What Is An Aquatic Ecosystem?-Features, Classification, And Productivity
A system in water where living and non-living components exchange material and transfer energy is called an aquatic ecosystem. In contrast to the terrestrial ecosystem, it is an ecosystem that is formed by organisms inhabiting aquatic habitats.
Classification Of Aquatic Ecosystem
The aquatic ecosystem is classified into the freshwater ecosystem and marine (salty) ecosystem.
Marine Ecosystems
The marine ecosystem includes salt-water oceans and sea. These are the largest ecosystems on the earth. They constitute 71% of the surface of the earth.
Freshwater Ecosystem
The freshwater ecosystem covers less than 1% of the properties of water. Water has some unique properties. These properties develop some common features in the aquatic ecosystem.
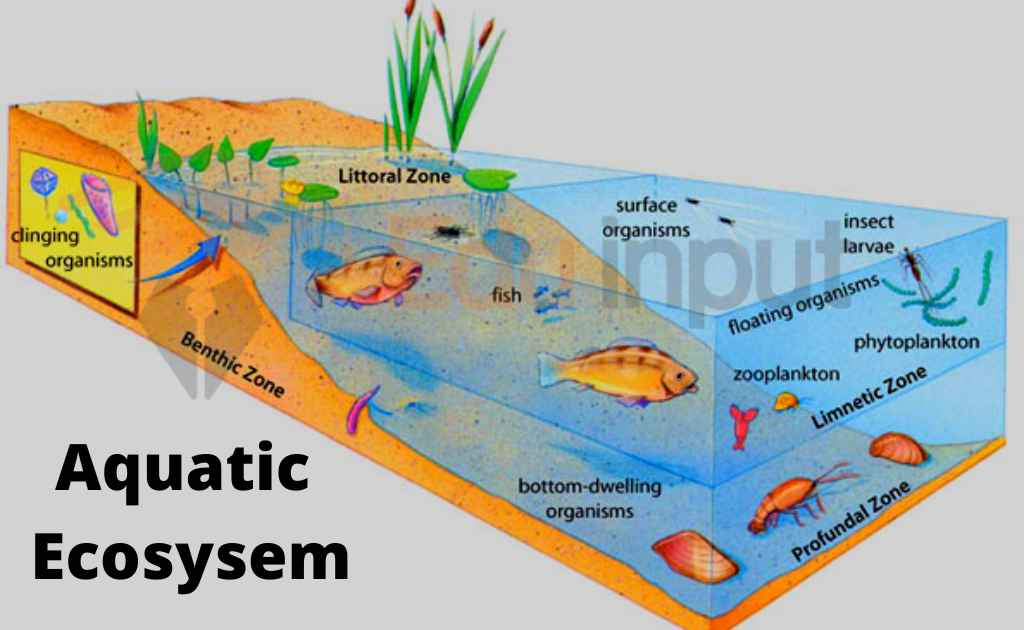
Features Of Aquatic Or Hydrospheric Ecosystem
Properties of water develop some particular features in the aquatic ecosystem. These features are:
1. Temperature: Water changes its temperature more slowly than air. So the temperature in the aquatic ecosystem remains moderate to support life.
2. Absorption of energy: Water is quite transparent. It can absorb a large amount of light energy. This energy sustains life on the earth. The intensity of light decreases rapidly with an increase in the depth of water. So there is little light at the depth of 600 feet that cannot support photosynthesis.
3. Nutrients: Light level is much lower at the bottom sediments of water. Thus photosynthesis cannot take place in it. So it cannot support life. Therefore, nutrients in the aquatic ecosystem concentrate near the bottom water. Thus these nutrients support life.
4. Abundant water with appropriate temperature: Water is an essential requirement for life. It is available abundantly in the aquatic ecosystem to support life. Energy and nutrient are the major factors in water. They determine the quantity and type of life in aquatic ecosystems.
Appropriate temperature is present in the aquatic ecosystem to carry out all metabolic processes.
Productivity of Aquatic Ecosystem
The amount of biomass formed in unit time in an ecosystem is called productivity. There are two ways to determine productivity.
(a) CO and O Method: CO₂ is consumed and oxygen is released during photosynthesis. Measurement of these gases can give the amount of productivity.
(b) Light And Nutrient Method: The productivity of the aquatic ecosystem is determined by light and nutrients. Light intensity and quality vary with the water depth. So the primary productivity also varies with the light. The number of nutrients that form also changes with the season. Productivity also varies from zone to zone.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the 5 aquatic ecosystems?
The aquatic ecosystem includes;
Oceans
Lakes
Wetland
Rivers
Streams
What is the meaning of aquatic?
The word Aquatic refers to an environment consisting of frequent water.
What animals live in an aquatic habitat? Give examples.
Following animals inhabit the aquatic ecosystem;
Fishes
Protozoa
Bacteria
Sea reptiles
Crustaceans
Seals (Marine mammals)
What are the types of aquatic ecosystems?
There are two main types of aquatic ecosystems;
Marine Ecosystems
Freshwater Ecosystem
Where are aquatic ecosystems located?
Aquatic ecosystems are diverse and span across the globe, encompassing oceans, lakes, rivers, ponds, wetlands, estuaries, and even some underground aquifers.





Leave a Reply