Nutrition in Plants-Modes of Nutrition and Examples
Plant nutrition is the process by which plants get nutrients they need to survive, grow, and reproduce. Unlike animals, plants are autotrophs, meaning they can produce their own food.
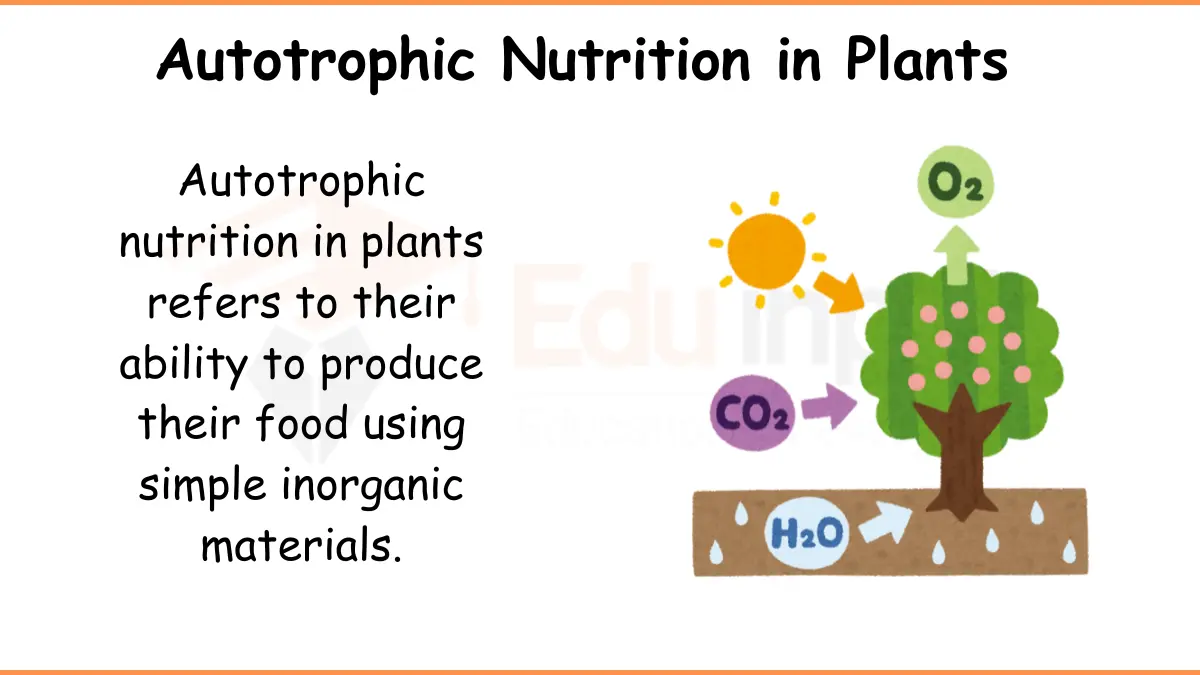
Organisms can be divided into two groups based on their mode of nutrition, Autotrophs and heterotrophs. Autotrophs can synthesize their food from simple inorganic materials, while heterotrophs obtain organic material from other sources.
Modes Of Nutrition
The three main modes of nutrition in plants are:
Autotrophic Nutrition
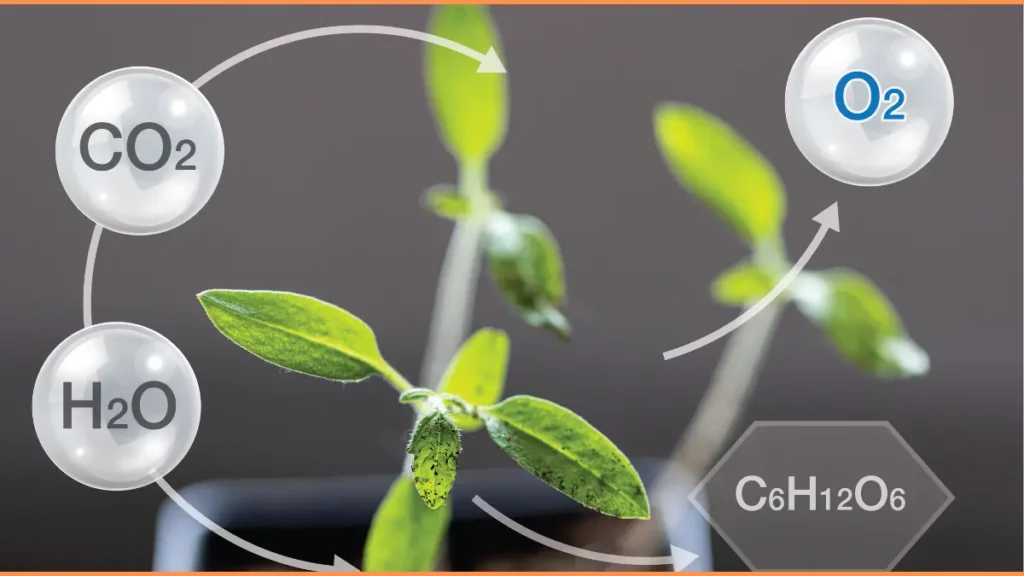
Autotrophic nutrition is the process by which plants synthesize their own food from inorganic sources. Photosynthesis is the primary autotrophic mode of nutrition in plants.
In this process, plants use light energy from the sun, carbon dioxide from the air, and water from the soil to synthesize glucose and other organic compounds.
Most plants are autotrophs and use photosynthesis for their nutritional needs.

Examples
Almost all green plants, including:
- Trees (pines, oaks, maples)
- Grasses
- Shrubs
Saprophytic Nutrition
Saprophytic nutrition is a mode of nutrition in which plants obtain their nutrients from decaying organic matter or dead organisms. Plants that exhibit this mode of nutrition are called saprophytes. Examples include fungi (such as mushrooms), some bacteria, and certain non-photosynthetic plants like Indian pipe plant (Monotropa uniflora) and ghost plant (Monotropa hypopitys).

Examples
- Mushrooms
- Bracket fungi
- Mold
Parasitic Nutrition
In parasitic nutrition, plants derive their nutrients from other living organisms, known as hosts. These plants are called parasites. They establish a direct connection with the host plant or organism to obtain water, minerals, and sometimes even organic nutrients.

There are two main types of parasitic plants:
- Holoparasites – These plants lack chlorophyll and are entirely dependent on their hosts for nutrients and water. Examples include dodder (Cuscuta), broomrape (Orobanche), and ghost pipe (Monotropa uniflora).
- Hemiparasites – These plants possess chlorophyll and can perform photosynthesis to some extent, but they also obtain water and nutrients from their hosts. Examples include mistletoe (Viscum), yellow rattle (Rhinanthus), and Indian painted-leaf (Peristrophe).
Examples
- Venus flytrap
- Pitcher plants
- Dodder (parasitic vine)
Mineral Nutrition in Plants
There are many other mineral elements present in the plants. Oxygen and hydrogen are the predominant elements of the plants. The plants obtain the composition of plants. These are
1. Nitrogen: It is present in protein-nucleic acids and many other compounds.
2. Phosphorus: It is present in ATP,
3. Magnesium: It is present in chlorophyll.
4. Iron: Iron is present in Cytochromes.



Leave a Reply