Potentiometer | Determination of Unknown emf
The potentiometer is defined as A very simple instrument that can measure and compare potential differences accurately without drawing any electric current from the circuits is called a potentiometer.
Download the pdf notes of the Potentiometer Class 12 Physics
Principle of Potentiometer
The potential difference across any length of a wire of uniform cross-section area is directly proportional to its length when a constant current passes through it.
Construction of Potentiometer
It consists of a resistor R in the form of a wire connected between points A and B.
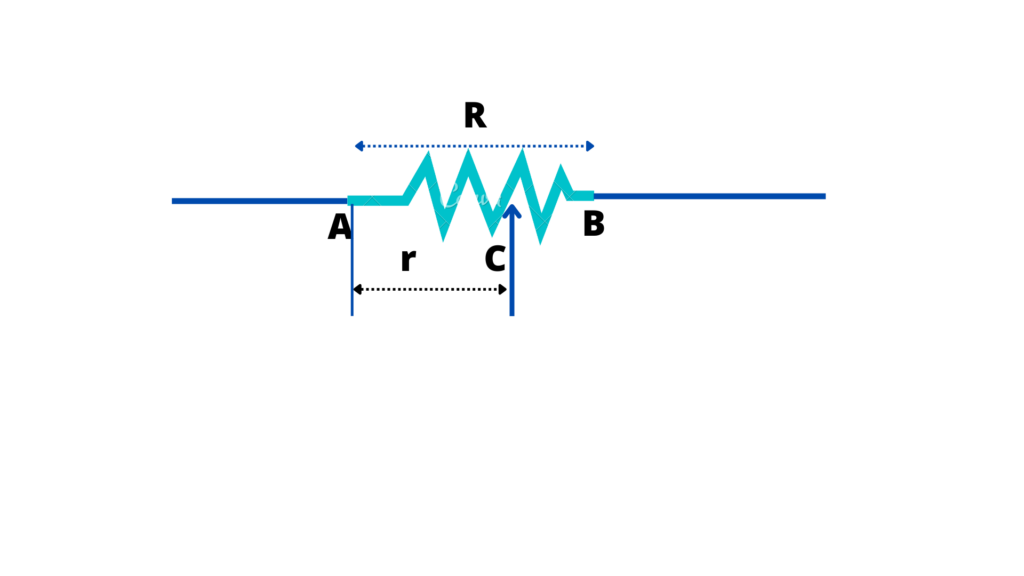
A terminal C can slide on it. The resistance between A and C can be varied from 0 to R on the sliding contact C is moved from A to B.
When a battery of emf E is connected across R, the current following through it is given by:
E=IR
Or
I=E/R
Let r be the resistance between points A and C Then the potential drop between these points is given by:
Vac=E/R × r
What is a Potential divider?
As ‘C’ moves from A to B. varies from 0 to R and potential drop changes from 0 to E. Such an arrangement is known as a “Potential Divider”.
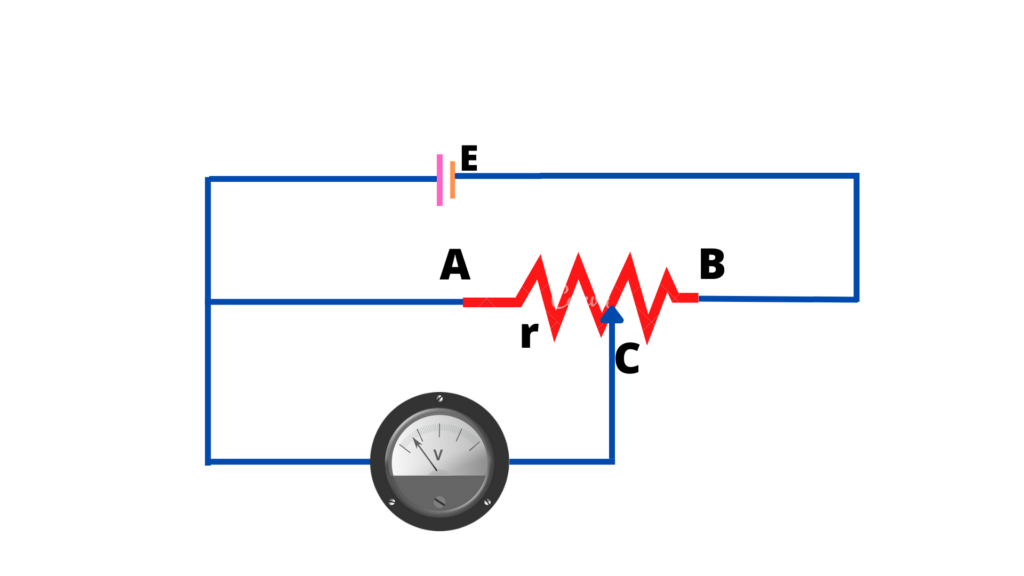
Determination of unknown emf
Consider a cell of emf “Ex” which is to be determined. It is connected between A and sliding contact C through a galvanometer.
The positive terminal of Ex and potential divider are commonly connected at point A.
In the loop AGCA, if the point C and the negative terminal of Ex are at the same potential, then the potential and no current will flow through the galvanometer.
Thus to measure the potential Ex the position of C is so adjusted that the galvanometer shows no deflection. In such a case emf Ex of the cell is equal to the potential difference between A and C
Ex=E×r/R
But resistances are proportional to their respective lengths.
r∝l
R∝L
Ex=E×l/L
Where L is the total length of the wire AB and I is the length from A to C. The unknown emf Ex should not exceed Ex otherwise null condition will not be satisfied. Thus potentiometer is the most accurate method for measuring potent
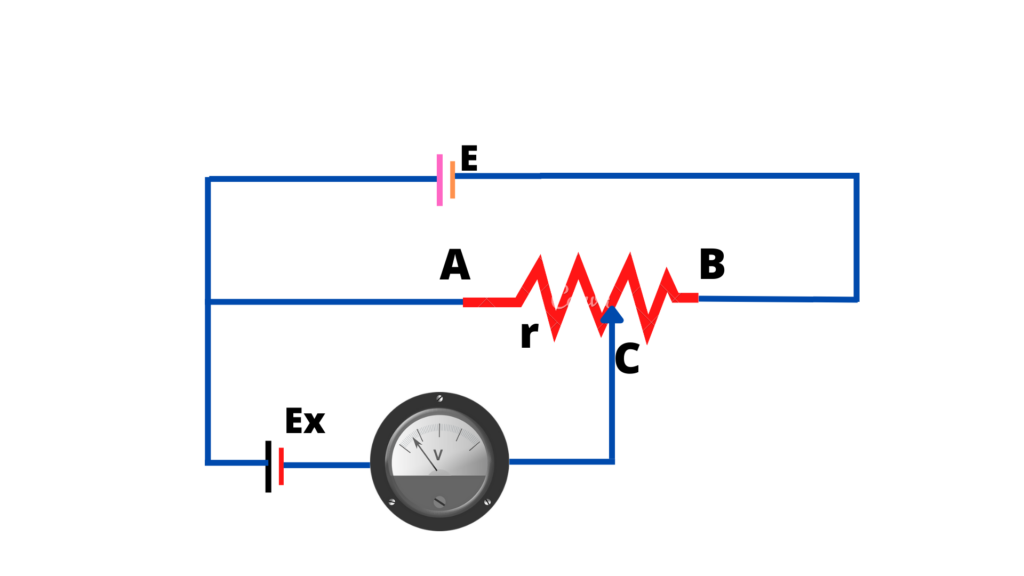
Comparison of the emf’s of two cells
The method for measuring the emf of a cell can be used to compare the emf’s E1 and E2 of two cells.
The balancing lengths l1 and I2 are determined separately for the two cells
For the first cell
E1=Exl1/L
For the second cell
E2=Exl2/L
Dividing the two equations
E1/E2=l1/l2
Thus the ratio of the EMFs is equal to the ratio of their balancing lengths
Why do we use a potentiometer?
Potential difference is usually measured by an instrument known as a voltmeter.
A voltmeter measures the P.D correctly only when its resistance is very large than the resistance of the circuit so that no current is passing through it. An ideal voltmeter has infinite resistance.
Some other potential measuring instruments are a digital voltmeter and a cathode-ray oscilloscope. They have large resistance and draw no current from the circuit. But these instruments are very expensive and are difficult to use.
Frequently Asked Questions-FAQs
What is a potentiometer used for?
A potentiometer is a type of position sensor. They can be used to measure displacement in different directions. The displacement and rotation of the linear and rotary potentiometers are measured by them.
What are the 4 types of potentiometers?
These are four types of potentiometer
Slide
Dual side
Multi-turn slide
Motorized fader
Is a potentiometer a resistor?
A variable resistor with 3 terminals is called a potentiometer. Two of the terminals are connected to the opposite ends of a resistive element, and the third terminal is connected to a sliding contact that moves over the resistive element.






Leave a Reply