Nitrogen-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
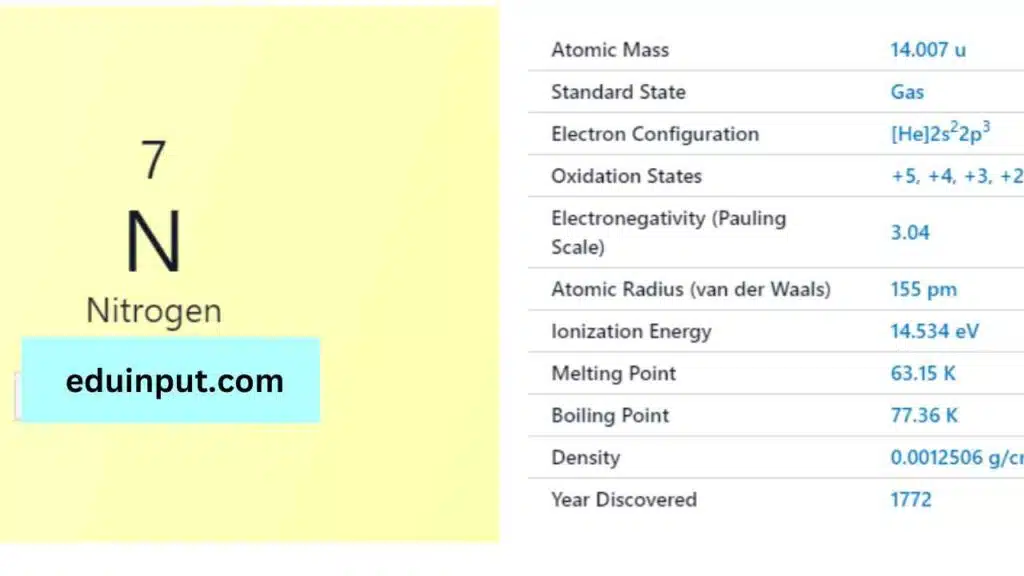
Nitrogen is a chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. It is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that makes up 78% of the Earth’s atmosphere by volume. Nitrogen is an essential element for life, as it is a key component of proteins and nucleic acids.
| Property | Value |
| Name | Nitrogen |
| Symbol | N |
| Atomic number | 7 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | The group in periodic table |
| Standard state | Gas at 298 K |
| Appearance | Colourless |
| Classification | Non-metallic |
| Block in the periodic table | 15 |
| Period in the periodic table | Pnictogen |
| The group in the periodic table | 2 |
| The group in the periodic table | p |
| Shell structure | 2.5 |
| CAS Registry | 7727-37-9 |
Discovery
Nitrogen was first discovered by the Scottish physician Daniel Rutherford in 1772. He called it “noxious air” because it could not support combustion or life.
Physical Properties
Nitrogen is a non-metallic element and exists in its gaseous form at standard temperature and pressure. It has a boiling point of -195.79°C and a melting point of -209.86°C. Nitrogen is a diatomic molecule, which means it exists as N2. It is relatively inert and does not react readily with other elements.
Chemical Properties
Nitrogen is a non-metal and has five electrons in its outermost energy level. It tends to form covalent bonds with other elements, as it has a high ionization energy and electronegativity. Nitrogen can form a wide variety of compounds, including ammonia, nitric acid, and nitrogen oxides.
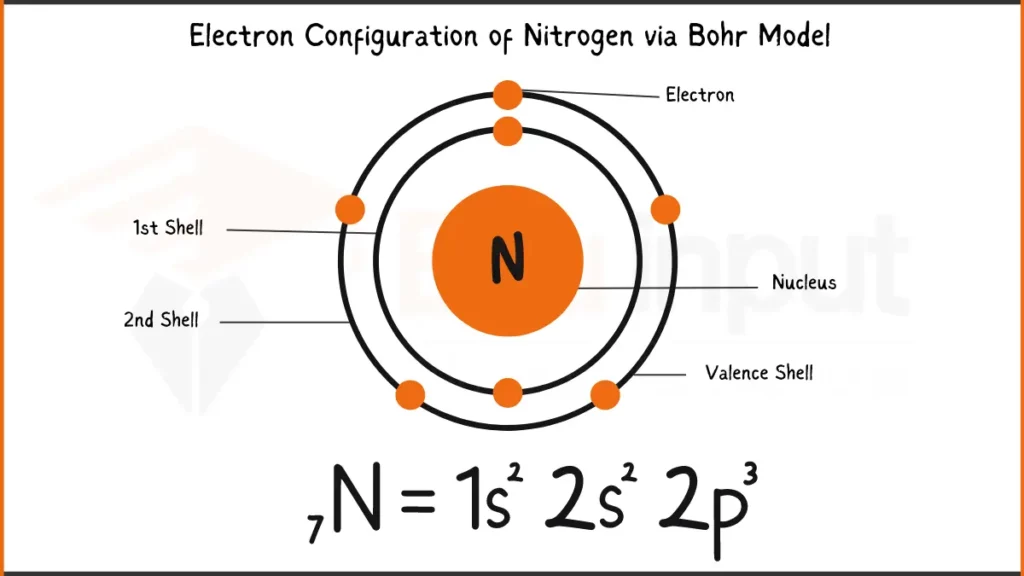
Electronic Configuration of Nitrogen
Nitrogen (N), essential for life, has 7 electrons: 1s²2s²2p³. In simpler terms, its first two shells hold 2 electrons each, and the outermost one holds 3. This arrangement influences how Nitrogen bonds with other elements.
Electronic Configuration of Nitrogen via Bohr Model
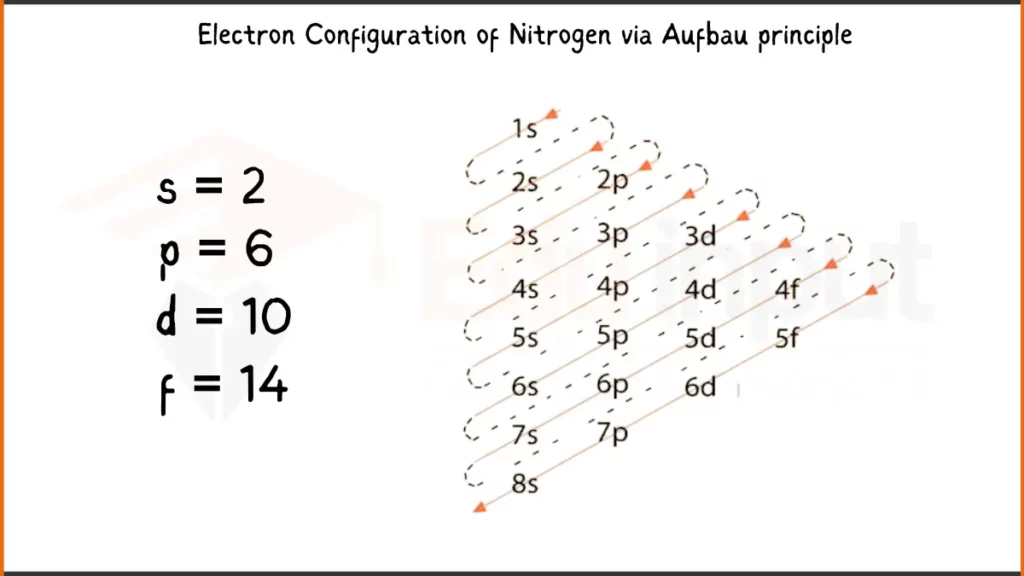
Electronic Configuration of Nitrogen via Aufbau Principle
Facts
- Nitrogen is the most abundant gas in Earth’s atmosphere, making up 78% of it by volume.
- Nitrogen gas is used in many industrial processes, including the production of fertilizers, the freezing of food, and the manufacturing of electronics.
- Nitrogen is also used in the production of explosives and as a coolant in the nuclear industry.
- Liquid nitrogen is a common coolant used in cryogenics, which is the study of the production of low temperatures.
Applications
Nitrogen has a wide range of applications in various industries. Some of the most common applications include:
- Fertilizers: Nitrogen is a key component of fertilizers, which are used to help plants grow and increase crop yields.
- Food Industry: Nitrogen is used as a coolant to freeze and store food products.
- Medical Industry: Nitrogen is used in the production of liquid nitrogen, which is used to freeze and store biological samples, including sperm and eggs.
- Industrial Processes: Nitrogen is used in the production of electronics, metals, and chemicals.
- Aerospace Industry: Nitrogen gas is used as a coolant in the aerospace industry to prevent overheating in engines and other systems.





Leave a Reply