Magnesium-Discovery, Properties, And Applications
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol ‘Mg’ and atomic number 12. It is a lightweight, silvery-white metal that is highly reactive and can be found abundantly in the Earth’s crust. Magnesium is essential for human health and has a range of industrial applications.
| Property | Value |
| Name | Magnesium |
| Symbol | Mg |
| Atomic number | 12 |
| Relative atomic mass (Ar) | 24.305 range: [24.304, 24.307] |
| Standard state | Solid at 298 K |
| Appearance | Silvery white |
| Classification | Metallic |
| Group in periodic table | 2 |
| Group name | Alkaline earth metal |
| Group in the periodic table | 3 |
| Block in periodic table | Period in the periodic table |
| Shell structure | 2.8.2 |
| CAS Registry | 7439-95-4 |
Discovery
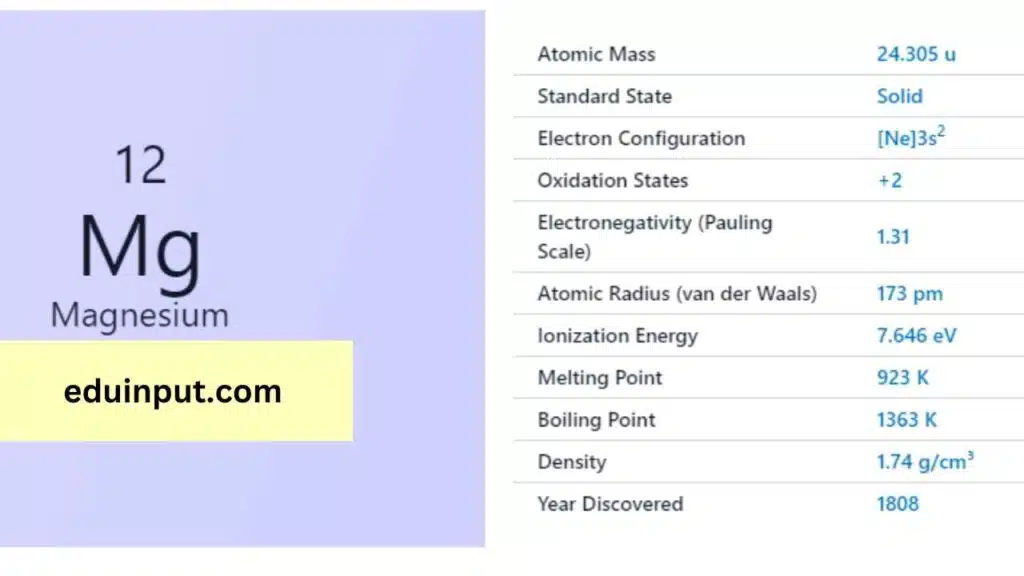
Magnesium was first discovered in 1808 by Sir Humphry Davy. He isolated the element from magnesium oxide using electrolysis.
Physical Properties
Magnesium is a lightweight metal with a density of 1.74 g/cm3. It has a melting point of 650°C and a boiling point of 1,090°C. Magnesium is a highly reactive element and can ignite spontaneously when exposed to air.
Chemical Properties
Magnesium is a highly reactive element and reacts with a variety of other elements and compounds. It reacts vigorously with oxygen to form magnesium oxide and with water to form magnesium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. Magnesium also reacts with acids to form magnesium salts.
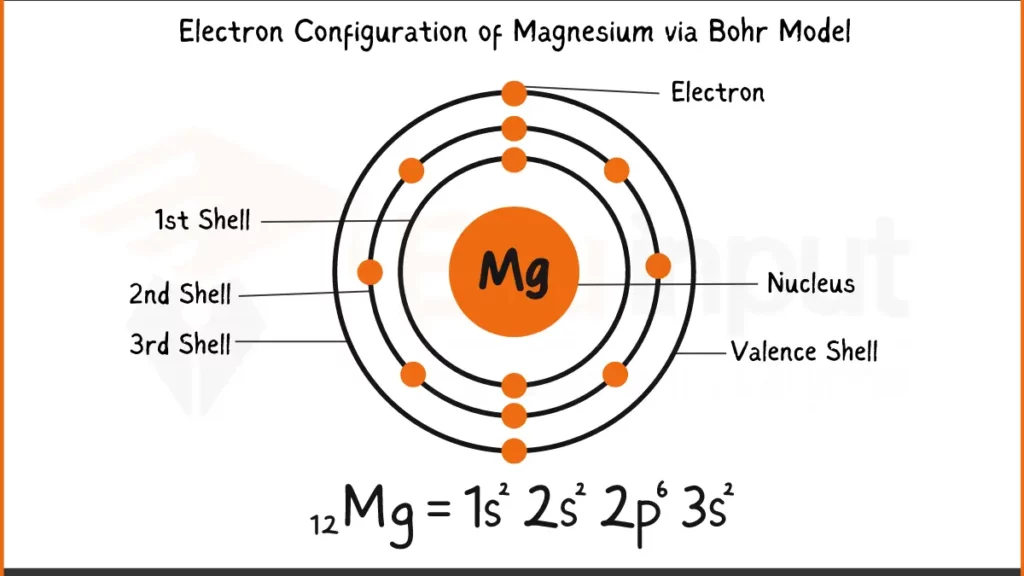
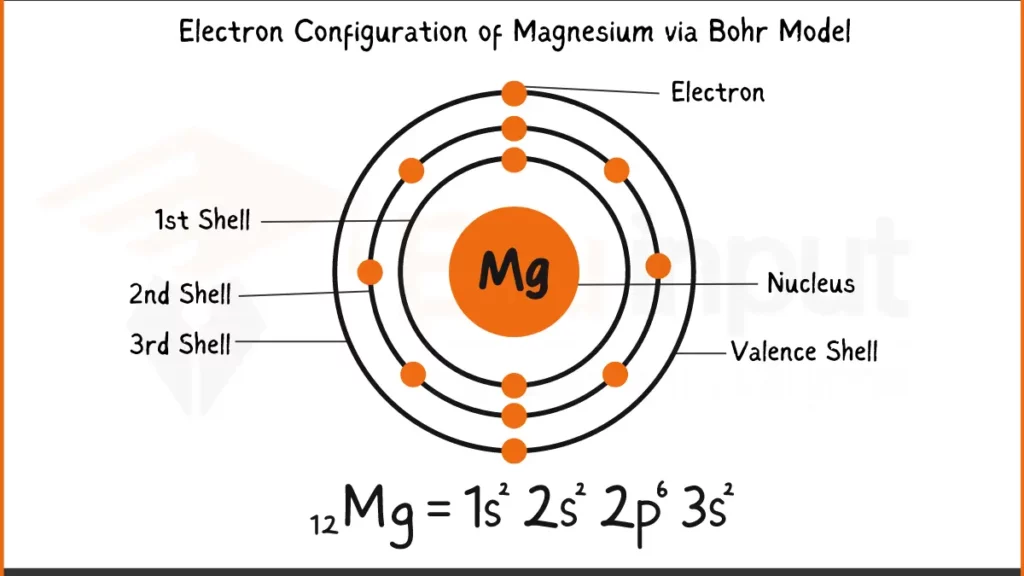
Electronic Configuration of Magnesium
Magnesium (Mg) packs 12 electrons. Its configuration can be written as 1s²2s². The key to its bonding behavior lies in the outermost shell, 2s. Unlike some elements that tends to have complete outer shell, Magnesium holds just two electrons (2s²) in this subshell.
Electronic Configuration of Magnesium via Bohr Model
Electronic Configuration of Magnesium via Aufbau Principle
Facts
- Magnesium is the eighth most abundant element in the Earth’s crust.
- Magnesium is essential for human health and is involved in over 300 biochemical reactions in the body.
- Magnesium is used in the production of lightweight alloys, such as magnesium-aluminum alloys, which are used in the aerospace and automotive industries.
- Magnesium is also used as a deoxidizer and desulfurizer in the production of steel.
Applications
Magnesium has a range of applications in various industries. Some of the major applications of magnesium include:
- Aerospace industry: Magnesium-aluminum alloys are used in the aerospace industry to make parts for airplanes and spacecraft due to their lightweight and strong properties.
- Automotive industry: Magnesium-aluminum alloys are also used in the automotive industry to make parts for cars, such as engine blocks and wheels, to reduce weight and improve fuel efficiency.
- Medical applications: Magnesium is used in some medical treatments, such as antacids and laxatives.
- Pyrotechnics: Magnesium is used in pyrotechnics to produce a bright, white light.
Magnesium is a lightweight, versatile metal that has a range of industrial applications. It is essential for human health and is involved in numerous biochemical reactions in the body. Magnesium-aluminum alloys have revolutionized the aerospace and automotive industries, while its use in pyrotechnics produces a bright, white light. Magnesium’s unique physical and chemical properties make it a valuable element for various applications.






Leave a Reply