What is Adverb? – Types, Placement, Usage, and Confusions
What is Adverb?
An adverb is a word that modifies a verb, adjective, or another adverb. Adverbs provide more information about how, when, where, how much, or to what extent an action is performed, or a quality exists.

Some common examples of adverb include quickly, slowly, well, often, always, never, here, there, everywhere, now, yesterday, today, tomorrow, soon, recently etc.
Types of Adverbs
Here are some types of adverbs:
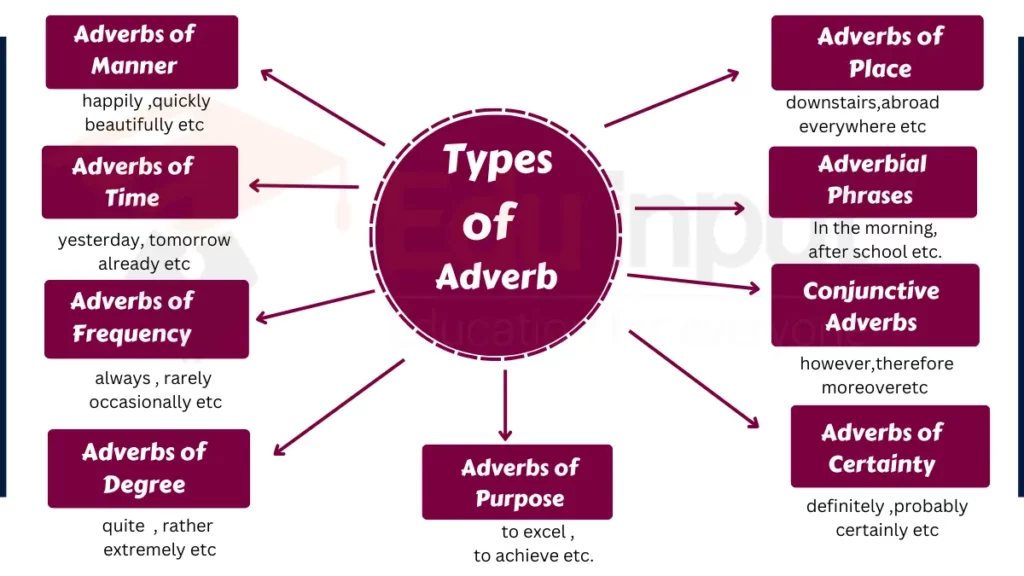
1. Adverbs of Manner
Adverbs of manner describe how an action is performed. These adverb describe the way in which an action takes place. Some common adverbs of manner include quickly, slowly, badly, carefully, loudly, quietly, well, etc.
Example
- She sang beautifully at the concert.
- The kids played happily in the park.
- He typed the email quickly before going to lunch.
2. Adverbs of Time
Adverbs of time specify when an action takes place. These adverbs provide important context by showing the timing or sequence of actions .Some common adverbs of time include today, tomorrow, now, then, yesterday, later, currently, afterwards, already, etc.
Example
- She called me yesterday.
- We are traveling to Paris tomorrow.
- I have already eaten dinner.
3. Adverbs of Frequency
Adverbs of frequency indicate how often an action or event occurs. Some common adverbs of frequency include always, usually, often, sometimes, never, rarely, occasionally, frequently, daily, weekly, etc.
Example
- I always brush my teeth before bed.
- She rarely goes out on weeknights.
- They occasionally visit their grandparents.
4. Adverbs of Degree
Adverbs of degree specify the intensity or extent of an action or quality. These adverbs indicate the strength or weakness of an action or quality to the reader. Some common adverbs of degree include almost, barely, hardly, too, very, extremely, quite, rather, so, enough, etc.
Example
- I was extremely tired after the long hike.
- She was quite upset about failing the test.
- This assignment is rather difficult.
5. Adverbs of Place
Adverbs of place indicate where an action is performed. These adverbs specify the location or physical context of an action. Some common adverbs of place include here, there, outside, upstairs, downstairs, abroad, somewhere, anywhere, nowhere, everywhere, etc.
Example
- She waited patiently downstairs.
- I looked everywhere for my keys.
- He is traveling abroad next month.
6. Adverbial Phrases
Adverbial phrases function as adverbs but contain multiple words rather than a single adverb. These adverbs tell when, where, how, or to what extent actions take place. Some examples of adverbial phrases include in the morning, After school, At home, During the night, To the left, In a hurry etc.
Example
- In the morning, I like to drink coffee.
- She always studies after school in the library.
- They walked to the left around the corner.
7. Conjunctive Adverbs
Conjunctive adverbs connect independent clauses and indicate a particular relationship between them. Some common conjunctive adverbs include however, moreover, therefore, consequently, furthermore, nevertheless, instead, etc.
Example
- I planned to go jogging this morning; however, it started raining heavily.
- Kelly wasn’t feeling well last night; therefore, she decided to stay home from work.
- The traffic was terrible; moreover, my car was running low on gas.
8. Adverbs of Certainty
An adverb of certainty is a type of adverb that conveys the degree of confidence or assurance associated with an action, statement, or occurrence. These adverbs provide information about how sure or certain someone is about the truth or likelihood of a particular situation.
Examples
- He will definitely attend the event.
- She probably knows the answer.
- They are certainly coming to the party.
9. Adverbs of Purpose
An adverb of purpose is a type of adverb that provides information about the intention or reason behind an action. It explains why someone performs a particular activity or the goal they aim to achieve. Adverbs of purpose often answer the question “why” or “for what reason.”
Examples
- She studied hard to excel in her exams.
- He spoke softly not to disturb the sleeping baby.
- I work diligently to achieve my goals.
Adverb Placement
Where you place an adverb in a sentence, it can affect the meaning of sentence. Here are some guidelines for adverb usage in sentences:
- Adverbs of frequency are typically placed before the main verb.
For example: She always takes the train to work.
- Adverbs of manner are often placed at the end of a sentence or clause.
For example: He performed the dance impressively at the recital.
- Adverbs of time are usually placed at the beginning or end of a sentence.
- For example: Yesterday we went to the park. We will meet again tomorrow.
- Adverbs of place are commonly placed at the end of a sentence.
- For example: The kids played outside in the backyard.
- Adverbs that modify adjectives or other adverbs generally come before the word being modified.
- For example: She sang extremely well at the audition.
- Conjunctive adverbs like however, therefore, consequently are used to join independent clauses and are preceded by a semicolon or period.
- For example: I didn’t study last night; therefore, I don’t feel prepared for today’s test.
- Adverbs of purpose typically come before the main verb in a sentence. However, they can also be placed at the beginning or end of a sentence for emphasis.
- For example: To improve her skills, she practices daily.
- Adverbs of certainty are often placed before the main verb, but their placement can vary based on the sentence structure.
- For example: I will definitely attend the event.
Learn What are Adverb Clauses
Adverb Confusion Examples
Here are some common confusions related to adverbs:
1. Adjective vs. Adverb
Adjectives modify nouns and pronouns, while adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs.
Example
- Adjective: He gave a quick response. (quick describes the noun “response”)
- Adverb: He responded quickly. (quickly describes how he responded)
2. Adverb Placement Confusion
Adverb placement can sometimes be confusing. Putting an adverb in the wrong spot can change the meaning of a sentence.
Example
- He only told his brother. (He told no one else)
- He told only his brother. (He didn’t do anything else to his brother except tell him)
3. Double Negatives
Using two negatives in a sentence is considered incorrect.
Example
- Incorrect: I couldn’t barely see the screen.
- Correct: I could barely see the screen.
4. Adverb vs. Conjunction
Some words can function as either adverbs or conjunctions depending on context.
Example
- Adverb: I slept well, for I was very tired.
- Conjunction: We set out early, for we had a long way to go.
5. Adverb vs. Preposition
Some words act as prepositions in certain contexts but adverbs in others.
Example
- Preposition: We walked down the street.
- Adverb: He fell down.
6. Split Infinitives
Some argue infinitives (to + verb) shouldn’t be separated by adverbs.
Example
- Split : To boldly go
- Unsplit : To go boldly
Usage in Sentences
- She completed the puzzle quickly.
- He handled the fragile items carefully.
- The car stopped suddenly at the red light.
- She always arrives on time for meetings.
- The movie was very entertaining.
- The wind blew softly through the trees.
- She speaks French well.
- We will leave for the airport soon.
- The students worked quietly in the library.
- The news was surprisingly positive.





Leave a Reply