Is Cellular Respiration An Endothermic Or Exothermic Process?
Cellular respiration is an exothermic process because it involves a series of energy-releasing chemical reactions that break down glucose and other nutrients, releasing heat as a byproduct.
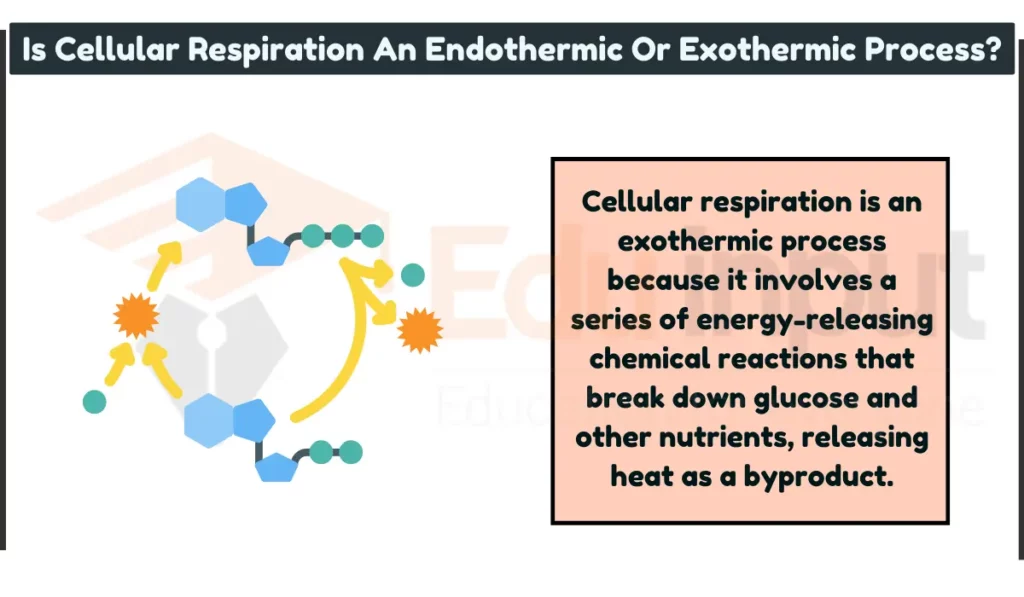
Why Is Cellular Respiration An Exothermic Process?
Cellular respiration is an exothermic process for the following reasons:
1. Breaking chemical bonds
Glucose and other nutrients have chemical bonds that store energy. During cellular respiration, these bonds break and release the stored energy as heat.
Foe instance, Imagine breaking apart a stack of firewood; the stored energy in the wood is released as heat as you break it.
2. Energy transfer
The released energy doesn’t simply disappear; it’s transferred into different forms. Some directly heats the surrounding cells and contributes to our body temperature rise. Another portion fuels cellular processes like muscle contraction, nerve impulses, and molecule synthesis.
3. ATP production
A portion of the released energy is captured in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the cellular energy currency. ATP powers various life processes, making cellular respiration crucial for sustaining life.
4. Net energy gain
While some energy is released as heat, the total energy captured in ATP is greater than the energy used to break down the nutrients. This net energy gain makes cellular respiration an energy-releasing (exothermic) process.
Therefore, cellular respiration is exothermic due to the combined effect of energy release from bond breaking, which transfers energy into different forms



Leave a Reply