Auxiliary verb-Types, Usage, and Examples
What is Auxiliary verb?
Auxiliary verb is also known as a helping verb. It is a verb that is used in combination with a main verb to indicate the tense, voice, mood, or aspect of a sentence.
Auxiliary verbs are used to create complex verb forms, such as the progressive tense, perfect tense, and passive voice, among others.

Types of Auxiliary verb
There are three types of auxiliary verbs in English:
- Primary auxiliary verbs
- Modal auxiliary verbs
- Semiauxiliary verbs
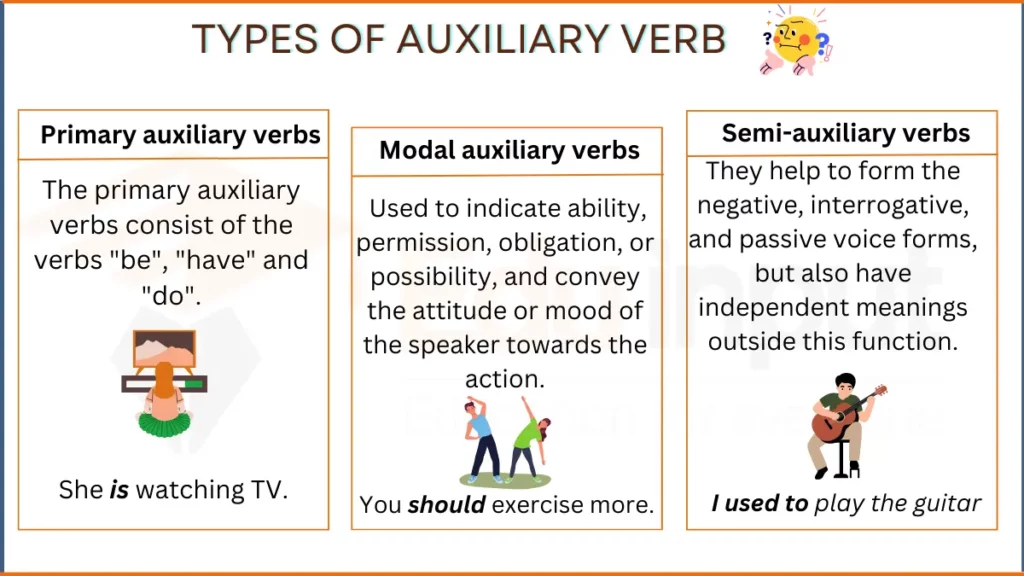
1. Primary auxiliary verbs
The primary auxiliary verbs consist of the verbs “be”, “have” and “do”. They are used to form various tense, voice, mood, and aspect constructions.
Examples
- She is watching TV.
- They are playing tennis in the park.
- He will be working late tonight.
- They have finished their work.”
- Do you speak Spanish?”
2. Modal auxiliary verbs
Modal auxiliary verbs are used to indicate ability, permission, obligation, or possibility, and convey the attitude or mood of the speaker towards the action.
The modal auxiliary verbs include: “will”, “would”, “shall”, “should”, “can”, “could”, “may”, “might”, “must”, and “ought to”.
Examples
- I can speak French fluently
- You should exercise more
- He may come to the party tonight
- They must finish their homework before watching TV
3. Semi auxiliary verbs
Semi auxiliary verbs are verbs that function as both lexical and auxiliary verbs. They help to form the negative, interrogative, and passive voice forms, but also have independent meanings outside this function.
Examples
Some examples of semi-auxiliary verbs include:
“Need”, “dare”, “used to”, and “ought to”.
Usage
- They need not worry about the exam
- Dare you ask her out on a date?
- I used to play the guitar
- He ought to apologize for his behavior
List of auxiliary verbs

- Be: am, is, are, was, were, been, being
- Have: has, have, had, and having
- Do: do, does, did, and doing
- Will: will
- Shall: shall
- Would: would
- Should: should
- Can: can, could
- May: may, might
- Must: must
- Ought to: ought to
- Used to: used to
- Need to: need to
- Dare to: dare to
Uses of auxiliary verbs
Here are the uses of auxiliary verbs in English grammar along with examples under each heading:
1. To form the tenses
Auxiliary verbs are commonly used to create various tenses in English, such as simple present, simple past, future, present perfect, past perfect, etc.
Examples
- He is reading a book. (Present continuous)
- They have finished their dinner. (Present perfect)
- I had seen the movie before. (Past perfect)
2. To form the passive voice
Auxiliary verbs are used to form passive voice in which the subject of the sentence is not the doer of the action.
Examples
- The cake was baked by my mom. (Past simple passive)
- The package will be delivered tomorrow. (Future passive)
3. To ask questions
Auxiliary verbs help us form questions that we use to ask for information.
Examples
- Can you help me with my homework? (Simple present interrogative)
- Has she finished her project? (Present perfect interrogative)
4. To form negatives
Auxiliary verbs are used to form negative sentences, which are sentences that express a negative condition or deny something.
Examples:
- She does not understand the problem. (Simple present negative)
- They were not invited to the party. (Past simple negative)
5. To express possibility, permission, necessity, or advice
Modal auxiliary verbs convey a range of meanings related to possibility, permission, necessity, or advice.
Examples
- I can swim in the ocean. (Possibility)
- You may borrow my bike. (Permission)
- We should exercise regularly. (Necessity)
- He ought to apologize for being rude. (Advice)
6. To show likelihood or ability
Modal auxiliary verbs also express likelihood or ability in different contexts.
Examples:
- It might rain this afternoon. (Likelihood)
- She can dance very well. (Ability)



Leave a Reply