Radon-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
Radon is a chemical element with the symbol Rn and atomic number 86. It is a radioactive, colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas. Radon occurs naturally as an intermediate step in the normal radioactive decay chains through which thorium and uranium slowly decay into lead and various other short-lived radioactive elements. Being a noble gas, radon is chemically inert and does not readily form chemical compounds.

| Property | Value |
| Name | Radon |
| Symbol | Rn |
| Atomic number | 86 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | Block in the periodic table |
| Standard state | Gas at 298 K |
| Appearance | Colourless |
| Classification | Non-metallic |
| The group in the periodic table | 18 |
| Group name | Noble gas |
| Group in the periodic table | 6 |
| Period in the periodic table | p |
| Shell structure | 2.8.18.32.18.8 |
| CAS Registry | 10043-92-2 |
Discovery
Radon was first observed in 1899 by Ernest Rutherford and Robert B. Owens at McGill University in Montreal, Canada. They discovered that radon was emitted by thorium compounds.
Friedrich Ernst Dorn, a German chemist, independently discovered radon in 1900 while studying radium decay. Radon is named after the element radium from which it is derived.
Physical properties
Radon is a dense gas at standard conditions, and easily forms compounds with other elements. It has a melting point of -71°C and a boiling point of -61.7°C. Radon is the heaviest known gas and is nine times denser than air. Its atomic radius is about 120 picometers.
Chemical properties
As a noble gas, radon is inert and does not form compounds with other elements. It is, however, capable of forming weakly bound compounds such as radon fluoride and radon oxide under extreme conditions.
Electronic Configuration of Radon
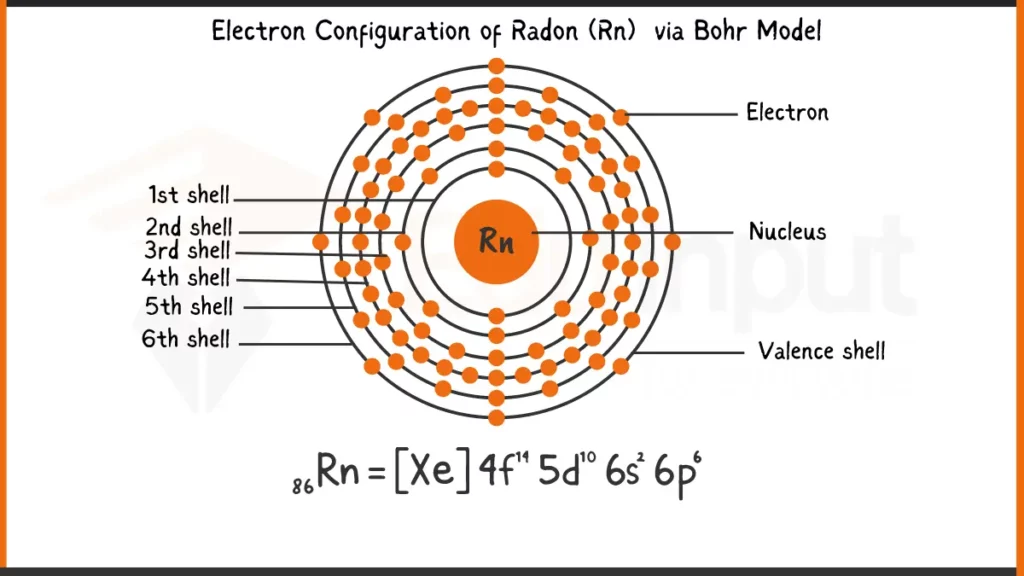
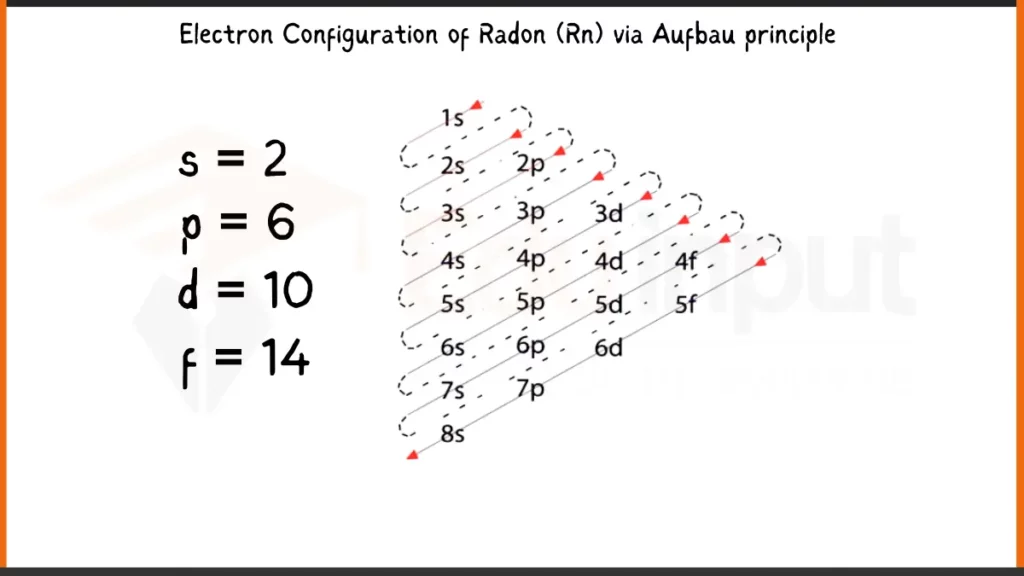
Radon (Rn) boasts 86 electrons filling its orbitals according to the Aufbau principle. This principle shows that electrons occupy the lowest energy levels first. The full electron configuration for Radon thus becomes: 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶4s²3d¹⁰4p⁶5s²4d¹⁰5p⁶6s²6p⁶. This detailed form shows each subshell and the number of electrons (represented by the superscript) occupying them.
Electronic Configuration of Radon via Bohr Model
Electronic Configuration of Radon via Aufbau Principle
Facts
- Radon is a radioactive gas that is produced naturally in the ground from the radioactive decay of uranium and radium.
- Radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer after smoking.
- Radon is present in all soils, and its concentration is generally higher in soils overlying granite, shale, and phosphate deposits.
- Radon is used in radiation therapy to treat cancer.
Applications
Radon has no practical use except in radiation therapy. It is used as a radiation source in brachytherapy, a form of cancer treatment. Brachytherapy involves the insertion of a radioactive source into the body near the tumor. The radiation destroys the cancer cells without damaging nearby healthy tissue. Radon is used in this form of therapy because it decays quickly and produces a large amount of radiation.




Leave a Reply