Lawrencium-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
Lawrencium, represented by the symbol ‘Lr’ and bearing the atomic number 103, is a superheavy element that resides at the far end of the periodic table. This section delves into the critical properties that distinguish it from other elements.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Name | Lawrencium |
| Symbol | Lr |
| Atomic number | 103 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | [262] |
| Period in the periodic table | 7 |
| Group in the periodic table | 3 (Actinide) |
| Block in the periodic table | f |
| Shell structure | 2.8.18.32.32.9.2 |
Discovery
Lawrencium’s discovery and nomenclature are intriguing stories that showcase the collaborative effort of the scientific community.
Lawrencium was first synthesized in 1961 by a team of scientists at the University of California, Berkeley, led by Albert Ghiorso. It was named in honor of American physicist Ernest O. Lawrence, the inventor of the cyclotron particle accelerator, for his significant contributions to the field of nuclear physics.
Physical Properties
As a synthetic element, the physical properties of lawrencium are not as well-established as those of naturally occurring elements. Due to its radioactivity and extremely short half-life, it is challenging to observe these properties directly.
Chemical Properties
The chemical properties of lawrencium are not extensively explored due to its synthetic nature and instability. However, it is classified as an actinide, which means it shares some chemical similarities with other elements in this group, such as uranium and thorium.
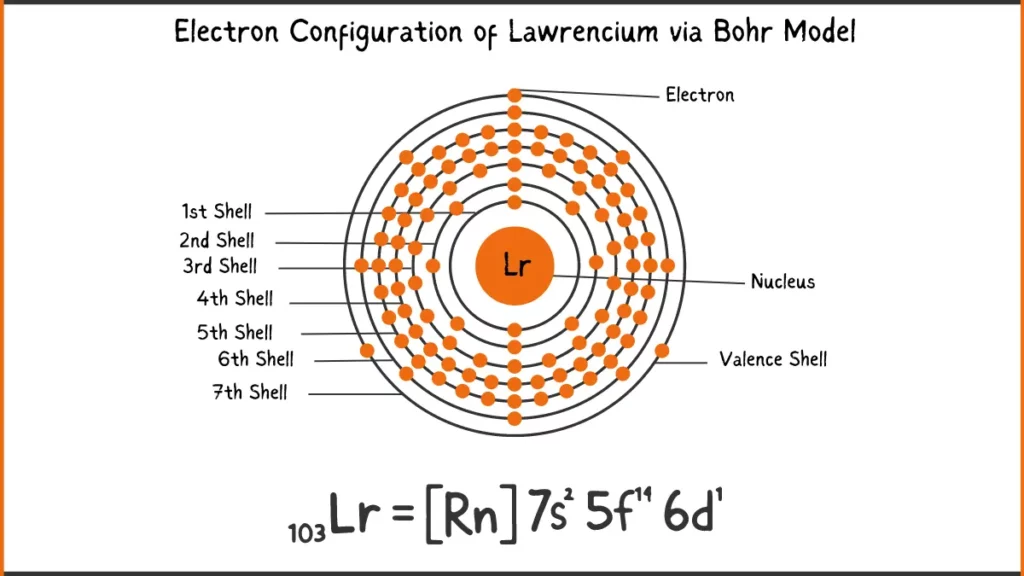
Electron Configuration of Lawrencium
The electronic configuration of Lawrencium (Lr) is [Rn] 5f¹⁴ 7s² 7p. Here, [Rn] refer to the noble gas radon, which represents the filled electron shells up to 6s²6p⁶. The remaining electrons occupy the 5f, 7s, and 7p orbitals. There are 14 electrons in the 5f subshell, 2 in the 7s subshell, and 1 in the 7p subshell.
Electron Configuration of Lawrencium via Bohr Model
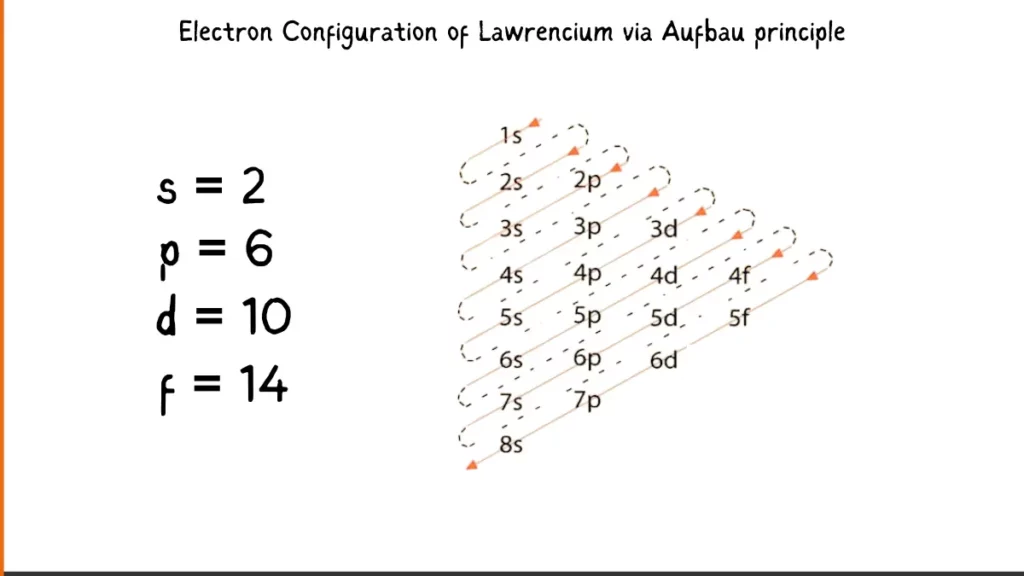
Electron Configuration of Lawrencium via Aufbau Principle
Facts
- Lawrencium is an extremely radioactive element, and its most stable isotope, Lr-262, has a half-life of milliseconds.
- It is primarily of scientific interest, with no known practical applications.
Applications
Lawrencium is not used in any practical applications outside of scientific research. Its production is highly resource-intensive and is mainly used for advancing our understanding of the behavior of superheavy elements. Scientists study lawrencium to gain insights into the properties and stability of such heavy elements, contributing to our knowledge of the periodic table.







Leave a Reply