Laboratory Equipment | Laboratory Apparatus for Various Disciplines: A Comprehensive Guide
Laboratory equipment plays a crucial role in the scientific community, enabling researchers and students to conduct experiments, analyze data, and deepen their understanding of various disciplines.

From chemistry to biology, physics to microbiology, and even mathematics and geography, each field relies on specific equipment tailored to its unique requirements.
In this article, we will explore the essential laboratory equipment across these disciplines and delve into their diverse uses.
I. Chemistry Lab Equipment
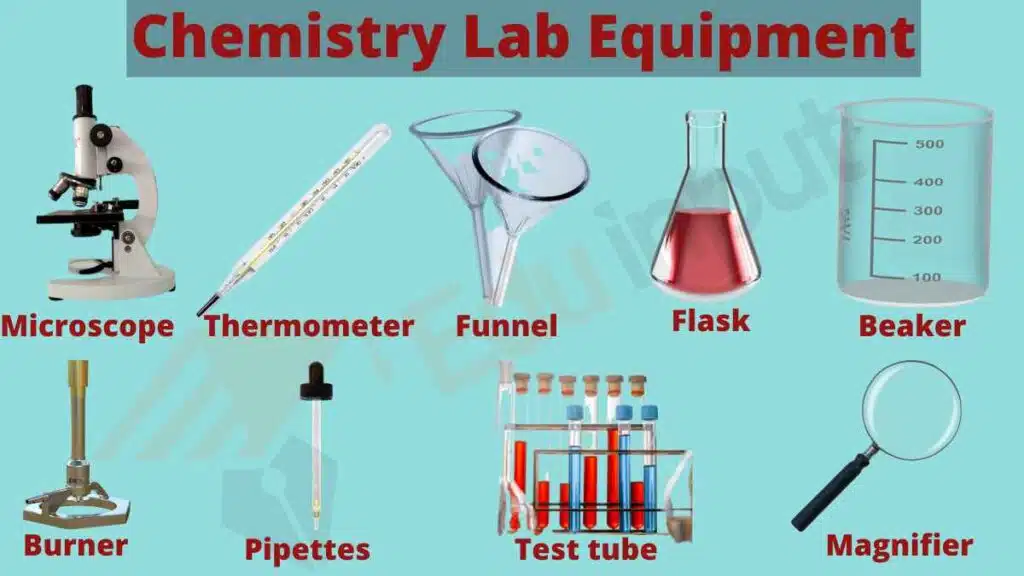
- Beakers and Erlenmeyer Flasks: Used for holding, mixing, and measuring liquid solutions during chemical reactions.
- Bunsen Burner: Provides a controlled flame for heating substances and conducting experiments.
- Test Tubes and Test Tube Rack: Small cylindrical containers for holding and observing small-scale reactions or samples.
- Pipettes and Burettes: Precise tools for measuring and transferring small volumes of liquids during experiments.
- Balance: Used for accurate measurement of mass, crucial for chemical calculations.
II. Physics Lab Equipment

- Oscilloscope: An electronic instrument for observing and measuring electrical waveforms.
- Vernier Calipers: Used for precise measurement of length, diameter, or thickness in physics experiments.
- Optical Bench: A long, flat platform for conducting experiments related to light, optics, and interference.
- Mass Spectrometer: Analyzes the masses and relative concentrations of atoms and molecules in a sample.
- Electromagnets and Power Supplies: Used to generate magnetic fields and perform experiments related to electricity and magnetism.
III. Biology Lab Equipment

- Microscopes: Vital for observing microscopic organisms, cells, and tissues in detail.
- Centrifuges: Used to separate and isolate components of a mixture based on density or molecular weight.
- Petri Dishes: Flat, shallow containers with lids for culturing and observing microorganisms.
- Incubators: Provide controlled temperature and humidity conditions for culturing bacteria and growing cells.
- PCR Machine: Polymerase Chain Reaction device for amplifying DNA segments, crucial in genetic analysis.
IV. Microbiology Lab Equipment
- Autoclave: Sterilizes laboratory equipment, media, and waste by using high-pressure steam.
- Bunsen Burner and Inoculating Loop: Used to perform aseptic techniques for bacterial culturing.
- Microbiological Safety Cabinet: Provides a sterile and safe environment for handling infectious materials.
- Microbial Incubator: Maintains optimal temperature and conditions for microbial growth and identification.
- Gram Staining Kit: Essential for differentiating and classifying bacteria based on their cell wall structure.
V. Math Lab Equipment

- Graphing Calculators: Used to perform complex mathematical calculations, graph functions, and solve equations.
- Geometric Solids: Physical models representing 3D shapes to aid in understanding geometry concepts.
- Measuring Tools: Rulers, protractors, compasses, and tape measures for accurate measurement in geometry experiments.
- Data Loggers: Devices that collect and record data during mathematical experiments or statistical analysis.
- Statistical Software: Enables statistical analysis, data visualization, and mathematical modeling.
VI. Geography Lab Equipment
- Maps and Globes: Fundamental tools for studying and analyzing geographical features, regions, and landscapes.
- GPS Devices: Enable accurate positioning, navigation, and mapping in outdoor and field-based geography studies.
- Weather Station: Measures and records atmospheric conditions such as temperature, humidity, and wind speed.
- Soil Testing Kit: Helps analyze soil composition, pH levels, and nutrient content for agricultural or environmental studies.
- Compass and Clinometer: Instruments used for measuring angles, bearings, and slope gradients in surveying and mapping.
Laboratory equipment is the backbone of scientific exploration and understanding. From the precise measurements and analysis in chemistry to the observation of microscopic life in biology, these instruments enable researchers, students, and educators to push the boundaries of knowledge. By recognizing the specific equipment and their applications within each discipline, scientists can conduct experiments, collect data, and unlock the mysteries of the natural world.
Whether it’s the glassware in a chemistry lab, the microscopes in a biology lab, or the mathematical tools in a math lab, each piece of equipment serves a vital purpose in its respective field. As science continues to advance, new technologies and equipment will emerge, further expanding our understanding and capabilities within the laboratory setting.






Leave a Reply