Ball and socket joint- Definition, Anatomy and Functions
What is ball and socket joint?
“Ball and socket joint is a type of synovial joint that allows movement in more than one direction.” It is made up of a ball-shaped surface in a bone, which fits and goes inside the cup-like socket of the other bone. It helps in rotational and circular movements.
The Ball-and-socket joint can rotate easily in many directions around a central point, which gives it a wide range of motion. So, it is considered as the most freely moveable joint among all types of joints.
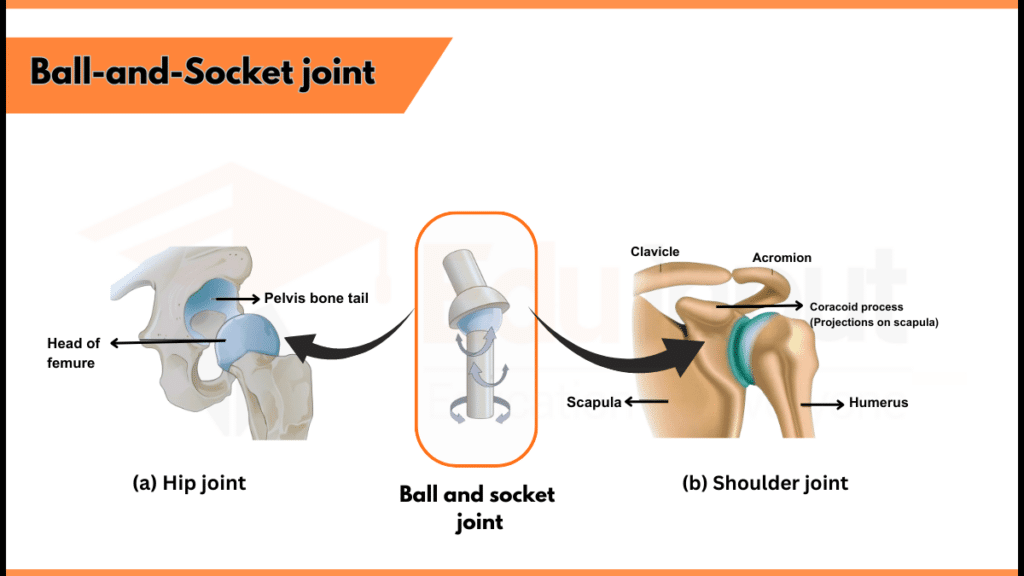
Example: The Hip joint- between the thighbone (femur) and the pelvis, is an example of ball and socket joint. Another example is the shoulder joint.
Anatomy of ball-and-socket joint
A ball and socket joint is a synovial joint, which means it helps in smooth movement between two bones. Within the joint, one bone contains a spherical end, giving it a ball shape, while the other bone contains a rounded and socket-shaped end. The ball slides and spins within the socket to allow movement of the joint in multiple directions. Ball and socket joint moves in more than one plane, that’s why it is the most moveable joint of the body.
Functions and features of ball-and-socket joint
1. Provides Flexibility
The ball and socket joint allows movement in multiple directions, providing a wide range of flexibility.
2. Reduces Friction between Bones
The ball and socket joint contains synovial fluid in its cavity. This fluid works like a lubricant and reduces friction between the bones.
3. Supports Multi-directional Motion
The joint structure, a ‘key and lock fit’, enables movement across multiple axes. It allows movements like rotations, flexion (bending), and extension (straightening).
4. Ensures Stability While Allowing Movement
Dense connective tissue, that binds the bones together, provides stability to the joint while allowing free movement.
5.Absorbs Stress and Reduces Impact on Bones
The unique structure distributes pressure across the joint, which helps reducing impact on individual bones. It also aids in shock absorption during activities.



Leave a Reply