Is A Cell Membrane Prokaryotic Or Eukaryotic?
The cell membrane is an important component of all cells, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic. It is a selectively permeable barrier that regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell. The cell membrane also plays a role in cell signaling, cell adhesion, and cell division.
Cell Membrane in Prokaryotic Cells
The cell membrane of prokaryotic cells is a simple structure made up of a phospholipid bilayer. The phospholipid bilayer is a two-layer sheet of phospholipid molecules.
The phospholipid molecules are arranged so that their hydrophobic tails face inward, towards the center of the membrane, and their hydrophilic heads face outward, towards the aqueous environment.
The cell membrane of prokaryotic cells also contains a variety of proteins. These proteins are involved in a variety of functions, including transport, cell signaling, and cell adhesion.
Cell Membrane in Eukaryotic Cells
The cell membrane of eukaryotic cells is more complex than the cell membrane of prokaryotic cells. In addition to the phospholipid bilayer, the cell membrane of eukaryotic cells contains cholesterol molecules.
Cholesterol molecules help to stabilize the cell membrane and make it more fluid.
The cell membrane of eukaryotic cells also contains a variety of specialized proteins. These proteins are involved in a variety of functions, including transport, cell signaling, and cell adhesion.
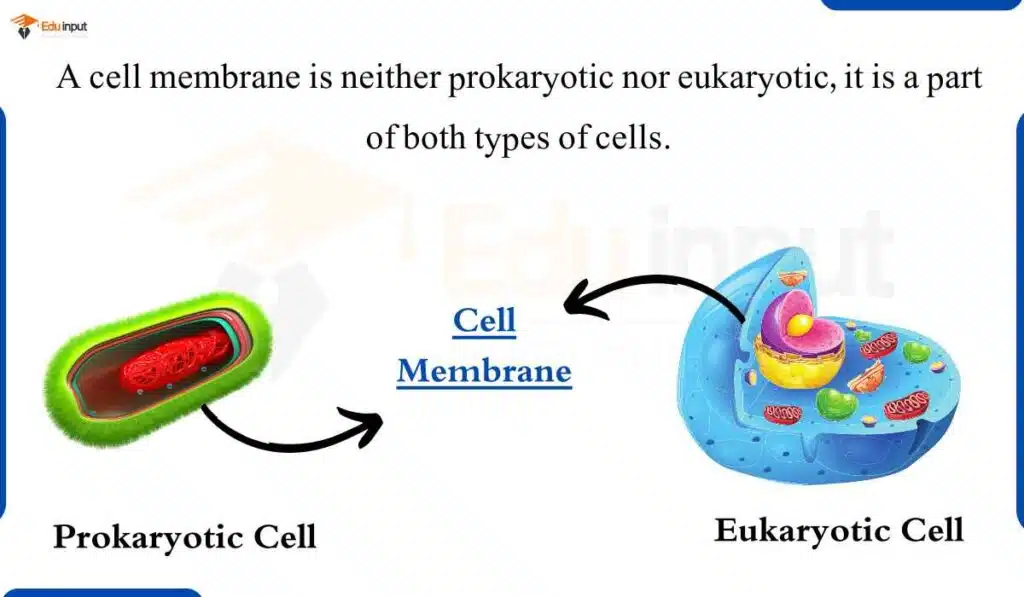
Is the Cell Membrane Eukaryotic or Prokaryotic?
The cell membrane is neither prokaryotic nor eukaryotic. It is a part of both types of cells. The cell membrane has some structural and functional differences in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, but it is the same basic structure in both types of cells.
Implications of the Cell Membrane Not Being Eukaryotic or Prokaryotic
The fact that the cell membrane is not eukaryotic or prokaryotic has some implications for the evolution of cells and the development of new diseases.
For example, the cell membrane is thought to have played a role in the evolution of cells from prokaryotic to eukaryotic cells. The cell membrane of prokaryotic cells is relatively simple, but the cell membrane of eukaryotic cells is more complex.
The addition of cholesterol molecules to the cell membrane of eukaryotic cells is thought to have made the cell membrane more fluid and allowed for the evolution of more complex cells.
The cell membrane is also involved in the development of new diseases. For example, some viruses can enter cells by binding to proteins on the cell membrane. If the cell membrane is changed, it can make it more difficult for viruses to enter cells and cause disease.




Leave a Reply