Titanium-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol ‘Ti’ and atomic number 22. It is a strong, lustrous, and corrosion-resistant metal that is widely used in various industrial, medical, and aerospace applications. Titanium is also found in nature, in the form of minerals such as ilmenite and rutile.
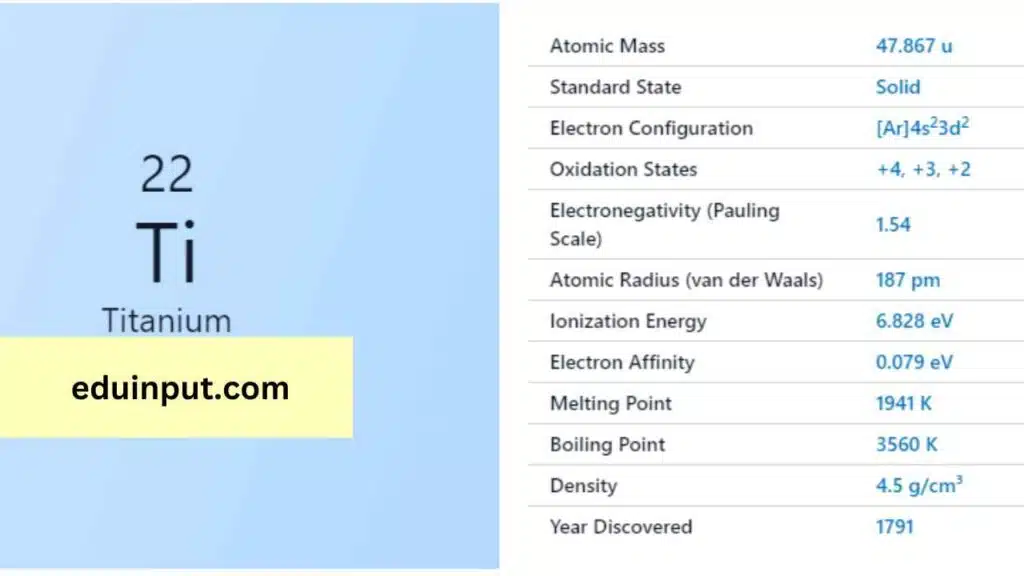
| Property | Value |
| Name | Period in the periodic table |
| Symbol | Ti |
| Atomic number | 22 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | 47.867 |
| Standard state | Solid at 298 K |
| Appearance | Silvery metallic |
| Classification | Metallic |
| Group in periodic table | 4 |
| Group name | (none) |
| Block in the periodic table | 4 |
| Group in the periodic table | d |
| Shell structure | 2.8.10.2 |
| CAS Registry | 7440-32-6 |
Discovery
Titanium was discovered in 1791 by the British mineralogist William Gregor, who found a black, magnetic sand that he called ‘menachanite’. A few years later, German chemist Martin Heinrich Klaproth identified a new element in the sand, which he named ‘titanium’ after the Titans of Greek mythology.
Physical Properties
Titanium is a strong, lightweight, and corrosion-resistant metal that is silver-gray in color. It has a density of 4.5 g/cm3, a melting point of 1,660°C, and a boiling point of 3,287°C. Titanium is also non-magnetic and non-toxic, making it an ideal material for medical implants.
Chemical Properties
Titanium is a highly reactive metal that readily forms compounds with other elements. It is resistant to corrosion, even in harsh environments such as seawater and chlorine gas. Titanium is also biocompatible, which makes it an ideal material for medical implants and prosthetics.
Facts
- Titanium is the ninth most abundant element on Earth and is found in rocks, soils, and sediments.
- Titanium has a high strength-to-weight ratio, which makes it ideal for use in aircraft, spacecraft, and military equipment.
- Titanium is also used in jewelry and watches, due to its durability and lustrous appearance.
Applications
Titanium has a wide range of applications in various industries, including aerospace, medical, and military. Some of the major applications of titanium include:
- Aerospace: Titanium is widely used in the aerospace industry due to its strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. It is used in aircraft components such as landing gear, engine parts, and structural elements.
- Medical: Titanium is an ideal material for medical implants and prosthetics, due to its biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and strength. It is used in dental implants, joint replacements, and surgical instruments.
- Military: Titanium is used in military equipment such as armor plating, missile casings, and submarine hulls, due to its strength and durability.
- Other Applications: Titanium is also used in other applications such as jewelry, watches, bicycle frames, and golf clubs, due to its durability, lustrous appearance, and lightweight.
Titanium is a versatile and strong metal with wide-ranging applications in various industries. Its strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility make it an ideal material for aerospace, medical, and military applications. As technology continues to advance, the potential uses of titanium may expand, making it an important element for the future.







Leave a Reply