Zirconium-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
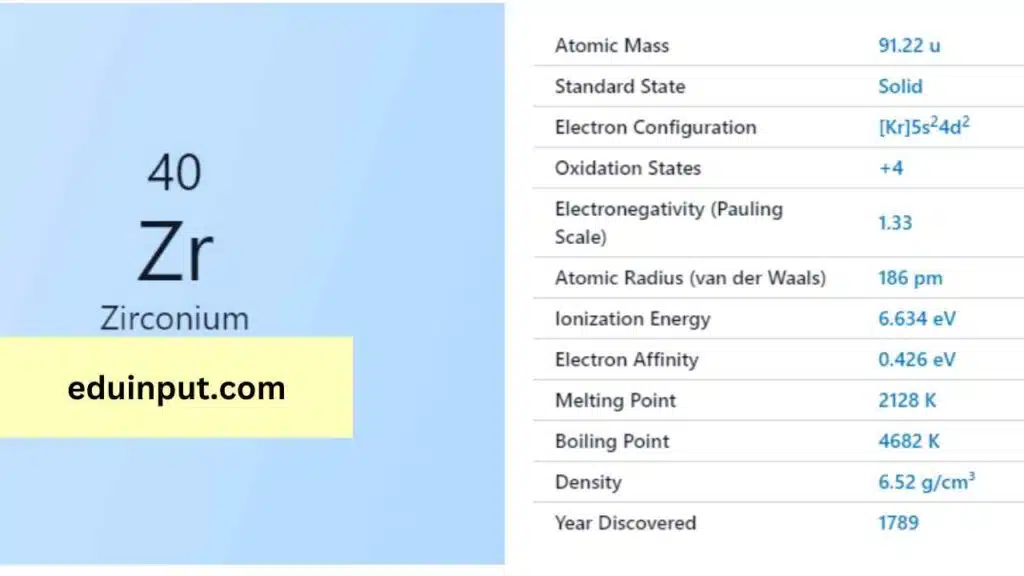
Zirconium is a chemical element with the symbol ‘Zr’ and atomic number 40. It is a strong, lustrous, and corrosion-resistant metal that is widely used in various industrial, nuclear, and biomedical applications. Zirconium is also found in nature, in the form of minerals such as zircon and baddeleyite.
| Property | Value |
| Name | Zirconium |
| Symbol | Zr |
| Atomic number | 40 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | 91.224 (2) g |
| Standard state | Solid at 298 K |
| Appearance | Silvery white |
| Classification | Metallic |
| Group in periodic table | 4 |
| Group name | (none) |
| Period in periodic table | 5 |
| Block in periodic table | d |
| Shell structure | 2.8.18.10.2 |
| CAS Registry | 7440-67-7 |
Discovery
Zirconium was first discovered in 1789 by the German chemist Martin Heinrich Klaproth, who isolated an oxide of the metal from the mineral zircon. However, the element was not fully characterized until 1824 by the Swedish chemist Jöns Jakob Berzelius.
Physical Properties
Zirconium is a strong, ductile, and lustrous metal that is silver-gray in color. It has a density of 6.52 g/cm3, a melting point of 1,852°C, and a boiling point of 3,578°C. Zirconium is also highly resistant to corrosion, due to the formation of a stable oxide layer on its surface.
Chemical Properties
Zirconium is a highly reactive metal that readily forms compounds with other elements. It is also highly resistant to corrosion, due to the formation of a protective oxide layer on its surface. Zirconium is also biocompatible, which makes it an ideal material for dental implants and other biomedical applications.
Facts
- Zirconium is the 20th most abundant element on Earth, and is found in rocks, soils, and sediments.
- Zirconium is used in nuclear reactors as a cladding material for fuel rods, due to its high neutron absorption cross-section.
- Zirconium is also used in the production of various alloys, such as zircaloy, which is used in the nuclear industry.
Applications
Zirconium has a wide range of applications in various industries, including nuclear, aerospace, and biomedical. Some of the major applications of zirconium include:
- Nuclear: Zirconium is used in nuclear reactors as a cladding material for fuel rods, due to its high neutron absorption cross-section and resistance to corrosion.
- Aerospace: Zirconium is used in aerospace applications due to its high strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to corrosion. It is used in components such as jet engine parts and aircraft structural elements.
- Biomedical: Zirconium is used in biomedical applications due to its biocompatibility and resistance to corrosion. It is used in dental implants, artificial hip and knee joints, and other medical devices.
- Other Applications: Zirconium is also used in other applications such as ceramics, refractory materials, and pigments, due to its high melting point and chemical stability.
Zirconium is a durable and versatile metal with applications in various industries. Its resistance to corrosion, biocompatibility, and high strength-to-weight ratio make it an ideal material for nuclear, aerospace, and biomedical applications. As technology continues to advance, the potential uses of zirconium may expand, making it an important element for the future.






Leave a Reply