Roentgenium-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
Roentgenium, also known as element 111, is a synthetic element that was first synthesized in 1994 by a team of German and Russian scientists. It is a highly radioactive metal and is currently the heaviest known member of the group 11 elements.

| Property | Value |
| Name | Roentgenium |
| Symbol | Rg |
| Atomic number | 111 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | Group in the periodic table |
| Standard state | Presumably a solid at 298 K |
| Period in the periodic table | Unknown, probably metallic and silvery white or grey in appearance |
| Classification | Metallic |
| Group in periodic table | 11 |
| Group name | (none) |
| Block in the periodic table | 7 |
| Block in periodic table | d |
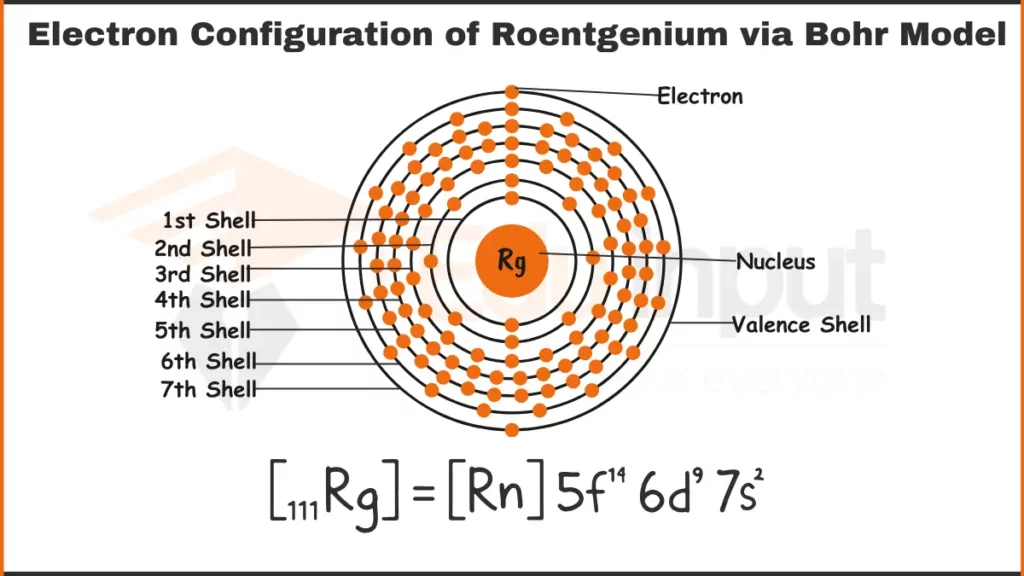
| Shell structure | 2.8.18.32.32.18.1 |
| CAS Registry | 54386-24-2 |
Discovery
Roentgenium was first synthesized in 1994 by a team of scientists at the Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung (GSI) in Darmstadt, Germany. The team, led by Peter Armbruster and Gottfried Münzenberg, bombarded a bismuth-209 target with accelerated nuclei of nickel-64 to produce roentgenium-272.
Physical Properties
Roentgenium is a highly radioactive metal that has only been produced in very small amounts, so its physical properties are not well known. However, it is believed to be a dense metal that is similar in appearance to silver.
Chemical Properties
Roentgenium is a highly unstable element and undergoes radioactive decay with a half-life of only a few seconds. Because of its short half-life, it is impossible to study the chemical properties of roentgenium directly. However, based on its position in the periodic table, it is expected to have chemical properties that are similar to those of its group 11 counterparts, copper, silver, and gold.
Electronic Configuration of Roentgenium
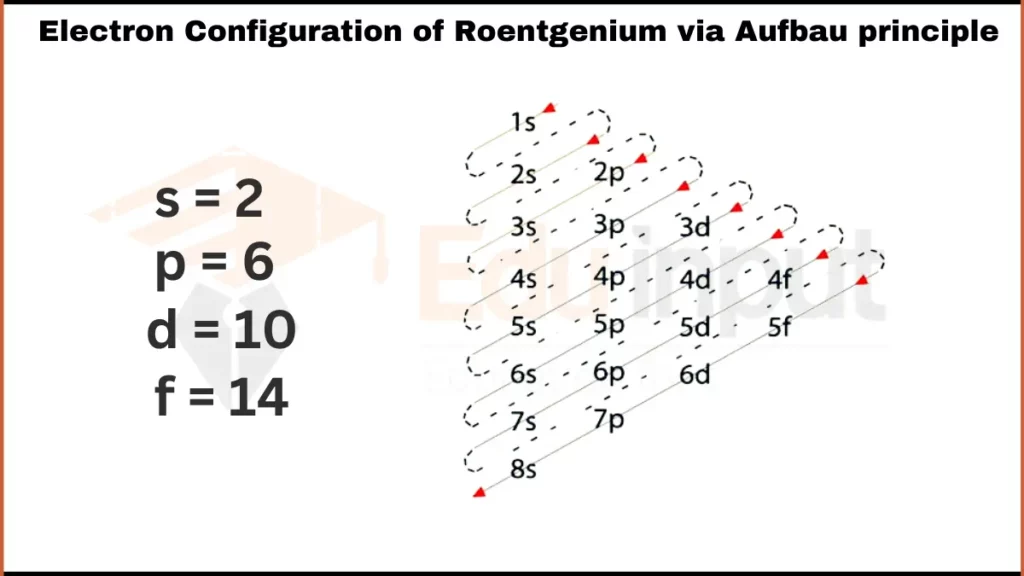
The electronic configuration of Roentgenium is [Rn] 5f14 6d97s2. It indicates that it fills the 7s subshell after the 5f and 6d orbitals similar to group 11 elements.
Electron Configuration of Roentgenium via Bohr Model
Electron Configuration of Roentgenium via Aufbau Principle
Facts
- Roentgenium was named after Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen, who discovered X-rays in 1895.
- Roentgenium has only been produced in very small amounts, and only a few atoms have ever been synthesized.
- Roentgenium is highly radioactive and decays quickly, making it difficult to study.
- Roentgenium is a member of the group 11 elements, which also includes copper, silver, and gold.
Applications
Because of its short half-life and highly radioactive nature, roentgenium has no practical applications at this time. However, its study may provide valuable insights into the behavior and properties of heavy, unstable elements.





Leave a Reply