Photosynthesis-Process, Factors, Formula, Adaptations
Photosynthesis Definition
Photosynthesis is a natural process that converts light energy into chemical energy in the form of sugars. During photosynthesis, glucose molecules (or other sugars) are produced from water and carbon dioxide, while oxygen is released as a byproduct. This process is driven by light energy and provides organisms with two essential resources: energy and fixed organic carbon.
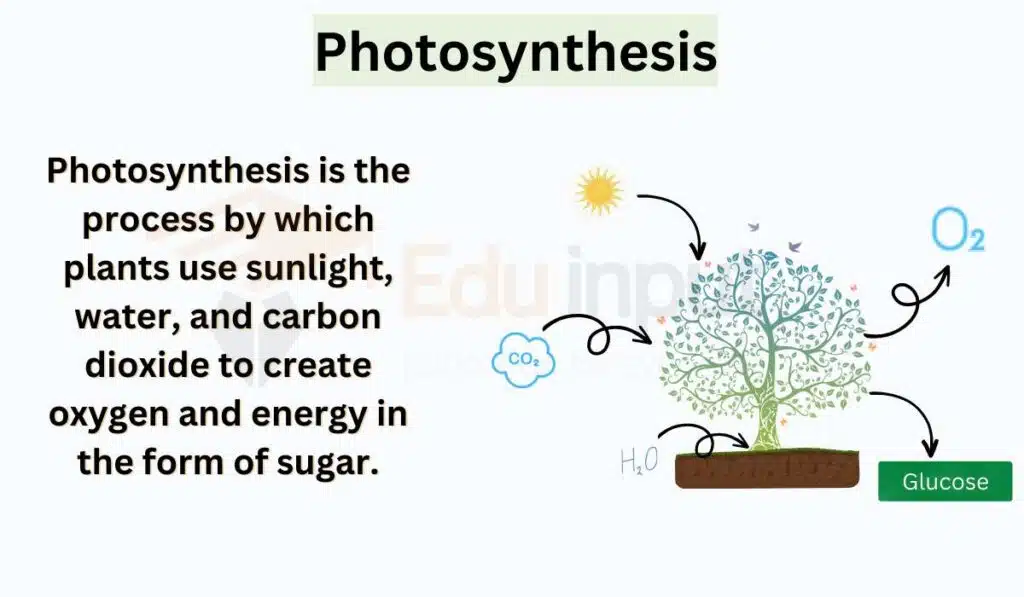
Process of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a redox process in which light energy drives the oxidation of water, resulting in the production of oxygen gas, hydrogen ions, and electrons. The electrons and hydrogen ions are then transferred to carbon dioxide, which is reduced to organic products, such as carbohydrates.
The process of photosynthesis consists of two stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions.
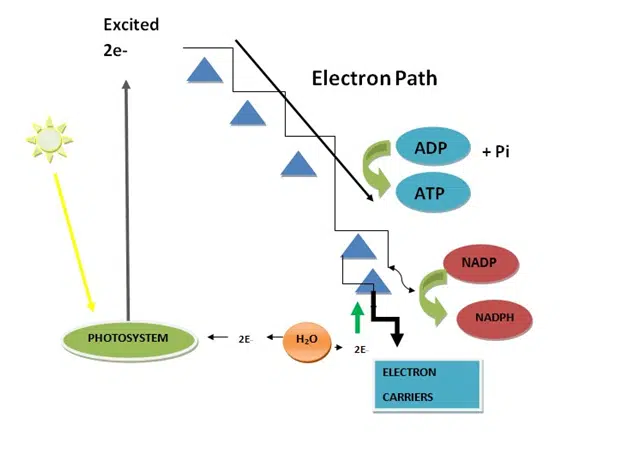
- The light-dependent reactions take place in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts and require sunlight to function. They involve the absorption of light energy by pigments such as chlorophyll, which is then used to generate
- ATP and the electron carrier NADPH through an electron transport chain.
During the light-dependent reactions, water molecules are split into oxygen, hydrogen ions (H+), and electrons, which are used to replenish the electrons lost in the electron transport chain. - The ATP and NADPH generated in the light-dependent reactions are then used in the light-independent reactions, also known as the Calvin cycle or dark reactions.
- The light-independent reactions take place in the stroma of the chloroplasts and do not require sunlight to function. They involve the fixation of carbon dioxide (CO2) into organic compounds using the ATP and NADPH generated in the light-dependent reactions.
- The Calvin cycle involves a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions that use ATP and NADPH to convert CO2 into glucose and other sugars.
- The light-independent reactions also involve a process called photorespiration, which occurs when there is a shortage of CO2 in the chloroplasts.
- The electron transport chain is an important component of both the light-dependent and light-independent reactions. It involves a series of redox reactions in which electrons are passed from one carrier to another, generating a proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis.
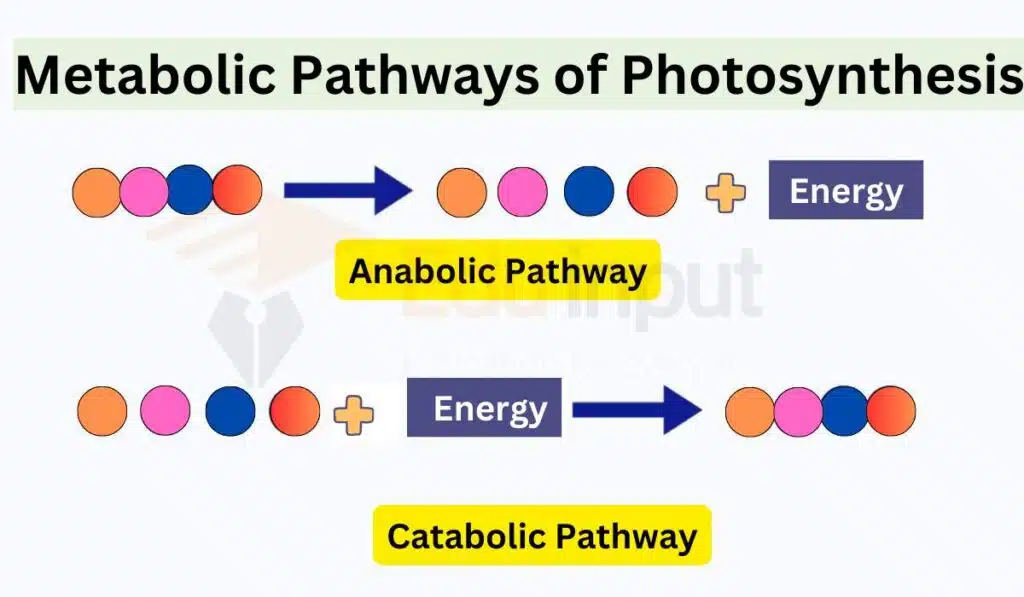
Metabolic Pathway of Photosynthesis
The metabolic pathway of photosynthesis consists of two main parts: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions, which are categorized as anabolic and catabolic pathways, respectively.
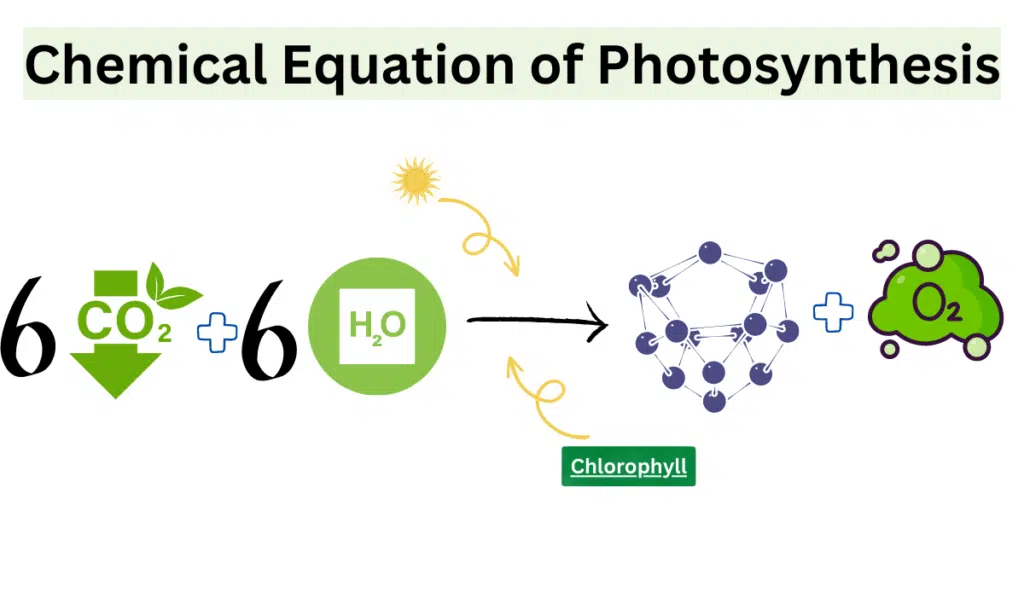
Chemical Equation of Photosynthesis
The chemical equation for photosynthesis can be represented as:
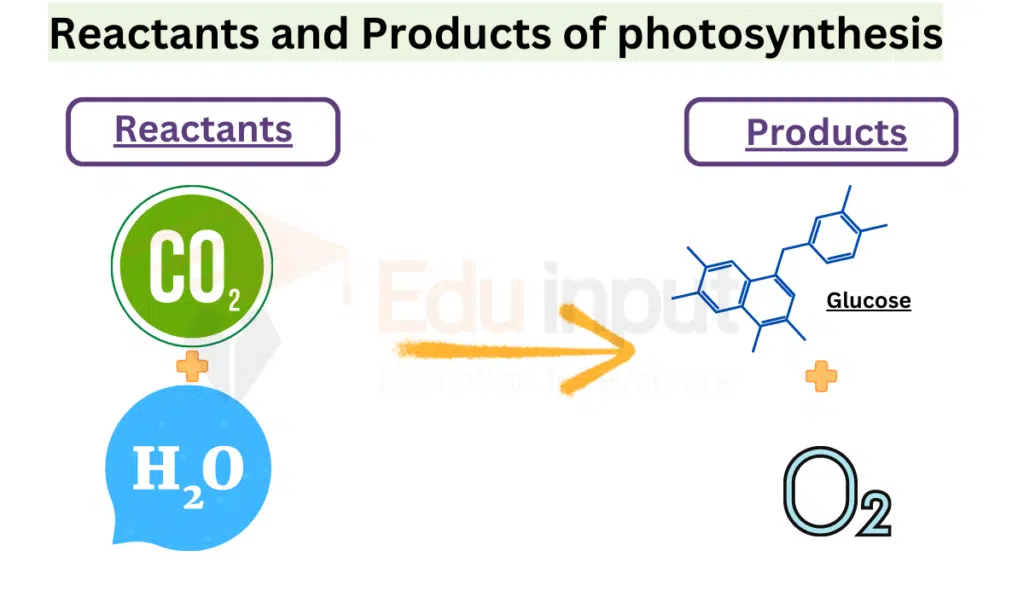
Reactants And Products Of Photosynthesis
Here are reactants and products of photosynthesis;
Reactants of Photosynthesis
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
- Water (H2O)
- Sunlight (light energy)
Products of Photosynthesis
- Glucose (C6H12O6)
- Oxygen (O2)
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of organic compounds, such as glucose. This process is essential for life on earth as it produces oxygen and food for organisms.
However, photosynthesis is affected by several factors that can limit its efficiency and productivity. It is important to maintain an optimal level of all the factors required for photosynthesis to ensure optimal plant growth and development. Here are some of the factors that affect photosynthesis:
1. Light Intensity
Light is the primary source of energy for photosynthesis. Plants require a certain amount of light energy to carry out the process of photosynthesis. Increased light intensity results in a higher rate of photosynthesis as it provides more energy for the process. On the other hand, low light intensity results in a lower rate of photosynthesis, which can limit the growth and development of plants.
2. The concentration of CO2
Carbon dioxide is one of the essential raw materials for photosynthesis. Higher concentration of carbon dioxide helps in increasing the rate of photosynthesis. Usually, carbon dioxide in the range of 300 – 400 parts per million (PPM) is adequate for photosynthesis. However, if the concentration of carbon dioxide decreases, it can limit the efficiency of photosynthesis.
3. Temperature
Temperature plays a vital role in the process of photosynthesis. For efficient execution of photosynthesis, it is important to have a temperature range between 25° to 35° Celsius. The rate of photosynthesis is high at a temperature range of 30°C, but it decreases as the temperature goes beyond this range. At lower temperatures, the enzymes required for photosynthesis are less active, and at higher temperatures, the enzymes are denatured, which can limit the efficiency of photosynthesis.
4. Water:
Water is an essential factor for photosynthesis as it helps in the transport of nutrients, including carbon dioxide, to the plant cells. As water is an important factor in photosynthesis, its deficiency can lead to problems in the intake of carbon dioxide. The scarcity of water leads to the refusal of stomatal opening to retain the amount of water they have stored inside. Water scarcity can also lead to wilting of leaves, which can limit the efficiency of photosynthesis.
5. Pollution
Industrial pollutants and other particulates may settle on the leaf surface. This can block the pores of stomata, which makes it difficult to take in carbon dioxide. This can limit the efficiency of photosynthesis, leading to a reduction in plant growth and development.
Photosynthetic Organelles
Photosynthesis takes place in organelles called chloroplasts in plants and algae. The chloroplast has a phospholipid inner membrane, a phospholipid outer membrane, and an intermembrane space enclosing an aqueous fluid called the stroma. Stacks of thylakoids, which are flattened disks, are embedded within the stroma and serve as the site of photosynthesis.
The thylakoid membrane encloses the thylakoid space, and integral and peripheral membrane protein complexes of the photosynthetic system are embedded within it.
Most chloroplasts are found in leaves, and the interior mesophyll cells of a leaf can contain between 450,000 and 800,000 chloroplasts per square millimeter of leaf.
The surface of the leaf is coated with a waxy cuticle that protects the leaf from excessive water evaporation and decreases the absorption of ultraviolet or blue light to minimize heating. The transparent epidermis layer allows light to pass through to the palisade mesophyll cells where most of the photosynthesis takes place.
Photosynthetic Pigments
Photosynthetic pigments play a vital role in capturing light energy for photosynthesis.
- Chlorophyll (used primarily by plants, but also by algae and some bacteria)
- Carotenes (used by plants and some bacteria)
- Xanthophylls (used by plants and some algae)
- Chlorophyll is the primary pigment used by plants to absorb light energy. It is embedded in antenna proteins and arranged to work together in a light-harvesting complex. Besides chlorophyll, plants also use pigments such as carotenes and xanthophylls to absorb light energy from different parts of the visible light spectrum.
These pigments are embedded in plants and algae in complexes called antenna proteins, which work in concert to harvest light energy for photosynthesis. Algae also use chlorophyll, but they have various other pigments present, such as phycocyanin, carotenes, and xanthophylls in green algae, phycoerythrin in red algae, and fucoxanthin in brown algae and diatoms, resulting in a wide variety of colors.
The presence of different pigments allows plants and algae to adapt to different environmental conditions and utilize different wavelengths of light for energy production.
Adaptations For Photosynthesis In Plants
Plants have evolved various adaptations to carry out photosynthesis effectively in different environments. Some of these adaptations include:
- Small openings on the leaves and stems of plants allow the exchange of gases required for photosynthesis, such as carbon dioxide and oxygen.
- The mesophyll layer of a leaf is where most of the photosynthesis occurs. It has a large surface area and contains many chloroplasts.
- Organelles within plant cells containing pigments, such as chlorophyll, convert light energy into chemical energy.
- Membrane-bound structures within chloroplasts that contain the photosynthetic pigments and enzymes necessary for light reactions.
- Plants contain a variety of pigments, including chlorophyll a and b, carotenoids, and phycobilins, that help them capture different wavelengths of light for photosynthesis.
- Plants that grow in low light conditions, such as the forest floor, often have larger and thinner leaves to capture more light and may have adaptations to increase the efficiency of light capture.
- Plants that grow in high-light conditions, such as deserts, often have smaller and thicker leaves to reduce water loss and protect against high light and heat levels.



Leave a Reply