What Is Central Dogma?-Definition and Steps
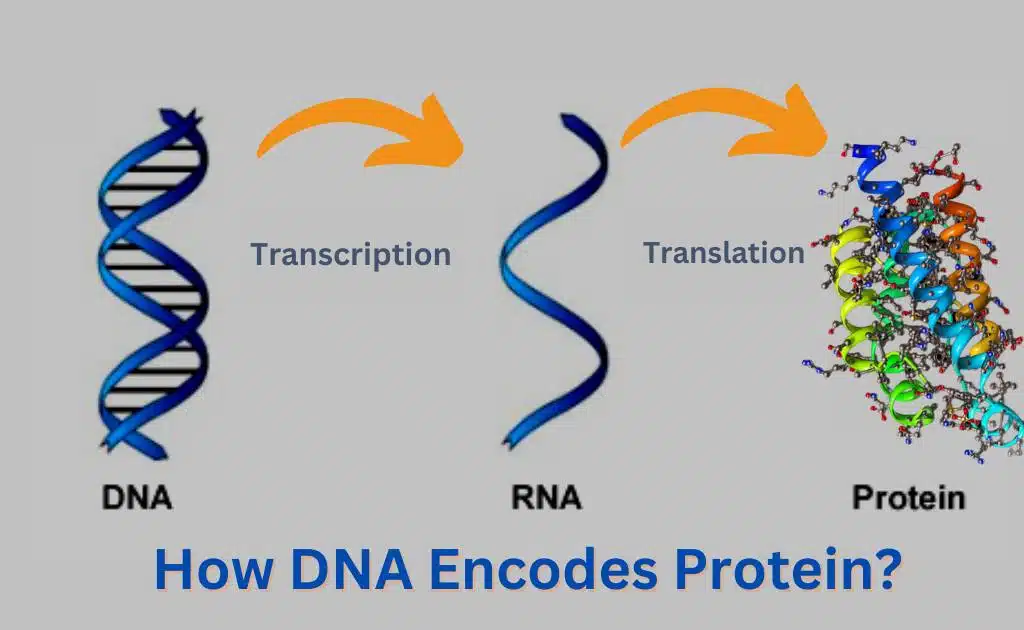
Central dogma refers to the theory that DNA is transcribed into RNA, then translated into proteins. The central dogma states that information flows from DNA to RNA to protein. This flow of information is essential for the growth and development of living things.
DNA is the genetic material found in every living cell. The Double helix structure of DNA consists of two complementary strands held together by hydrogen bonds. Each strand contains four types of chemical compounds called nucleotides. These nucleotides form the basis of the Genetic code.
What Is Central Dogma?
The mechanism of reading and expressing the gene by transcription and translation is called central dogma. All organisms use the same basic mechanism. The central dogma is composed of transcription and translation.
These two steps of central dogma are also collectively called gene expression. Genetic information is present in DNA. It is also the main fountainhead. The genetic information flows down into RNA. RNA then converts them into protein.
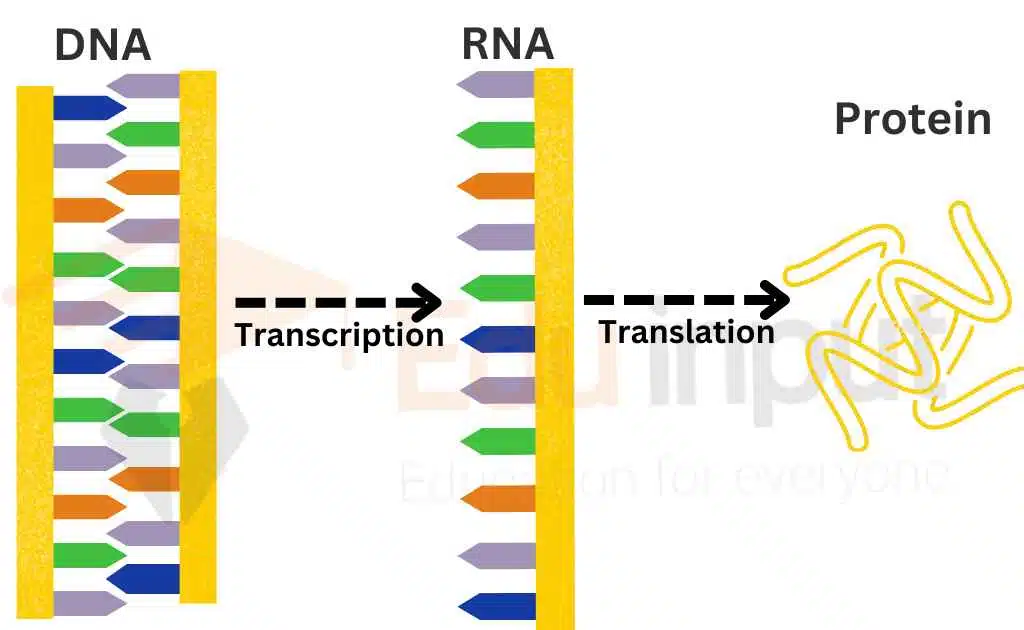
Steps of Central Dogma
The following steps take place in the central dogma:
Transcription:
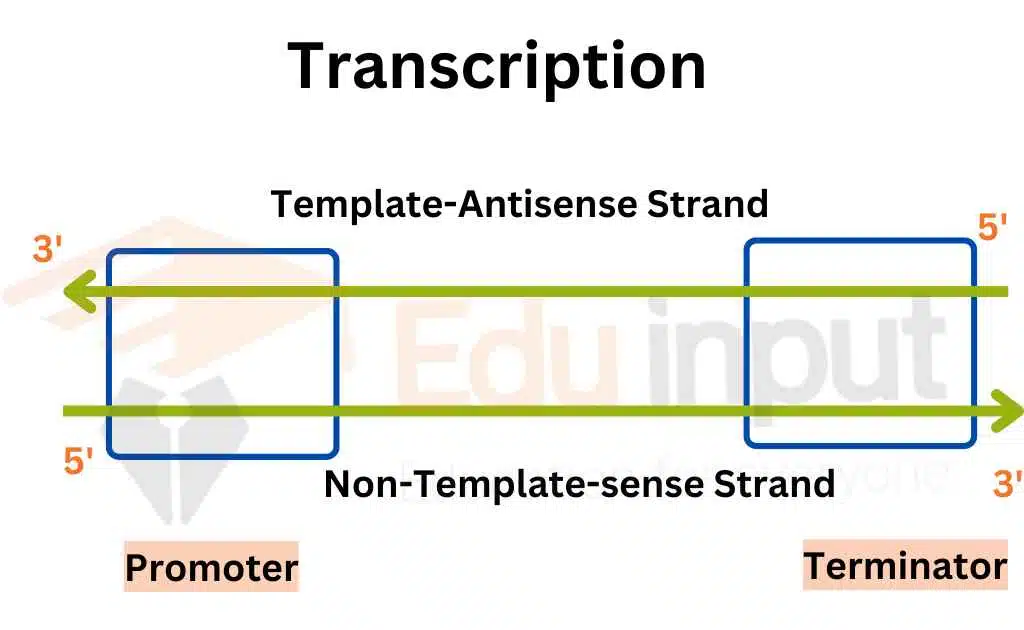
The synthesis of mRNA from the DNA is called transcription. The first step of central dogma is the transfer of information from DNA to RNA. The enzyme RNA polymerase binds to a particular binding site called a promoter. It starts the transcription. The promoter is located at the beginning of the gene.
The enzyme then moves along the strand and mRNA is synthesized. The stop signals are present on the other end of the gene. The enzyme disengages itself from the DNA on these stop signals. Thus the newly assembled RNA chains are released. This chain is a complementary transcript (copy) of the gene.
Translation:
The synthesis of protein from RNA is called translation. It is the second step of the central dogma. It transfers the information from RNA to proteins. The ribosomes synthesize a direct copy of polypeptides from the information of mRNA. Thus the nucleotide sequence of the mRNA is translated into an amino acid sequence in the polypeptide. So this process is called translation.
Types Of RNA
There are following three types of RNA:
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): It is found in the ribosome. The rRNA provides the site for the synthesis of polypeptides during translation.
Transfer RNA (tRNA): Transfer RNA molecules read the message (code) on the mRNA and transport the amino acids to the ribosomes. These amino acids are used in building polypeptides. The tRNA is also responsible for the exact position of each amino during the elongating polypeptide chain. Human cells contain about 45 different kinds of tRNA molecules.
Messenger RNA (mRNA): The mRNA is long strands of RNA. It is transcribed from DNA. It travels to the ribosomes and assembles amino acids into a polypeptide.”
Frequently Asked Questions-FAQs
What is Central Dogma?
Central Dogma is the flow of information from DNA to RNA, and then into proteins.
Who proposed the concept of central dogma?
Francis Crick proposed the concept of Central Dogma in molecular biology.
What are the steps of Central Dogma?
There are two steps of gene expression/ Central Dogma;
Transcription (RNA Synthesis)
Translation (Protein Synthesis)




Leave a Reply