Scandium-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
Scandium is a chemical element with the symbol ‘Sc’ and atomic number 21. It is a rare metal that has a unique set of properties that make it useful in a variety of applications, from aerospace to electronics. Despite its rarity, scandium has become an increasingly important element in modern technology.
| Property | Value |
| Name | Scandium |
| Symbol | Sc |
| Atomic number | 21 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | Period in the periodic table |
| Standard state | Solid at 298 K |
| Appearance | Silvery white |
| Classification | Metallic |
| Block in the periodic table | 3 |
| Group name | (none) |
| Group in the periodic table | 4 |
| Block in periodic table | d |
| Shell structure | 2.8.9.2 |
| CAS Registry | 7440-20-2 |
Discovery
Scandium was discovered in 1879 by Swedish chemist Lars Fredrik Nilson. He isolated scandium from the mineral euxenite and named it after Scandinavia. Scandium is found in small quantities in various minerals and ores and is mainly extracted from the residues of uranium and thorium processing.
Physical Properties
Scandium is a silvery-white metal that is relatively soft and light. It has a density of 2.98 g/cm3, a melting point of 1,541°C, and a boiling point of 2,836°C. Scandium is also a paramagnetic element, which means that it is attracted to magnetic fields.
Chemical Properties
Scandium is a relatively reactive element that readily forms compounds with other elements. It reacts with oxygen in the air to form scandium oxide, and with acids to form scandium salts. Scandium also has a high affinity for oxygen and is often used as a scavenger in metallurgical processes to remove impurities from metals.
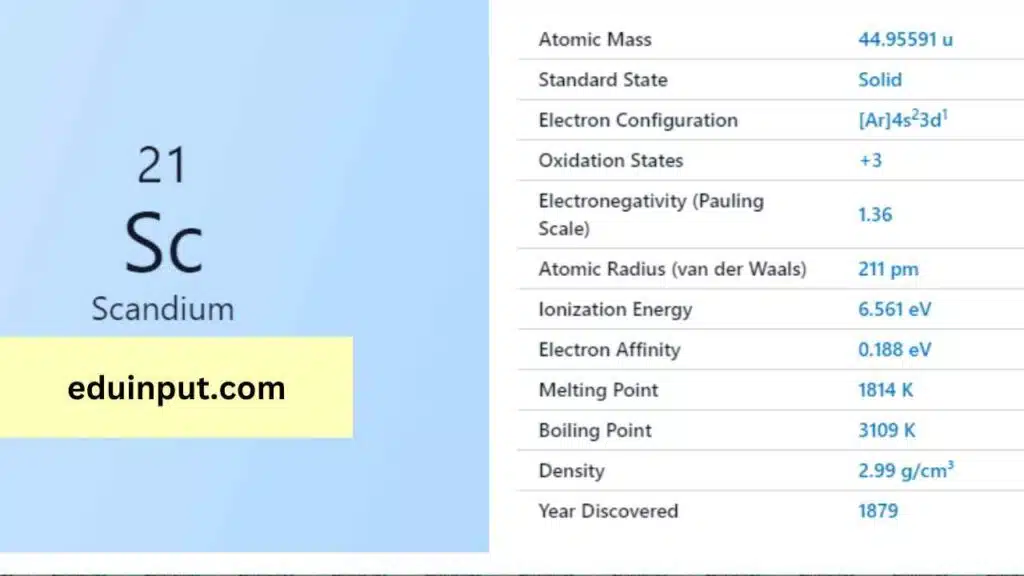
Electron Configuration of Scandium
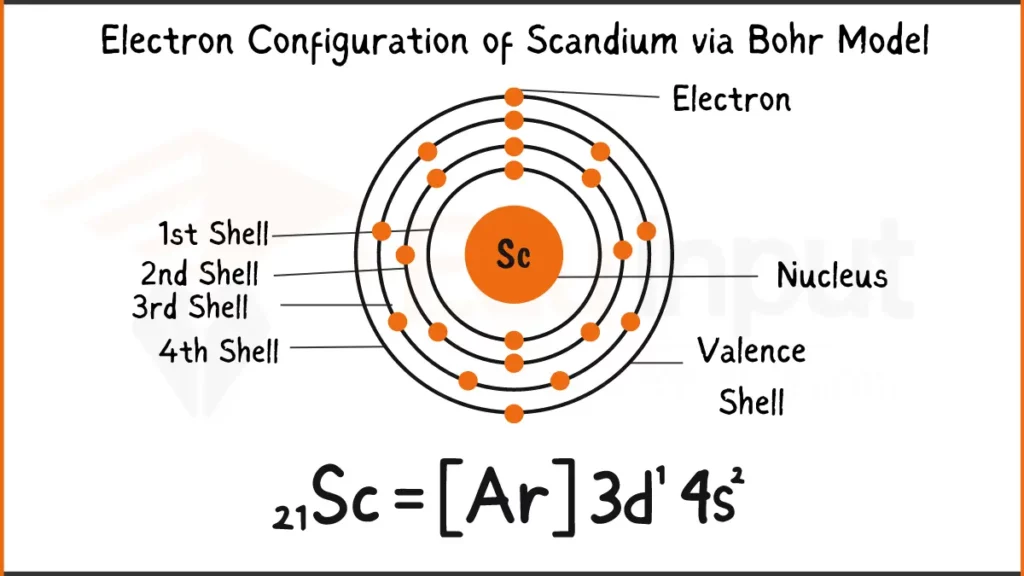
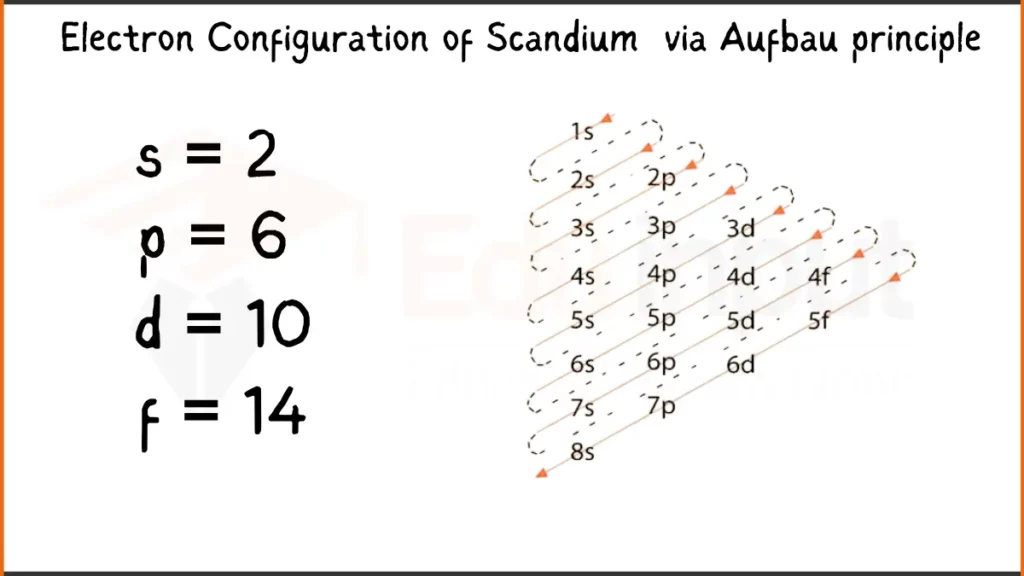
Scandium (Sc) has 21 electrons. Its configuration is 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶4s¹ or [Ar]3d¹. Scandium places its last electron in the 3d subshell, a transition metal trait.
Electron Configuration of Scandium Via Bohr Model
Electron Configuration of Scandium Via Aufbau Principle
Facts
- Scandium is a rare element that is found in small quantities in various minerals and ores.
- Scandium is often alloyed with aluminum to make stronger and more corrosion-resistant alloys.
- Scandium is a key element in high-performance materials used in aerospace, sports equipment, and electronics.
Applications
Scandium has a wide range of applications in various fields, including aerospace, sports equipment, and electronics. Some of the major applications of scandium include:
- Aerospace: Scandium is used in the production of high-performance aluminum-scandium alloys, which are lightweight and strong. These alloys are used in the aerospace industry to make aircraft parts that require high strength and resistance to corrosion.
- Sports equipment: Scandium is used in the production of high-performance sports equipment, such as baseball bats and lacrosse sticks. Scandium alloys are lightweight, strong, and have excellent shock-absorbing properties, making them ideal for use in sports equipment.
- Electronics: Scandium is used in the production of high-performance electronic components, such as solid-state lighting and flat-panel displays. Scandium-doped gallium nitride is used to produce blue and green LEDs, which are used in a wide range of electronic devices.
Scandium is a rare and versatile metal that has become increasingly important in modern technology. Its unique properties, such as its strength, lightweight, and resistance to corrosion, make it ideal for use in a wide range of applications, from aerospace to electronics. As technology continues to advance, the demand for scandium is likely to increase, making it an important element for the future.






Leave a Reply