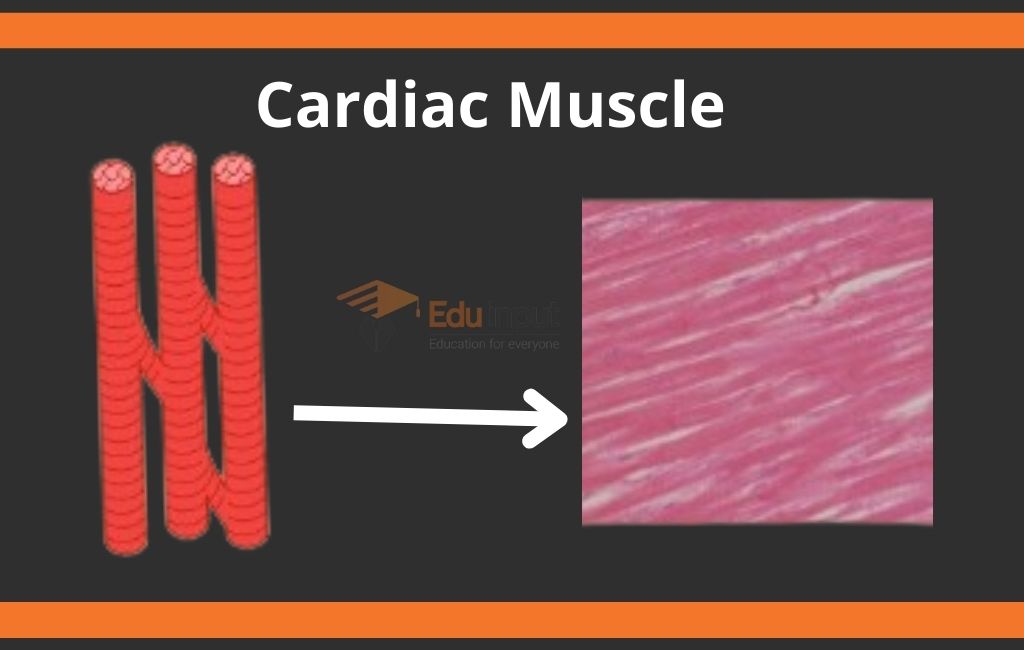
Cardiac Muscle:
The muscles of the heart are called cardiac muscles. They are striated and involuntary muscles that are present only in the heart. They constitute most of the mass of the heart wall. The basic function of cardiac muscles is to help in pumping blood.
Smooth Muscles:
The visceral and non-striated muscles are called smooth muscles. They are involved in the involuntary movement. They are present in internal body organs like the stomach and small intestine. They are long and spindle-shaped.
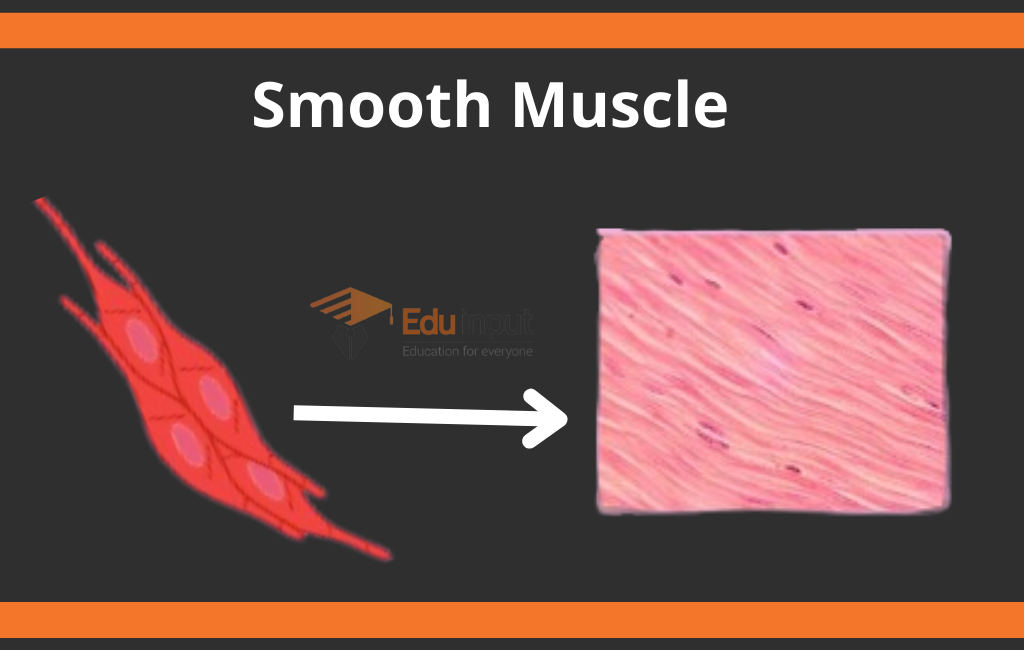
Functions of Smooth Muscles
Here are some important functions of smooth muscles:
- Regulation of blood flow and pressure
- Food digestion
- Nutrient collection
- Heat generation
Frequently Asked Questions-FAQs
What are Muscles?
Muscles and bones are responsible for movement in the animal’s body. The term muscle was derived from the Latin word ‘musculus’ which means a little mouse. It may refer to the shape of some muscles or the shape of muscle when it contracts.
What are muscle made up of?
The muscle cell comprises four types of proteins Actin, Myosin, Troponin, and Tropomyosin. According to the sliding filament model, these proteins form a cross-bridge to cause the movement of muscle.
What are muscles and types of muscles?
There are three types of muscles in vertebrates:
1. Skeletal muscles
2. Cardiac muscles
3. Smooth muscles




Leave a Reply