Arteries-Composition, Types, And Processes in Arteries
Arteries are the blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood away from the heart (cardiac) toward other parts of the body. They also carry deoxygenated blood back to the lungs, where carbon dioxide is exchanged for oxygen.
Arteries become narrower as they get closer to the heart because their walls thicken. This narrowing, or stenosis, makes it harder for blood to flow through the artery. When this happens, it causes symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, arm claudication, and leg cramps. Some of these problems can be treated with medication or surgery.
Arteries are very important because they provide life-giving blood flow to our organs, muscles, tissues, and bones. They also transport hormones, oxygen, and other essential materials throughout the body.
Structure of Arteries
The blood vessels which carry the blood away from the heart to different parts of the body are called arteries. The arteries are composed of three-layer;
- Intima
- Media
- Adventitia/Externa
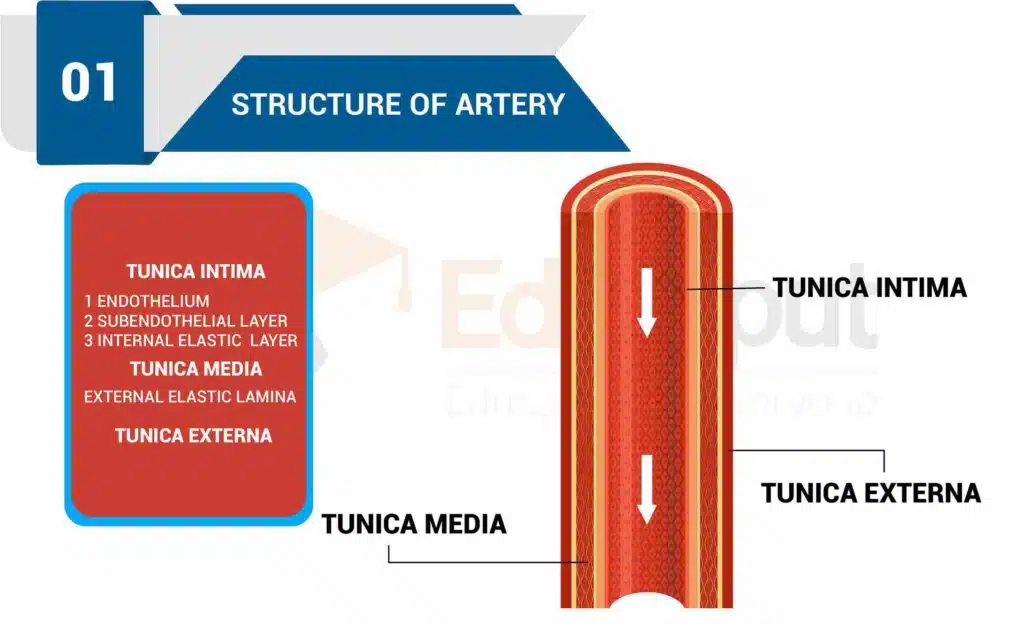
Adventitia
Adventitia is a thick outer coat of connective tissue, which supports the artery walls.
Media
Media is the middle layer of the blood vessel, consisting mainly of smooth muscle cells. circular. This is an important layer. It withstands high blood pressure during ventricular systole.
Intima
Intima consists of endothelium, which lines the inner surface of the artery wall. The arteries are divided into small vessels called arterioles. The arterioles have more circular muscles than elastic tissues. The nervous and endocrine systems control the contraction of circular muscles of the arteries and arterioles.
Types Of Arteries
The arteries are divided into two types:
- Muscular Arteries
- Elastic Arteries
Muscular Arteries
Muscular arteries have smooth muscle cells that contract and relax to regulate the flow of blood.
Elastic Arteries
Elastic arteries have no smooth muscle cells and expand and contract to regulate the flow of the blood.
Processes in Arteries
Two processes take place in the blood vessels;
Vasoconstriction:
The contraction of the wall of blood vessels is called vasoconstriction. The circular muscles are stimulated and contract. So they cause vasoconstriction of the arterioles. The vasoconstriction reduces the flow of blood in them. This causes less oxygen and nutrients to reach the cells.
Vasodilation:
The dilation of the blood vessels is called vasodilation. The circular muscles relax and cause the dilation of arterioles and arteries.
Vasoconstriction and vasodilation are essential processes in the body. Without the vasodilation, the blood vessels will collapse and there will be a drop in blood pressure.
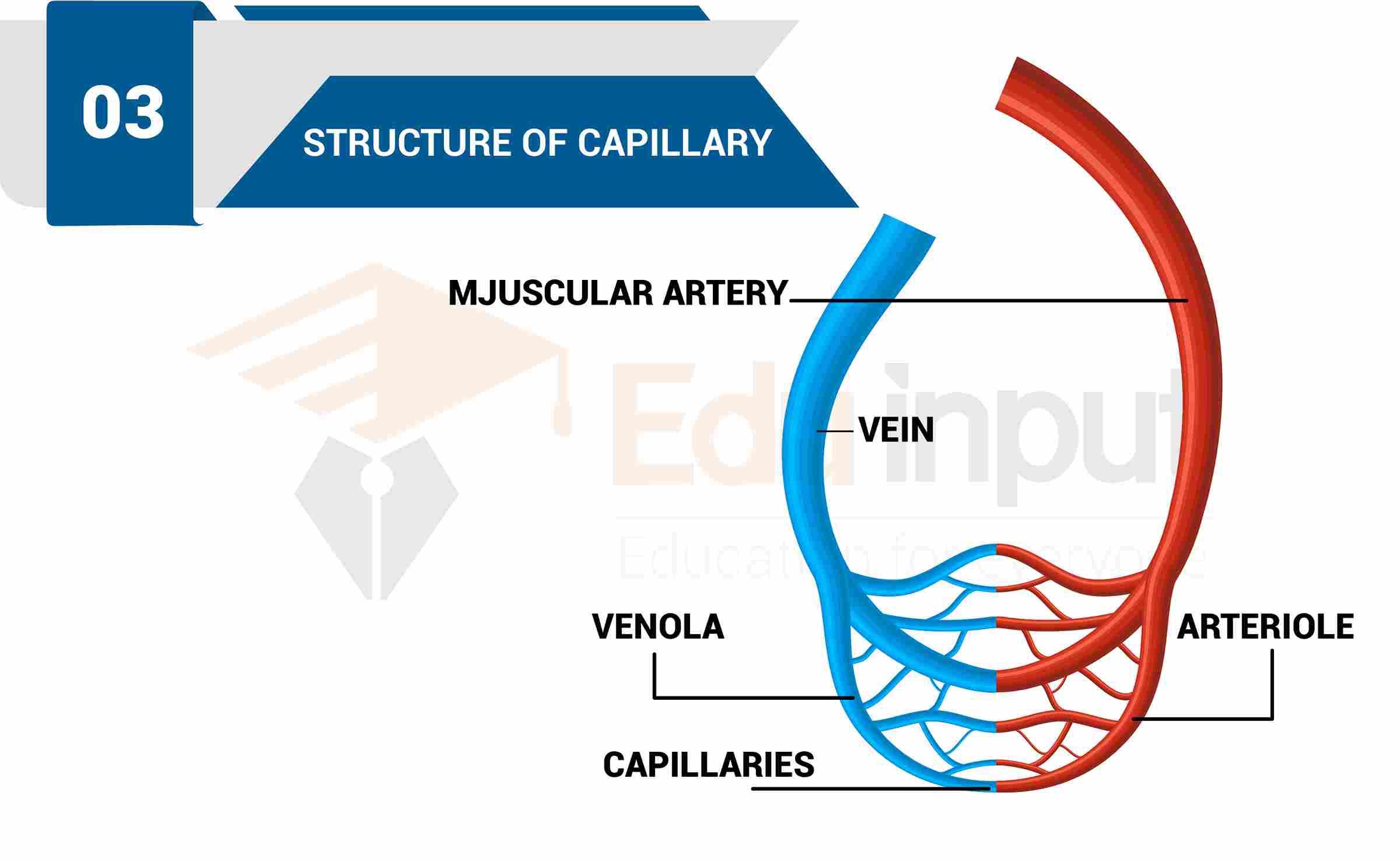
The arterioles are divided repeatedly and they form a dense network of microscopic vessels called capillaries. These capillaries are present between every cell of the living tissues.
Atherosclerosis
The narrowing and hardening of the arteries are called atherosclerosis. It is caused due to atheroma. The deposition of the hard yellow plague of lipid material in the innermost layer of the arteries is called atheroma.
A plaque is a deposit of lipids, cholesterol, cellular debris, fibrin, platelets, and leukocytes exuded from ruptured atherosclerotic plaques. Plaque may occur anywhere in the circulatory system, including coronary arteries, carotid arteries, cerebral arteries, and others. It may be caused due to high level of cholesterol in the blood.
Arteriosclerosis is a degenerative arterial change. It is associated with age. Primarily, it causes thickening of the middle layer of arteries. It is usually associated with some degree of atheroma. It increases the risk of thrombus formation. It is fatal to the brain and heart. So atherosclerosis is the major cause of heart attack.



Leave a Reply