Autotrophic Nutrition in Plants
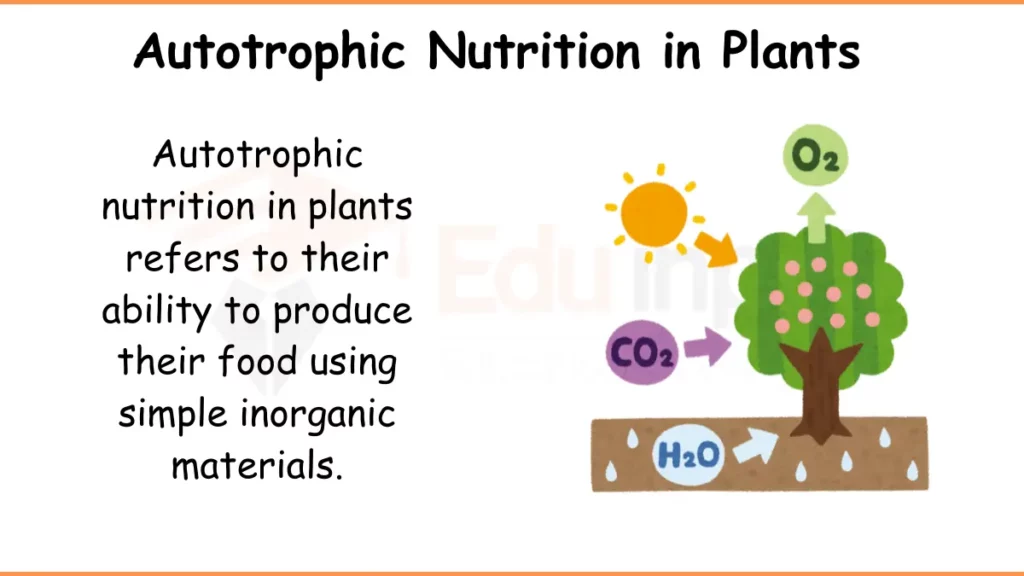
Autotrophic nutrition in plants refers to their ability to produce their food using simple inorganic materials. Autotrophic means “self-feeding.” Plants don’t rely on consuming other organisms for their energy needs. Through the process of photosynthesis, plants convert these simple materials into organic compounds, primarily glucose (a sugar).
Process of Photosynthesis
Plants absorb water through their roots from the soil. They take in carbon dioxide through tiny pores called stomata on their leaves. Sunlight provides the energy plants need.
During photosynthesis, plants use sunlight energy, water, and carbon dioxide to produce glucose (sugar) and oxygen.
This can be represented by the equation as follows:
light energy + water + carbon dioxide → glucose + oxygen.
A green pigment called chlorophyll helps plants trap sunlight for this process.
Supporting Structures for Photosynthesis
The process of photosynthesis relies on several specialized structures within plant cells and leaves to efficiently capture sunlight energy, obtain carbon dioxide and water. They carry out chemical reactions. Some supporting structures include:
Chloroplasts
These are the organelles found in plant cells where photosynthesis occurs. Chloroplasts contain stacked membrane structures called grana, which house the chlorophyll pigment molecules that absorb sunlight.
Leaf Structure
Leaves contain several tissue layers optimized for photosynthesis:
The palisade mesophyll has elongated cells arranged in rows to allow maximum absorption of light energy.
The spongy mesophyll has irregularly shaped cells with air spaces to allow movement of carbon dioxide.
The epidermis has a waxy cuticle to prevent water loss and guard cells that form stomata to regulate gas exchange.
Stomata
These microscopic pores on leaf surfaces allow for intake of carbon dioxide while letting out oxygen produced by photosynthesis. Guard cells surrounding the stomata control their opening and closing in response to factors like light intensity and water availability.
Vascular Tissues
The xylem tissue transports water and minerals from roots up to the leaves for photosynthesis. The phloem tissue moves the glucose and other organic products away from the leaves to the rest of the plant.
Roots
The root system has an expansive surface area that absorbs water and minerals from the soil to be used in the photosynthetic process occurring in the leaves above ground.
Importance of Photosynthesis
Here is why photosynthesis is important for plants with autotrophic mode of nutrition:
- Photosynthesis allows plants to make glucose, which is their primary food source. Plants use this glucose for growth, repair, and energy.
- Herbivores (plant-eaters) consume plants. They obtain energy from the glucose produced by photosynthesis.
- Carnivores (meat-eaters) then eat herbivores. They indirectly rely on the plant-produced energy.
- A byproduct of photosynthesis is oxygen, which is released into the air. This oxygen is necessary for respiration in plants, animals, and other living things.



Leave a Reply